Page 1
6N135/6N136
6N135/6N136
General Purpose Type
Photocoupler
■Features
1. High speed response t
(6N135:MAX. 1.5µs at R
(6N136:MAX. 0.8µs at R
2. High common mode rejection voltage
(CMH:TYP. 1kV/µ
3. Standard dual-in-line package
4. Recognized by UL, file No. E64380
PHL
, t
PLH
=4.1kΩ
L
=1.9kΩ
L
)
s
)
)
■Applications
1. Computers, measuring instruments, control
equipment
2. High speed line receivers, high speed logic
3. Telephone sets
4. Signal transmission between circuits of
different potentials and impedances
■Absolute Maximum Ratings (Ta=25˚C
Parameter Symbol Rating Unit
Forward current I
*1
Input
Peak forward current
Peak transient
*2
forward current
I
I
FM
Reverse voltage V
Power dissipation P 45 mW
Supply voltage V
Output voltage V
Output
Emitter-base reverse withstand voltage (Pin 5 to 7
Average output current
Peak output current I
Base current (Pin 7
)
)
V
EBO
I
OP
I
Power dissipation P
*3
Isolation voltage V
Operating temperature
T
Storage temperature T
*4
Soldering temperature
*1 50% duty cycle, Pulse width:1ms
Decreases at the rate of 1.6mA/˚C if the external temperature is 70˚C or more.
*2 Pulse width<=1µs, 300
*3 40 to 60% RH, AC for 1 minute
*4 For 10 seconds
P/S
T
F
F
R
-0.5 to+15
CC
-0.5 to+15
O
O
B
O
2 500
iso
-55 to+100
opr
-55 to+125
stg
so1
25 mA
50 mA
1A
5V
5V
8mA
16 mA
5mA
100 mW
260 ˚C
)
V
V
V
rms
˚C
˚C
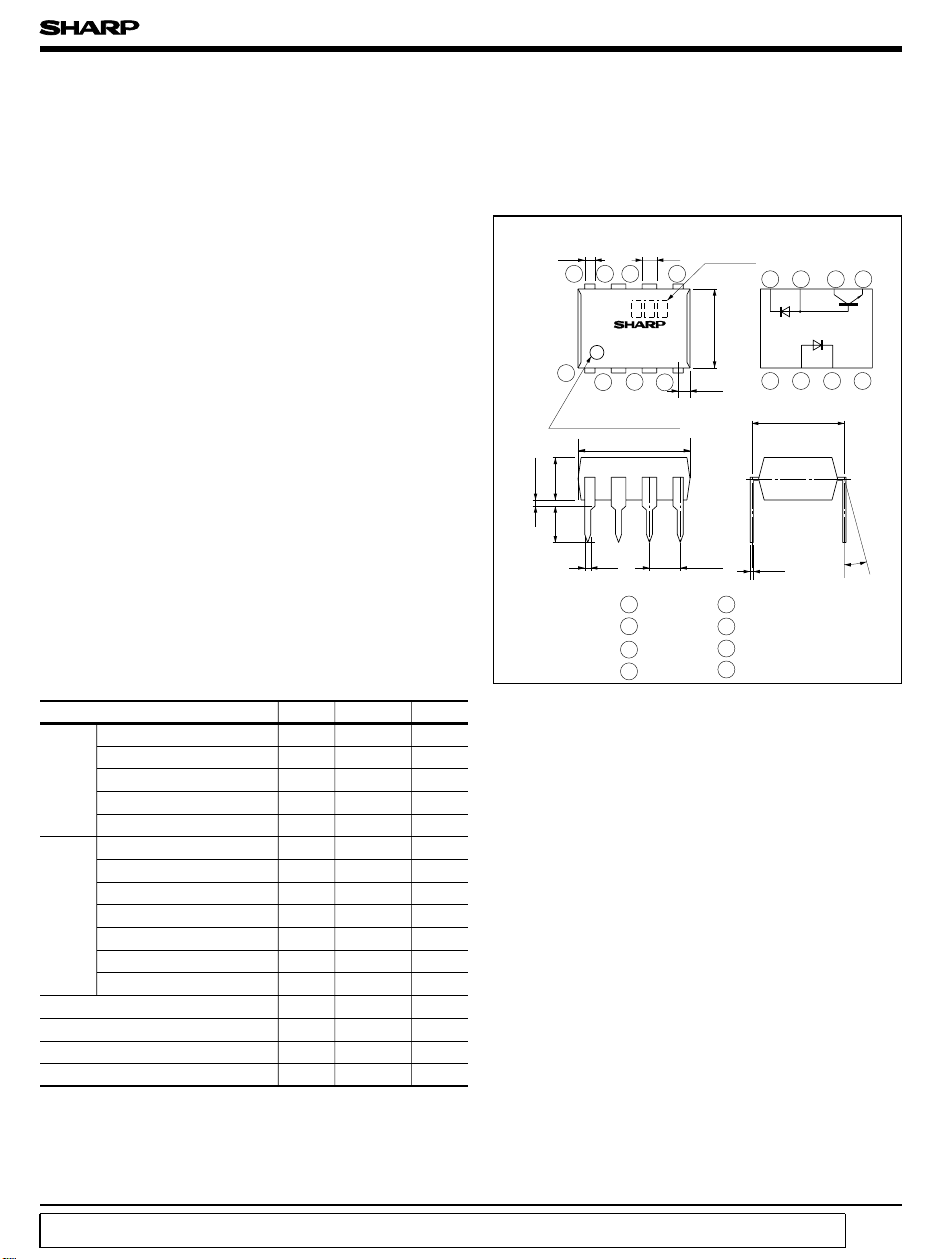
■Outline Dimensions
Model
±0.3
0.85
6N
1
234
Primary side mark
(
Sunken place
9.22
± 0.5
0.5TYP
3.5
± 0.5
3.7
* “OPIC” (Optical IC) is a trademark of the SHARP Corporation.
An OPIC consists of a light-detecting element and signal processing circuit integrated onto a single chip.
0.5
±0.1
1.2
5678
)
±0.5
1 NC
2 Anode
3 Cathode
4 NC
±0.3
2.54
No.
± 0.5
6.5
0.8
±0.25
5 GND
6 V
7 V
8 V
(
Unit:mm
Internal
connection
diagram
1234
±0.3
7.62
θ=0 to 13˚
θ
±0.1
0.26
O
B
CC
)
5678
“In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that occur in equipment using any of SHARP's devices, shown in catalogs,
data books, etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest version of the device specification sheets before using any SHARP's device.”
Page 2
6N135/6N136
■ Electro-optical Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
*5
Current transfer
ratio
6N136 CTR(1
6N135 CTR(2
6N136 CTR(2
Logic (0) output voltage V
Logic (1) output current
Logic (0) supply current I
Logic (1) supply current
Input forward voltage V
Input forward voltage
temperature coefficient
Input reverse voltage BV
Input capacitance C
6N135 CTR(1
*6
Leak current
(
input-output
*6
Isolation resistance
(
input-output
*6
Capacitance (input-output
)
)
)
Transistor current
amplification factor
*5 Current transfer ratio is the ratio of input current and output
current expressed in % .
*6 Measured as 2-pin element (Short 1, 2, 3, 4
*7 6N135 :IO= 1.1mA, 6N136 :IO= 2.4mA
)
Ta = 25˚C, IF= 16mA
)
V
O
)
)
OL
(1)
I
OH
(2)
I
OH
(3)
I
OH
CCL
(1)
I
CCH
(2)
I
CCH
F
/ ∆TaIF= 16mA - - 1.9 - mV/˚C
∆V
F
R
IN
I
I-O
R
I-O
C
I-O
h
FE
= 16mA, VO= 0.5V
I
F
V
CC
*7
IF= 16mA, VCC= 4.5V - 0.1 0.4 V
=25˚C, IF=0
T
a
V
CC=VO
=25˚C, IF=0
T
a
V
CC=VO
= 0, VCC=VO= 15V - - 50 A
I
F
IF= 16mA, VCC= 15V
V
O
=25˚C, VCC= 15V
T
a
V
F
V
CC
V
O
Ta=25˚C, IF= 16mA - 1.7 1.95 V
Ta=25˚C, IR= 10 A 5.0 - - V
VF= 0, f = 1MHz - 60 T
= 25˚C, 45 %RH, t = 5s
a
V
I-O
V
I-O
f = 1MHz - 0.6 VO= 5V, IO= 3mA - 70 -
)
(
Ta = 0 to + 70˚C unless otherwise specified
7.0 40 - %
= 0.4V, VCC= 4.5V
19 40 - %
5.0 43 - %
= 4.5V
= 5.5V
= 15V
= open
= open, IO=0
= 15V
= open, IF=0
15 43 - %
- 3.0 500 nA
- 0.01 1.0 A
- 200 - A
- 0.02 1.0 A
- - 2.0 A
µ
= 3kVDC
- - 1.0 A
= 500VDC - 10
Note) Typical volue : at Ta = 25˚C
)
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
pF
µ
12
- Ω
pF
Page 3

6N135/6N136
■ Switching Characteristics
*8
*9
*8
*9
*10,11
*10,11
*13
*8 R
*10 Instantaneous common mode rejection voltage “ output (1)” represents a common
Parameter
Propagation
delay time
Output (1)→(0
Propagation
delay time
Output (0)→(1
Instantaneous common
mode rejection voltage
6N135
6N136
)
6N135
6N136
)
“ output (1)”
Instantaneous common
mode rejection voltage
“ output (0)”
Bandwidth
= 4.1k Ω is equivalent to one LSTTL and 6.1kΩ pull-up resistor. R =1.9kΩ is equivalent to one TTL and 5.6kΩ pull-up resistor.
L L
mode voltage variation that can hold the output above (1) level (V
Instantaneous common mode rejection voltage “ output (0)” represents a common
mode voltage variation that can hold the output above (0) level (V
*12 6N135 :RL= 4.1k Ω 6N136 :RL= 1.9kΩ
Symbol Conditions MIN. TYP. MAX. Unit
t
PHL
t
PHL
t
PLH
t
PLH
CM
CM
BW R
RL= 4.1kΩ - 0.3 1.5 s
RL= 1.9kΩ - 0.3 0.8 s
RL= 4.1kΩ - 0.4 1.5 s
RL= 1.9kΩ - 0.3 0.8 s
*12
H
L
IF= 0, VCM= 10V
*12
VCM= 10V
= 100Ω - 2.0 - MHz
L
, IF= 16mA
P-P
> 2.0V).
O
< 0.8V).
O
(
Ta = 25˚C, VCC= 5V, IF=16mA
- - V/ s
P-P
1 000
- - V/ s
- 1 000
*13 Bandwidth represents a point where AC input goes down by 3dB.
*9 Test Circuit for Propagation Delay Time
Pulse
Pulse input
Duty ratio
= 1/10
IF monitor C
Generator
100Ω
I
F
1
2
3
4
8
R
7
6
5
L
0.01µF
V
CC
V
O
= 15pF
L
I
F
0
V
O
1.5V 1.5V
t
PHL
t
)
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
5V
PLH
*11 Test Circuit for Instantaneous Common Mode Rejection Voltage
B
V
FF
I
F
A
1
2
3
4
V
CM
+-
8
7
6
0.01µF
5
VCC= 5V
R
L
V
O
CM
CM
10V
V
CM
0V
V
V
H
O
I
L
O
IF= 16mA
90% 10%
10%
t
r
= 0
F
0.8V
90%
t
f
2V
5V
V
OL
Page 4

6N135/6N136
Fig. 1 Forward Current vs.
Ambient Temperature
30
25
)
mA
(
20
F
15
10
Forward current I
5
0
Ambient temperature T
Fig. 3 Forward Current vs.
Forward Voltage
100
)
10
mA
(
F
1
Forward current I
0.1
0.01
1.0
1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.2
Forward voltage V
Ta=0˚C
25˚C
50˚C
70˚C
Fig. 2 Power Dissipation vs.
Ambient Temperature
120
P
)
mW
(
100
O
80
O
60
45
40
Power dissipation P, P
20
0
(˚C)
1251007550250-55
a
-40P0 25 50 75 100 125
Ambient temperature T
70
(˚C)
a
Fig. 4 Relative Current Transfer Ratio vs.
Forward Current
150
)
%
(
100
50
Relative current transfer ratio
0
(V)
F
0.1
CTR = 100% at
I
= 16mA
F
1 10 100
Forward current I
F
(mA)
V
V
T
=5V
CC
= 0.4V
O
=25˚C
a
Fig. 5 Output Current vs. Output Voltage
20
V
=5V
CC
18
T
a
16
)
14
mA
(
O
12
10
8
6
Output current I
4
0
022
=25˚C
4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Output voltage V
Dotted line shows
pulse characteristics
I
= 25mA
F
20mA
15mA
10mA
5mA
(V)
O
Fig. 6 Relative Current Transfer Ratio vs.
Ambient Temperature
110
)
%
100
(
90
80
70
Relative current transfer ratio
60
-60 -40 -20
0 20 40 60 80 100
Ambient temperature T
CTR = 100 % at T
I
= 16mA
F
= 0.4V
V
O
V
=5V
CC
=25˚C
a
(˚C)
a
Page 5

6N135/6N136
Fig. 7 Propagation Delay Time vs.
Ambient Temperature
800
)
ns
(
PLH
600
, t
PHL
400
200
Propagation delay time t
6N135 (R
6N136 (RL= 1.9k Ω
0
- 60 - 20 20 60 10080400-40
Ambient temperature T
= 4.1kΩ
L
)
)
t
PHL
t
PLH
a
I
VCC=5V
(˚C)
Fig. 9 Frequency Response
0
-5
)
-10
dB
(
V
-15
-20
Voltage gain A
-25
-30
0.1 0.2 0.5 1 2 5 10
R
= 100Ω
L
220Ω
470Ω
Frequency f (MHz
IF= 16mA
T
1kΩ
)
= 16mA
F
=25˚C
a
Fig. 8 High Level Output Current vs.
Ambient Temperature
-5
10
)
A
-6
(
10
OH
-7
10
-8
10
-9
10
High level output current I
-10
10
-11
10
- 60 - 40 - 20 0 20 100806040
Ambient temperature T
V
CC=VO
(˚C)
a
=5V
Test Circuit for Frequency Characteristic
5V
AC
Input
1
2
20kΩ
3
4
560Ω
100Ω
1.6V DC
0.25V AC
-
PP
8
R
7
L
6
5
15V
V
O
■ Precautions for Use
(1)
It is recommended that a by-pass capacitor of more than 0.01 F be added between V
GND near the device in order to stabilize power supply line.
(2)
Transistor of detector side in bipolar configuration is apt to be affected by static electricity
for its minute design. When handling them, general counterplan against static electricity
should be taken to avoid breakdown of devices or degradation of characteristics.
As for other general cautions, please refer to the chapter “ Precautions for Use ” .
●
(Page 78 to 93
)
µ
CC
and
 Loading...
Loading...