Page 1

SECTION 0B
GENE RAL INFORMATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications 0B--2.............................
Technical Data 0B--2............................
Vehicle Dimensions and Weights 0B--6............
Standard Bolts Specifications 0B--7...............
Maintenance and Repair 0B--8....................
Maintenance and Lubrication 0B--8...............
Normal Vehicle Use 0B--8........................
Explanation of Scheduled Maintenance
Services 0B--8...............................
Scheduled Maintenance Charts
(Gasoline Engine) 0B--9.......................
Scheduled Maintenance Charts
(Diesel Engine) 0B--11.........................
Owner Inspections and Services 0B--13...........
While Operating the Vehicle 0B--13...............
At Each Fuel Fill 0B--13..........................
At Least Tw ice A Month 0B--13...................
At Least Monthly 0B--13.........................
At Least Tw ice a Year 0B--13.....................
Each Time The Oil is Changed 0B--14.............
At Least Annually 0B--14.........................
Recommended Fluids and Lubricants 0B--15.......
General Description and System
Operation 0B--16................................
General Repair Instructions 0B--16................
Vehicle Identification Number System 0B--17.......
Vehicle Lifting Procedures 0B--20.................
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 2

0B --2 GENERAL INFORMATION
SPECIFICATIONS
TECHNICAL DATA
Transaxle Performance
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA
Maximum Speed (Km/h) 140 134 148 154 165 176
Minimum Turning Radius (m) 5.8 5.8 5.8 5.8 5.8 5.8
2.0L
DOHC
2.3L
DOCH
3.2L
DOCH
Performance- Autumatic Transaxle
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA 2.3L DOCH 3.2L DOCH
Maximum Speed (Km/h) 140 137 140 160 170
Minimum Turning Radius (m) 5.8 5.8 5.8 5.8 5.8
Engine
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA
Engine Type 4Cylinder
DIESEL
Bore (mm) 89 89 89 89.9 90.9 89.9
Stroke (mm) 92.4 92.4 92.4 78.7 88.4 84
Total Displacement (cc) 2299 2874 2874 1998 2295 3199
Compression Ratio 22:1 22:1 22:1 9.6:1 10.4:1 10:1
Maximum Power (ps/rpm) 101/4000 95/4000 120/4000 135/5500 149/5500 222/5500
Maximum Torque (kg.m/rpm) 21.5/2400 19.6/2400 25.5/2400 19.3/4000 22.4/4000 31.6/3750
5Cylinder
DIESEL
5Cylinder
DIESEL
2.0L
DOHC
4Cylinder
GASOLINE
2.3L
DOCH
4Cylinder
GASOLINE
3.2L
DOCH
6Cylinder
GASOLINE
Ignition System
Application 2.0L DOHC 2.3L DOHC 2.0L DOHC
Ignition Type Distributorless Ignition
Ignition Timing (BOTH) 6°±2° 6°±2° 8°±2°
Ignition Sequence 1--3--4--2 1--3--4-- 2 1--5--3-- 6--2-- 4
Spark Plug Gap (mm) 0.8 ± 0.1 0.8 ± 0.1 0.8 ± 0.1
Spark Plug Maker Bosch, Chapion, Beru
Spark Plug Type F8DC4 (BOSCH)
C11YCC (CHAMPION)
14F8DU4 (BERU)
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 3

Clutch - Manual Type
GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--3
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA
Type Single Dry Diaphram
Outside Diameter (mm) 225 225 240 225 225 240
Inside Diameter (mm) 150 150 150 150 150 155
Thickness 9.2 9.2 9.2 9.2 9.2 9.3
Fluid Common use :Brake Fluid
2.0L
DOHC
2.3L
DOCH
3.2L
DOCH
Manual Transmission
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA
Maker TREMEC TREMEC TREMEC TREMEC TREMEC TREMEC
Type or Model T5 T5 T5 T5 T5 T5
Gear Ratio : 1st 3.969 3.969 3.969 3.969 3.969 3.969
2nd 2.341 2.341 2.341 2.341 2.341 2.341
3rd 1.457 1.457 1.457 1.457 1.457 1.457
4th 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
5th 0.851 0.851 0.851 0.851 0.851 0.851
Reverse 3.705 3.705 3.705 3.705 3.705 3.705
Final Drive Ratio 4.55 4.55 4.55 4.89 4.55 3.73
Oil Capacity (L) 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4 3.4
2.0L
DOHC
2.3L
DOCH
3.2L
DOCH
Auto Transmission
Application 661LA 662LA 2.3L DOCH 3.2L DOCH
Maker BTRA BTRA BTRA BTRA
Type or Model M74 4WD M74 4WD M74 4WD M74 4WD
Gear Ratio : 1st 2.741 2.741 2.741 2.741
2nd 1.508 1.508 1.508 1.508
3rd 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000
4th 0.708 0.708 0.708 0.708
Reverse 2.429 2.429 2.429 2.429
Final Drive Ratio 5.380 4.890 5.860 4.890
Oil Capacity (L) 9 9 9 9
Brake
Application Specifications
Booster Size
Master Cylinder Diameter (mm) φ 25.4
Booster Ratio 5.6 : 1
Front Brake : Disc Type
Rear Brake : Disc Type
non--ABS 8inch + 9inch
ABS 5.0 7inch + 8inch
ABS 5.3 8inch + 9inch
Ventilated
Solid
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 4

0B --4 GENERAL INFORMATION
Tire and Wheel
Application Specifications
Standard Tire Size P235/75 R15, 255/70 R15
Standard Wheel Size 7JJx15
Inflation Pressure At Full Lode
P235 / 75 : Front
Rear
P255 / 75 : Front
Rear
30 Psi
30 Psi
30 Psi
30 Psi
Steering System
Application Specifications
Gear T ype RACK & PINION
Wheel Alignment:
Front: Toe--in
Front: Caster
Front: Camber
Oil Capacity 1L
0--4mm
2°30′±30′
0°±30′
Suspension
Application Specifications
Front T ype Double Wishbone
Rear Type 5--Link
Fuel System
Application Specifications
Fuel Pump Type Electric Motor Pump
Fuel Capacity 70 L
Lubricating System
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA
Oil Pump Type External Gear pump
Oil Filter Type Combination (Full & Part) Full Flow
Oil Capacity (L)
(Including Oil Filter)
8.0 9.0 9.5 7.2 7.5 8.2
2.0L
DOHC
2.3L
DOCH
Cooling System
3.2L
DOCH
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA
Coolant Capacity (L) 9.5 -- 10 10.5 10.5 -- 11 10.5 10.5 11.3
Radiator Type Forced Circulation
Water Pump Type Centrifugal
2.0L
DOHC
2.3L
DOCH
3.2L
DOCH
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 5

Electric System
GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--5
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA
2.0L
DOHC
2.3L
DOCH
3.2L
DOCH
Battery (MF) 12V -- 90AH
Generator 75A 75A 75A 75A 115A 115A
Starter 2.2kw 2.2kw 2.2kw 1.2kw 1.2kw 1.7kw
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 6

0B --6 GENERAL INFORMATION
VEHICLE DIMENSION S AND WEIGHTS
Vehicle Dimensions
Application Specifications
Overall Length (mm) 4330
Overall Width (mm) 1841
Overall Height (mm) 1840
Wheel Base (mm) 2840
Tread: Front (mm)
Rear (mm)
Vehicle Weights
1510
1520
Application 661LA 662NA 662LA
Manual : Curb Weight (kg)
Gross Vehicle
Weight (kg)
Automatic : Curb Weight (kg)
Gross Vehicle
Weight (kg)
Passenger Capacity 5 5 5 5 5 5
1790
2515
1810
2515
1810
2515
1815
2515
1830
2515
1850
2515
2.0L
DOHC
1790
2515
--
--
2.3L
DOCH
1790
2515
1810
2515
3.2L
DOCH
1840
2515
1860
2515
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 7

Bolt*
4T 7T 9T 4T 7T 9T
M3 x 0.5 0.5 NSm
(4.5 lb-in)
M4 x 0.7 1.2 NSm
(11 lb-in)
M5 x 0.8 2.4 NSm
(22 lb-in)
M6 x 1.0 4.0 NSm
(36 lb-in)
M8 x 1.25 8.6 NSm
(77 lb-in)
M10 x 1.25 18.6 NSm
(14 lb-in)
M10 x 1.5 18.6 NSm
(14 lb-in)
M12 x 1.25 34.3 NSm
(25lb-in)
M12 x 1.75 32.3 NSm
(24 lb-in)
M14 x 1.5 54.0 NSm
(40 lb-in)
M16 x 1.5 81.3 NSm
(60 lb-in)
M18 x 1.5 117.6 NSm
(87 lb-in)
M20 x 1.5 166.6NSm
(123 lb-in)
M22 x 0.5 225.4NSm
(167 lb-in)
M24 x 1.5 284.2 NSm
(210 lb-in)
M24 x 2.0 274.4 NSm
(203 lb-in)
* Diameter X pitch in millimeters
GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--7
ST ANDARD BOLTS SPECIFICATIONS
Torque (NSm/Ib-in)
Standard Limit
0.9 NSm
(8 lb-in)
2.0 NSm
(18 lb-in)
4.0 NSm
(36 lb-in)
6.7 NSm
(60 lb-in)
15.7 NSm
(12 lb-in)
32.3 NSm
(24 lb-in)
30.4 NSm
(22 lb-in)
56.8 NSm
(42 lb-in)
53.9 NSm
(40 lb-in)
89.2 NSm
(66 lb-in)
107.8 NSm
(80 lb-in)
196.0 NSm
(145 lb-in)
274.4 NSm
(203 lb-in)
372.4 NSm
(276 lb-in)
480.2 NSm
(355 lb-in)
460.6 NSm
(341 lb-in)
1.3 NSm
(12 lb-in)
3.0 NSm
(27 lb-in)
5.6 NSm
(50 lb-in)
9.7 NSm
(87 lb-in)
22.5 NSm
(17 lb-in)
46.0 NSm
(34 lb-in)
44.1 NSm
(33 lb-in)
82.3 NSm
(61 lb-in)
77.4 NSm
(57 lb-in)
127.4 NSm
(94 lb-in)
196.0 NSm
(145 lb-in)
284.2 NSm
(210 lb-in)
392.0 NSm
(290 lb-in)
529.2 NSm
(392 lb-in)
686.0 NSm
(508 lb-in)
666.4 NSm
(493 lb-in)
0.7 NSm
(6.3 lb-in)
1.6 NSm
(14 lb-in)
3.1 NSm
(28 lb-in)
5.4 NSm
(49 lb-in)
12.7 NSm
(9 lb-in)
25.5 NSm
(19 lb-in)
24.5 NSm
(18 lb-in)
45.0 NSm
(33 lb-in)
43.1 NSm
(32 lb-in)
71.6 NSm
(53 lb-in)
107.8 NSm
(80 lb-in)
156.8 NSm
(116 lb-in)
215.6 NSm
(160 lb-in)
294.0 NSm
(218 lb-in)
382.2 NSm
(283 lb-in)
372.4 NSm
(276 lb-in)
1.2 NSm
(11 lb-in)
2.6 NSm
(23 lb-in)
5.2 NSm
(47 lb-in)
9.0 NSm
(81 lb-in)
20.6 NSm
(15.2 lb-in)
42.1 NSm
(31 lb-in)
41.2 NSm
(30 lb-in)
75.5 NSm
(56 lb-in)
71.5 NSm
(53 lb-in)
117.6 NSm
(87 lb-in)
186.2 NSm
(138 lb-in)
264.6 NSm
(196 lb-in)
362.6 NSm
(268 lb-in)
490.0 NSm
(362 lb-in)
637.0 NSm
(471 lb-in)
617.4 NSm
(457 lb-in)
17 NSm
(15 lb-in)
4.0 NSm
(36 lb-in)
7.6 NSm
(68 lb-in)
12.7 NSm
(114 lb-in)
30.4 NSm
(22 lb-in)
60.8 NSm
(31 lb-in)
58.8 NSm
(44 lb-in)
107.8 NSm
(80 lb-in)
98.0 NSm
(73 lb-in)
166.6 NSm
(123 lb-in)
264.6 NSm
(196 lb-in)
372.4 NSm
(276 lb-in)
519.4 NSm
(384 lb-in)
705.6 NSm
(522 lb-in)
921.2 NSm
(682 lb-in)
891.8 NSm
(660 lb-in)
DAEW OO MY_2000
YAA0B010
YAA5A5K0
Page 8

0B --8 GENERAL INFORMATION
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
MAINTENANCE AND
LUBRICATION
NORMAL VEHICLE USE
The maintenance instructions contained in the maintenance schedule are based on the assumption that the
vehicle will be used for the following reasons:
D Tocarry passengers and cargo within the limitation of
the tire inflation prassure. Refer to “T ire and Wheel” in
section 2E.
D To be driven on reasonable road surfaces and within
legal operating limits.
EXPLAN ATION OF SCHEDULED
MAINTENANCE SERVICES
The services listed in the maintenance schedule are further explained below. When the following maintenance
services are performed, make sure all the parts are replaced and all the necessary repairs are done before
driving the vehicle. Always use the proper fluid and lubricants.
Engine Oil and Oil Filter Change
Always use above the API SH grade or recommended
engine oil.
Engine Oil Viscosity
Engine oil viscosity (thickness) has an effect on fuel
economy and cold weather operation. Lower viscosity
engine oils can provide better fuel economy and cold
weather performance; however, higher temperature
weather conditions require higher viscosity engine oils
for satisfactory lubrication. Usi ng oils of any viscosity
other than those viscosities recommended could result
in engine damage.
D Diesel Engine : 30,000km (18,000 miles)
Replace the air cleaner more often under dusty condi-
tions.
Fuel Filter Replacement
Replace the engine fuel filter every.
D Gasoline Engine : 60,000km (36,000 miles)
D Diesel Engine : 45,000km (24,000 miles)
Spark Plug Replacement
Replace spark plugs with same type.
D Type : BOSCH : F8DC4
BERU : 14F--8DU4
Champion : C11YCC
D Gap : 0.8 ± 0.1 mm
Spark Plug Wire Replacement
Clean wires and inspect them for burns, cracks or other
damage. Check the wire boot fit at the Distributor and at
the spark plugs. Replace the wires as needed.
Brake System Service
Check the disc brake pads or the drum brake linings.
Check the pad and the lining thickness carefully.
Tire and Wheel Inspection and Rotation
Check the tires for abnormal wear or damage. Toequalize wear and obtain maximum tire life, rotate the tires. If
irregular or premature wear exists, check the wheel
alignment and check for damaged wheels. While the
tires and wheels are removed, inspect the brakes.
Tire Rotation (Left-hand Drive Type)
Cooling System Service
Drain, flushand refillthe system withnew coolant. Refer
to “Recommended Fluids And Lubricants“ in this section.
Air Cleaner Element Replacement
Clean the air cleaner element every.
D Gasoline Engine : 15,000km (10,000 miles)
D Diesel Engine : 10,000km (6,000 miles)
Replace the air cleaner element every .
D Gasoline Engine : 60,000km (36,000 miles)
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 9

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--9
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE CHARTS (GASOLINE ENGINE)
Engine
MAINTENANCE ITEM
Kilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
x1,000 km 1 15 30 45 60 75 90 105 120
Months -- 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
Drive belt I I I I I I I I I
Engine oil & filter (1) (3) I R R R R R R R R
Cooling system hose & connections I I I I I I I I I
Engine coolant (3) I I I I R I I I R
Fuel filter (2) -- -- -- -- R -- -- -- R
Fuel line & connections I I I I I I I I I
Air cleaner (2) -- I I I R I I I R
Ignition timing -- I I I I I I I I
Spark plugs -- I R I R I R I R
Charcoal canister & vapor lines -- -- -- I -- -- I -- --
Chart Symbols:
I -- Inspect these items and their related parts. If necessary, correct, clean, replenish, adjust or replace.
R -- Replace or change.
(1) If vehicle is operated under severe condition : short distance driving, extensive idling or driving in dusty condi-
tion. Change engine oil and the filter every 7,500 km or 6 months, whichever comes first.
(2) More frequent maintenance is required if under dusty driving condition.
(3) Refer to “Recommended fluids and lubricants”.
MAINTENANCE INTERVAL
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 10

0B --10 GENERAL INFORMATION
Chassis and Body
MAINTENANCE ITEM
MAINTENANCE INTERVAL
Kilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
x1,000 km 1 15 30 45 60 75 90 105 120
Months -- 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
Exhaust pipes & mountings -- I I I I I I I I
Brake/Clutch fluid (3)(4) -- I R I R I R I R
Parking brake/Brake pads F & R (5) -- I I I I I I I I
Brake line & connections (including booster) I I I I I I I I I
Manual transmission oil (3) I I I R I I R I I
Clutch & brake pedal free play -- I I I I I I I I
Front & Rear Differential Fluid (3) I I I R I I R I I
Transfer case fluid I I I R I I R I I
Automatic transmission fluid
(MB W4A040) (6)
I I I R I I I I I
Automatic transmission fluid (BTRA M74) I I I I I I I I I
Chassis & underbody bolts & nuts tight/secure I I I I I I I I I
Ti re condition & inflation pressure I I I I I I I I I
Wheel alignment (7) Inspect & adjust when abnormal condition is noted
Steering wheel & linkage -- I I I I I I I I
Power steering fluid & lines* (3) -- I I I I I I I I
Drive shaft boots -- I I I I I I I I
Seat belts, buckles & anchors I I I I I I I I I
Lubricate locks, hinges & bonnet latch -- I I I I I I I I
Chart Symbols:
I -- Inspect these items and their related parts. If necessary, correct, clean, replenish, adjust or replace.
R -- Replace or change.
(3) Refer to “Recommended fluids and lubricants”.
(4) Change the brake / clutch fluid every 15,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions:
-- Driving in hilly or mountainous terrain, or
-- Towing a trailer frequently
(5) More frequent maintenance is required if under severe condition : short distance driving, extensive idling, fre-
quent low -- speed operation in stop--and--go traffic or driving in dusty condition.
(6) Change automatic transaxle fluidand filter every 75,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe condi-
tions.
-- In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly reaches 32°C(90°F) or higher, or
-- In hilly or mountainous terrain, or
-- When doing frequent trailer towing, or
-- Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service.
(7) If necessary, rotate and balance wheels.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 11

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--11
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE CHARTS (DIESEL ENGINE)
Engine
MAINTENANCE ITEM
Kilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
x1,000 km 1 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Months -- 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60
Drive belt I I I I I I I I I I I
Engine oil & fillter (1) (3) R R R R R R R R R R R
Cooling system hose & connections -- -- I I I I I I I I I
Engine coolant (3) -- -- I -- -- -- R -- -- -- I
Fuel filter (2) -- -- -- -- R -- -- -- -- R -Fuel line & connections I I I I I I I I I I I
Glow plug -- -- I -- I -- I -- R -- I
Pre -- fuel filter -- I I R I I I I I I I
Air cleaner (2) -- I I I I I R I I R I
Ignition timing (see NOTE 1) -- I I I I I I I I I I
NOTE 1 : Injection Timing :
Adjust as required :
-- When excessive smoke is visible (black or white)
-- Poor performance/economy
Chart Symbols:
I -- Inspect these items and their related parts. If necessary, correct, clean, replenish, adjust or replace.
R -- Replace or change.
(1) If vehicle is operated under severe condition : short distance driving, extensive idling or driving in dusty condi-
tion, change engine oil every 5,000km or 3 months, whichever comes first.
(2) More frequent maintenance is required if under dusty driving conditing.
(3) Refer to “Recommended fluids and lubricants”.
MAINTENANCE INTERVAL
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 12

0B --12 GENERAL INFORMATION
Chassis and Body
MAINTENANCE ITEM
MAINTENANCE INTERVAL
Kilometers or time in months, whichever comes first
x1,000 km 1 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Months -- 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60
Exhaust pipes & mountings -- I I I I I I I I I I
Brake/clutch fluid (3) (4) I I I R I I R I I R I
Parking brake/Brake pads (F & R) (5) -- I I I I I I I I I I
Brake line & connections (including
booster)
-- I I I I I I I I I I
Manual transmission fluid (3) -- I I I I R I I I I R
Clutch & brake pedal free play -- I I I I I I I I I I
F & R Differential fluid (3) I I I I I R I I I I R
Transfer case fluid (3) -- I I I I R I I I I R
Automatic transmission
fluid (BTRA M74) (6)
Chassis & underbody bolts & nuts
tight/secure
-- I I I I I I I I I I
I I I I I I I I I I I
Ti re condition & inflation pressure I I I I I I I I I I I
Wheel alignment (7) Inspect & adjust when abnormal condition is noted
Steering wheel & linkage -- I I I I I I I I I I
Power steering fluid & lines* (3) -- I I I I I I I I I I
Drive shaft boots I I I I I I I I I I I
Seat belts, buckles & anchors I I I I I I I I I I I
Lubricate locks, hinges & bonnet latch I I I I I I I I I I I
Chart Symbols:
I -- Inspect these items and their related parts. If necessary, correct, clean, replenish, adjust or replace.
R -- Replace or change.
(3) Refer to “Recommended fluids and lubricants”.
(4) Change the brake / clutch fluid more regularly if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions :
-- Driving in hilly or mountainous terrain, or
-- Towing a trailer frequently
(5) More frequent maintenance is required if under severe condition : short distance driving, extensive idling, fre-
quent low
-- speed operation in stop--and--go traffic or driving in dusty condition.
(6) Change automatic transmission fluid every 70,000 km if the vehicle is mainly driven under severe conditions.
-- In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly reaches 32°C(90°F) or higher, or
-- In hilly or mountainous terrain, or
-- When doing frequent trailer towing, or
-- Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service.
(7) If necessary, rotate and balance wheels.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 13

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--13
OWNER INSPECTIONS AND SERVICES
WHIL E OPERATING THE VEHICLE
Horn Operation
Blowthe horn occasionallyto make sure it works. Check
all the button locations.
Brake System Operation
Be alert for abnormal sounds, increased brake pedal
travel or repeated puling to one side when braking.Also,
if the brake warning light goes on, or flashes, something
may be wrong with part of the brake system.
Exhaust System Operation
Be alert to any changes in the sound of the system or
the smellof the fumes. These are signsthat the system
may be leaking or overheating. Have the system inspected and repaired immediately.
Tires, Wheels and Alignment Operation
Be alert to any vibration of the steering wheel or the
seats at normal highway speeds. This may mean a
wheel needs to be balanced. Also, a pull right or left ona
straight, level road may show the need for a tire pressure adjustment or a wheel alignment.
Steering System Operation
Be alert to changes in the steering action. An inspection
is needed when the steering wheelis hard to turn or has
too much free play, or is unusual sounds are noticed
when turning or parking.
Headlight Aim
Take note of the light pattern occasionally. Adjust the
headlights if the beams seem improperly aimed.
A T EACH FUEL FILL
A fluid loss in any (except windshield washer) system
may indicate a problem. Have the system inspected and
repaired immediately.
Engine Oil Level
Check the oil level and add oil if necessary. The best
time to check the engine oil levelis whenthe oil is warm.
1. After stopping the engine, wait a few minutes for the
oil to drain back to the oil pan.
2. Pull out the oil level indicator (dip stick).
3. Wipe it clean, and push the oil level indicator back
down all the way.
4. Pull out the oil level indicator and look at the oil level
on it.
5. Add oil, if needed, to keep the oil levelabove the lower mark. Avoid overfilling the engine, since this may
cause engine damage.
6. Push the indicator all the way back down into the engine after taking the reading.
If you check the oil level when the oil is cold, do not run
the engine first. The cold oil will not drain back to the pan
fast enough to give a true oil level reading.
Engine Coolant Level and Condition
Check the coolant level in the coolant reservoir tank and
add coolant if necessary. Inspect the coolant. Replace
dirty or rusty coolant.
Windshield Washer Fluid Level
Check the washer fluid level in the reservoir. Add fluid if
necessary.
A T LEAST TWICE A MONTH
Tire And Wheel Inspection and Pressure
Check
Check the tire for abnormal wear or damage. Alsocheck
for damaged wheels. Check the tire pressure when the
tires are cold ( check the spare also, unless it is a stowaway). Maintain the recommended pressures. Refer to
“Tire and Wheel” is in section 0B.
A T LEAST MONTHL Y
Light Operation
Check the operation of the license plate light, the headlights (including the high beams), the parking lights, the
fog lights, the taillight, the brake lights, the turn signals,
the backup lights and the hazard warning flasher.
Fluid Leak Check
Periodically inspect the surface beneath the vehicle for
water, oil, fuel or other fluids, after the vehicle has been
parked for a while. Water dripping from the air conditioning system after use is normal. If younoticefuel leaksor
fumes, find the cause and correct it at once.
A T LEAST TWICE A YEAR
Power Steering System Reservoir Level
Check the power steering fluid level. Keep the power
steering fluid at the proper level. Refer to Section 6A,
Power Steering System.
Brake Master Cylinder Reservoir Level
Check the fluid and keep it at theproper level. A lowfluid
level can indicate worn disc brake pads which may need
to be serviced. Check the breather hole in the reservoir
cover to be free from dirt and check for an open passage.
Weather-Strip Lubrication
Apply a thin film silicone grease using a clean cloth.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 14

0B --14 GENERAL INFORMATION
EACH TIME THE OIL IS CHANGED
Brake System Inspection
This inspection should be done when the wheels are removed for rotation. Inspect the lines and the hoses for
proper hookup, binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Inspect the disc brake pads forwear. Inspect the rotors for
surface condition. Inspect other brake parts, theparking
brake, etc., at the same time. Inspect the brakes more
often if habit or conditions result in frequent braking.
Steering, Suspension and Front Drive Axle
Boot And Seal Inspection
Inspect the front and rear suspension and the steering
system for damaged, loose or missing parts, signs of
wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect the power steering
line and the hoses for proper hookup, binding, leaks,
cracks, chafing, etc. Clean and inspect the drive axle
boot and seals for damage, tears or leakage. Replace
the seals if necessary.
Exhaust System Inspection
Inspect the complete system (including the catalytic
converter if equipped). Inspect the body near the exhaust system. Look for broken, damaged, missing, or
out--of--position parts as well as open seams, holes,
loose connections, or other conditions which could
cause heat buildup in the floor pan or could let exhaust
fumes seep into the trunk or passenger compartment.
Throttle Linkage Inspection
Inspect the throttle linkage for interference or binding,
damaged, or missing parts. Lubricate all linkage joints
and throttle cable joints, the intermediate throttle shaft
bearing, the return spring at throttle valve assembly, and
the accelerator pedal sliding face with suitable grease.
Check the throttle cable for free movements.
Engine Drive Belts
Inspect all belts for cracks, fraying, wearand proper tension. Adjust or replace the belts as needed.
Hood Latch Operation
When opening the hood, note the operation of the secondary latch. It should keep the hood from opening all
the way when the primary latch is released. The hood
must close firmly.
A T LEAST ANNUALL Y
Lap and Shoulder Belts Condition and Operation
Inspect the belt system including: the webbing, the
buckles, the latch plates, the retractor, the guide loops
and the anchors.
Movable Head Restraint Operation
On vehicles with movable head restraints, the restraints
must stay in the desired position.
Spare Tire and Jack Storage
Be alert to rattles in the rear of the vehicle. The spare
tire, all the jacking equipment, and the tools must be securely stowed at all times. Oil the jack ratchet or the
screw mechanism after each use.
Key Lock Service
Lubricate the key lock cylinder .
Body Lubrication Service
Lubricate all the body door hinges including the hood,
the fuel door, the rear compartment hinges and the
latches, the glove box and the console doors, and any
folding seat hardware.
Underbody Flushing
Flushing the underbody will remove any corrosive materials used for ice and snow removal and dust control. At
least every spring clean the underbody. First, loosen the
sediment packed in closed areas of the vehicle. Then
flush the underbody with plain water.
Engine Cooling System
Inspect the coolant and freeze protection fluid. If the
fluid is dirty or rusty, drain, flush and refill the engine
cooling system with new coolant. Keep the coolant at
the proper mixture in order to ensure proper freeze
protection, corrosion protection and engine operating
temperature. Inspect the hoses. Replace the cracked,
swollen, or deteriorated hoses. Tighten the clamps.
Clean the outside of the radiator and the air conditioning
condenser. Wash the filler cap and the neck. Pressure
test the cooling system and the cap in order to help ensure proper operation.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 15

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--15
(Changewithfilter
)
ACEA;A2orA3
M
Bsh
g
RECOMMENDED FLUIDS AND LUBRICANTS
Usage Capacity Fluid/Lubricant
Engine Oil
(Change with filter)
Engine Coolant
Brake / Clutch Fluid Approx. 0.5L level must
Power Steering System 1.0 L ATF DEXRON--II
Parking Brake Cable As required Grease
Hood Latch Assembly As required Grease
Hood and Door Hinges
Fuel Door Hinge
Rear Compartment Lid Hinges
Weatherstrips As required Silicone grease
3.2L DOHC 8.2 L
2.3L DOHC 7.5 L
662LA 9.5 L
661LA 8.0 L
3.2L DOHC 11.3 L
2.3L DOHC 10.5 L
662LA 10.5 -- 11.0 L
661LA 9.5 -- 10.0 L
be maintained between
MAX&MINlevel
As required Spray type grease
Quality class -- API ; SH grade or above
ACEA ; A2 or A3
MB sheet ; 229.1
Viscosity -- MB sheet ; 224.1
Quality class -- API ; CG grade or above
ACEA ; B2 or B3
eet ; 228.1, 228.3,
228.5, 229.1
Viscosity -- MB sheet ; 224.1
ALUTEC P--78
DOT--3 & SAE J 1703
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 16

0B --16 GENERAL INFORMATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM OPERATION
GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS
D If a floor jack is used, the following precautions are
recommended.
D Park the vehicle on level ground, “block” the front or
rear wheels, set the jack against the frame, raise the
vehicle and support it with chassis stands and then
perform the service operation.
D Before performing the service operation, disconnect
the negative battery cable in order to reduce the
chance of cable damaged and burning due to short-cir cuiting.
D Use a cover on the body, the seats and the floor to
protect them against damage and contamination.
D Handle brake fluid and antifreeze solution with care
as they can cause paint damage.
D The use of proper tools, and the recommended es-
sential and available tools where specified, areimportant for efficient and reliable performance of the
service repairs.
D Use genuine DAEWOO parts.
D Discard used cotter pins, gaskets, O--rings, oilseals,
lock washers and self--locking nuts. Prepare new
ones for installation. Normal function of these parts
cannot be maintained if these parts are reused.
D Keep the disassembled parts neatly ingroups to facil-
itate proper and smooth reassembly.
D Keep attaching bolts and nuts separated, as they
vary in hardness and design depending on the position of the installation.
D Clean the parts before inspection or reassembly.
D Also clean the oil parts, etc. Use compressed air to
make certain they are free of restrictions.
D Lubricate rotating and slidi ngfaces of parts with oil or
grease before installation.
D When necessary, use a sealer on gaskets to prevent
leakage.
D Carefully observe all specifications for bolt and nut
torques.
D When service operation is completed, make a final
check to be sure service was done properly and the
problem was corrected.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 17

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--17
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER SYSTEM
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 18

0B --18 GENERAL INFORMATION
Manufacturer’s Plate
1 Type Approval No.
2 ehicle Identification Number.
Manufacturer’s Plate Location
Diesel Engine Gasoline Engine
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 19

GENERAL INFORMATION 0B--19
Gasolind Engine Number Diesel Engine Number
Engine Number Location
Diesel Engine
The engine number is stamped on the cylinder block in
front of injection pump.
IL6 3200 Gasolind Engine
The engine number is stamped on the lower rear side of
the alternator.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 20

0B --20 GENERAL INFORMATION
2300 DOHC Gasolind Engine
The engine number is stamped on the upper rear left-hand side of the cylinder block.
VEHICLE LIFTING PROCEDURES
To raise the vehicle, place the lifting equipment only at
the points indicated. Failure to use these precise positions may result in permanent vehicle body deformation.
Many dealer service facilities and service stations are
equipped with automative hoists that bear upon some
parts of the frame in order to lift the vehicle. If any other
hoist method is used, take special care to avoid damaging the fuel tank, the filter neck, the exhaust system, or
the underbody.
Vehicle Lifting Points
Using Jack
(Rearward of Front Tire)
Using Jack
(Forward of Rear Tire)
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 21

SECTION 1
ENGINE
SECTION 1A1 (M162 ENGINE)
GENERAL ENGINE INFORMA TION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications 1A1--2............................
Engine Specifications 1A1--2.....................
Component Locator 1A1--3.......................
Front View 1A1--3...............................
Side View 1A1--4...............................
Performance Curve 1A1--5........................
E32 Engine 1A1--5..............................
Diagnosis 1A1--6.................................
Oil Leak Diagnosis 1A1--6........................
Engine Cranking at The
FrontofCrankshaft 1A1--7.....................
Compression Pressure Test 1A1--8...............
Cylinder Pressure Leakage Test 1A1--10...........
General Information 1A1--12......................
Cleanliness and Care 1A1--12....................
On--Engine Service 1A1--12......................
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 22

1A1 --2 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
g
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Application E32 Engine
Engine Model M162.990
Displacement (CC) 3199
Cylinder (Bore x Stroke) (mm) 89.9 x 84.0
Fuel Injection / Ignition System MSE 3.62S
Compression Ratio 10 : 1
Number of Cylinders 6
Camshaft Valve Arrangement DOHC
Camshaft Drive Type Chain--Driven
Max. Output (ps/rpm) 222 / 5500
Max. Torque (kgSm/rpm) 31.6 / 3750
Firing Order 1--5--3-- 6--2-- 4
Ignition Type Distributorless Double Ignition
Ignition Timing BTDC 8°±2°
Valve Timing
Valve Clearance Adjustment Automatic Control
Idle Speed (rpm) 700 ± 50
Fuel Injection Pressure (kg/cm@) 3--4
Oil Capacity (liter) 8.2
Lubrication Type Forced by Gear Pump
Oil Filter Type Full Flow with Paper Filter
Fuel Unleaded Gasoline
Intake Open/Close ATDC 11° / ABDC 34°
Exhaust Open/Close BBDC 31° /BTDC14°
MSE 3.62S/3.53S (Motorsteuer Elektronik : German)
MSE : Engine Control Electronic
3.62S : 6 Cylinder Version
3.53S : 4 Cylinder Version
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 23

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A1--3
COMPONENT LOCATOR
FRONT VIEW
1 HFM Sensor
2 Intake Air Duct
3 Resonance Flap
4 Cylinder Head Cover
5 Exhaust Camshaft
6 Intake Camshaft
7 Cylinder Head
8 Spark Plug Connector
9 Valve Tappet
10 Injector
11 Exhaust Valve
DAEW OO MY_2000
12 Intake Manifold
13 Connecting Rod
14 Exhaust Manifold
15 Crankshaft
16 Engine Mounting Bracket
17 Starter
18 Crankcase
19 Oil Pump Sprocket
20 Oil Strainer
21 Oil Pan
22 Drain Plug
Page 24

1A1 --4 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
SIDE VIEW
23 Camshaft Adjuster
24 Cooling Fan and Viscous Clutch
25 Piston
26 Flywheel of Drive Plate
27 Oil Pump Drive Chain
28 Oil Return Pipe
29 Timing Chain
30 Oil Pump
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 25

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A1--5
PERFORMANCE CURVE
E32 ENGINE
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 26

1A1 --6 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
DIAGNOSIS
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. Onsome occasions a fluid leak may be
difficult to locate or repair. Thefollowingproceduresmay
help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid,
etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate location of the leak by the drippings on the paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol--type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating conditoins.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer’s directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into theengine oil fill
tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpoi nted and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determinednorder for it to berepaired properly.If a gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the new
gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange must be
repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak, check
for the following conditions and correct them as they
may cause a leak.
Gaskets
D The fluid level/pressure is too high.
D The crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
D The fasteners are tightened improperlyor the threads
are dirty or damaged.
D The flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
D There are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
D The gasket is damaged or worn.
D There is cracking or porosity of the component.
D An improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
D The fluid level/pressure is too high.
D The crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
D The seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
D The seal is damaged or worn.
D Improper installation is evident.
D There are cracks in the components.
D The shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
D A loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 27

ENGINE CRANKING AT THE FRONT OF CRANKSHAFT
Preceding Work: Removal of cooling fan
GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A1--7
1 Vibration Damper Assembly
2 Crankshaft Pulley
Notice
D Remove the negative ground cable before proceed-
ing the work.
D Rotate the pulley in normal engine rotating direction
when cranking.
3Bolt 8.6±0.9 NSm..........................
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 28
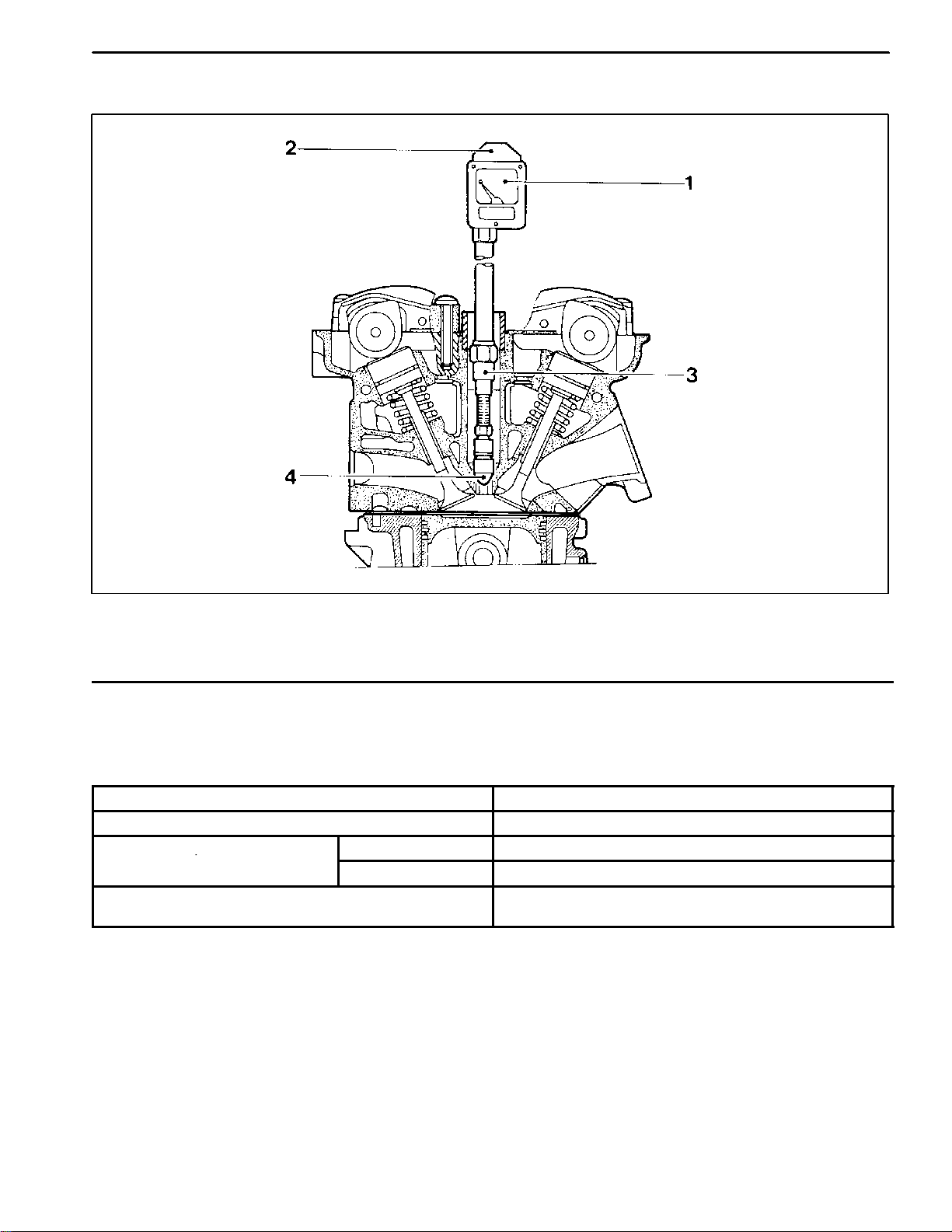
1A1 --8 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
p
COMPR ESSION PRESSUR E TEST
1 Compression Pressure Tester
2 Diagram Sheet
3 Adaptor
4 Sealing Cone
Standard Service Data
Compression Ratio 10 : 1
Normal Engine Temperature 80°C
Normal Compression Pressure
Permissible Pressure Difference Between Individual
Cylinders
General Min. 10 bar, Max. 14 bar
Fuel Optimization Min. 6 bar, Max. 10 bar
Max. 1.5 bar
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 29

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A1--9
Measuring Procedure
1. Warm the engine up to normal operating temperature.
2. Remove the spark plugs.
3. Place the diagram sheet to compression pressure
tester.
4. Connect the adaptor to compression pressure tester
and install it into the spark plug hole.
5. Crank the engine approx. eight revolutions by using
the start motor.
6. Compare the measurements of compression pressure tester with the specifications.
7. Measure the compressionpressure of the other cylinders in the same way.
8. If measured value is not within the specifications,perform the cylinder pressure leakage test.
Notice
D Discharge the combustion residues in the cylinders
before testing the compression pressure.
D Apply the parking brake before cranking the engine.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 30

1A1 --10 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
CYLINDER PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
3 Engine Oil Filler Cap
4 Vibration Damper
6 Cylinder Pressure Leakage Tester with
Connecting Hose
Permissible Pressure Leakage
At Whole Engine
At Valve and Cylinder Head Gasket Max. 10 %
At Piston and Piston Ring Max. 20 %
Max. 25 %
Cylinder Number By Mark On Vibration Damper At TDC
TDC Mark OT (TDC) a(120°) b (240°)
Cylinder Number 1, 6 2, 5 3, 4
Cylinder Pressure Leakage Tester
Universal T ool
Bosch, EFAW 210A
Sun, CLT 228
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 31

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A1--11
Leakage Test
1. Warm the engine up to normal operating temperature.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Check the coolant level by opening the coolant
surge tank cap and replenish if insufficient.
5. Open the engine oil filler cap.
6. Connect the tester to airpressure lineand adjustthe
scale of tester.
7. Install the connecting hose to spark plug hole.
8. Position the piston of No.1 cylinder at TDC by rotating the crankshaft.
9. Connect the connecting hose to tester and measure
the leakage volume after blowing up compressed
air.
Notice: Measure the leakage volume in the completely
opening condition of throttle valve by pulling the acceleration cable.
10. Perform the pressure test according to the firing order.
Notice:
FiringOrder:1--5--3--6--2--4
11. Compare the leakage pressure with the specifications.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 32

1A1 --12 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
GENERAL INFORMATION
CLEANLINESS AND CARE
An automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with tolerances that are measured in the ten-thousandths of an
inch. When any internal engine parts are serviced, care
and cleanlinessare important. A liberal coating of enigne
oil should beapplied tofriction areas during assembly ,to
protect and lubricate the surfaces on initial operation.
Propercleaningandprotection of machinedsurfacesand
friction areas is part of the repair procedure. This is considered standard shop practice even if not specifically
stated.
Whenever valve train components are removed for service, they should be kept in order. They should be
installedinthe samelocations, and withthe samemating
surfaces, as when they were removed.
Battery cables should be disconnectedbefore any major
work is performed on the engine. Failure to disconnect
cables may result in damage to wire harness or other
electrical parts.
ON-EN GINE SERVIC E
Caution: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit, or
when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help prevent personal injury and
damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in
LOCK unless otherwise noted.
Notice: Any time the air cleaner is removed, the intake
opening should be covered. This will protect against accidental entrance of foreign material, which could follow
the intake passage into the cylinder and cause extensive damage when the engine is started.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 33

1A2 --2 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
Application E23 Engine E20 Engine
Engine Model M161.970 M161.940
Displacement (CC) 2295 1998
Cylinder (Bore x Stroke) (mm) 90.9 x 88.4 89.9 x 78.7
Fuel Injection / Ignition System MSE 3.53S ←
Compression Ratio 10.4:1 9.6:1
Number of Cylinders 4 ←
Camshaft Valve Arrangement DOHC ←
Camshaft Drive Type Chain--Driven ←
Max. Output (ps/rpm) 149 / 5500 135 / 5500
Max. Torque (kgSm/rpm) 22.4 / 4000 19.3 / 4000
Firing Order 1-- 3--4-- 2 ←
Ignition Type Distributorless ←
Ignition Timing BTDC 6°± 2° ←
Valve
Timing
Valve Clearance Adjustment Automatic Control ←
Idle Speed (rpm) 750 ± 50 ←
Fuel Injection Pressure (kg/cm@) 3.2 -- 4.2 ←
Oil Capacity (liter) 7.5 ←
Lubrication Type Forced by Gear Pump ←
Oil Filter Type Full Flow with Paper Filter ←
Fuel Unleaded Gasoline ←
Intake Open/Close ATDC 19.25° / ABDC 28.76° ATDC 13.15° / ABDC 13.57°
Exhaust Open/Close BBDC 20.62° / BTDC 15.08° BBDC 16.58° / BTDC 17.05°
MSE 3.62S/3.53S (Motorsteuer Elektronik : German)
MSE : Engine Control Electronic
3.62S : 6 cylinder version
3.53S : 4 cylinder version
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 34

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A2--3
COMPONENT LOCATOR
FRONT VIEW
1 HFM Sensor
2 Intake Air Duct
3 Cylinder Head Cover
4 Ignition Coil
5 Spark Plug Connector
6 Fuel Distributor
7 Injector
8 Exhaust Camshaft
9 Intake Camshaft
10 Valve Tappet
11 Intake Valve
DAEW OO MY_2000
12 Intake Manifold
13 Cylinder Head
14 Exhaust Manifold
15 Dipstick Guide Tube and Gauge
16 Connecting Rod
17 Crankshaft
18 Engine Mounting Bracket
19 Starter
20 Crankcase
21 Oil Pump Sprocket
22 Oil Pan
Page 35

1A2 --4 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
SIDE VIEW
23 Camshaft Adjuster
24 Oil Filler Cap
25 Engine Hanger Bracket
26 Cooling Fan and Viscous Clutch
27 Oil Filter
28 Timing Chain
29 Oil Pump Drive Chain
30 Oil Strainer
31 Oil Pump
32 Ring Gear and Flywheel of Drive Plate
33 Piston
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 36

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A2--5
PERFORMANCE CURVE
E32 ENGINE
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 37

1A2 --6 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
E20 ENGINE
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 38

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A2--7
DIAGNOSIS
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. Onsome occasions a fluid leak may be
difficult to locate or repair. Thefollowingproceduresmay
help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid,
etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wait a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate location of the leak by the drippings on the paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol--type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating conditoins.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer’s directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into theengine oil fill
tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpoi nted and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determinednorder for it to berepaired properly.If a gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the new
gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange must be
repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak, check
for the following conditions and correct them as they
may cause a leak.
Gaskets
D The fluid level/pressure is too high.
D The crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
D The fasteners are tightened improperlyor the threads
are dirty or damaged.
D The flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
D There are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
D The gasket is damaged or worn.
D There is cracking or porosity of the component.
D An improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
D The fluid level/pressure is too high.
D The crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
D The seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
D The seal is damaged or worn.
D Improper installation is evident.
D There are cracks in the components.
D The shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
D A loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 39

1A2 --8 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
ENGINE CRANKING AT THE FRONT OF CRANKSHAFT
Preceding Work: Removal of cooling fan
1 Vibration Damper Assembly
2 Crankshaft Pulley
Notice
D Remove the negative ground cable before proceed-
ing the work.
D Rotate the pulley in normal engine rotating direction
when cranking.
3Bolt 8.6±0.9 NSm..........................
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 40

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A2--9
p
COMPR ESSION PRESSUR E TEST
1 Compression Pressure Tester
2 Diagram Sheet
3 Adaptor
4 Sealing Cone
Standard Service Data
Compression Ratio 10.4, 9.6
Normal Engine Temperature 80°C
Normal Compression
Pressure
Permissible Pressure Difference Between Individual
Cylinders
E23 Engine(e = 10.4) Min. 11 bar, Max. 15 bar
E20 Engine(e = 9.6) Min. 10.5 bar, Max. 14 bar
Max. 1.5 bar
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 41

1A2 --10 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
Measuring Procedure
1. Warm the engine up to normal operating temperature.
2. Remove the spark plugs.
3. Place the diagram sheet to compression pressure
tester.
4. Connect the adaptor to compression pressure tester
and install it into the spark plug hole.
5. Crank the engine approx. eight revolutions by using
the start motor.
6. Compare the measurements of compression pressure tester with the specifications.
7. Measure the compressionpressure of the other cylinders in the same way.
8. If measured value is not within the specifications,perform the cylinder pressure leakage test.
Notice
D Discharge the combustion residues in the cylinders
before testing the compression pressure.
D Apply the parking brake before cranking the engine.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 42

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A2--11
CYLINDER PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
3 Engine Oil Filler Cap
5 Vibration Damper
6 Cylinder Pressure Leakage Tester with
Connecting Hose
Permissible Pressure Leakage
At Whole Engine
At Valve and Cylinder Head Gasket Max. 10 %
At Piston and Piston Ring Max. 20 %
Max. 25 %
Cylinder Number By Mark On Vibration Damper At TDC
TDC Mark OT (TDC) UT (BDC : 180°)
Cylinder Number 1, 4 2, 3
Cylinder Pressure Leakage Tester
DAEW OO MY_2000
Universal T ool
Bosch, EFAW 210A
Sun, CLT 228
Page 43

1A2 --12 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
Leakage Test
1. Warm the engine up to normal operating temperature.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Check the coolant level by opening the coolant
surge tank cap and replenish if insufficient.
5. Open the engine oil filler cap.
6. Connect the tester to airpressure lineand adjustthe
scale of tester.
7. Install the connecting hose to spark plug hole.
8. Position the piston of No.1 cylinder at TDC by rotating the crankshaft.
YAA1A2080
9. Connect the connecting hose to tester and measure
the leakage volume after blowing up compressed
air.
Notice: Measure the leakage volume in the completely
opening condition of throttle valve by pulling the acceleration cable.
10. Perform the pressure test according to the firing order.
Notice: Firing Order : 1 -- 3 -- 4 -- 2
11. Compare the leakage pressure with the specifications.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 44

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A2--13
GENERAL INFORMATION
CLEANLINESS AND CARE
An automobile engine is a combination of many machined, honed, polished and lapped surfaces with tolerances that are measured in the ten-thousandths of an
inch. When any internal engine parts are serviced, care
and cleanlinessare important. A liberal coating of enigne
oil should beapplied tofriction areas during assembly ,to
protect and lubricate the surfaces on initial operation.
Propercleaningandprotection of machinedsurfacesand
friction areas is part of the repair procedure. This is considered standard shop practice even if not specifically
stated.
Whenever valve train components are removed for service, they should be kept in order. They should be
installedinthe samelocations, and withthe samemating
surfaces, as when they were removed.
Battery cables should be disconnectedbefore any major
work is performed on the engine. Failure to disconnect
cables may result in damage to wire harness or other
electrical parts.
ON-EN GINE SERVIC E
Caution: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit, or
when a tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable will help prevent personal injury and
damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in
LOCK unless otherwise noted.
Notice: Any time the air cleaner is removed, the intake
opening should be covered. This will protect against accidental entrance of foreign material, which could follow
the intake passage into the cylinder and cause extensive damage when the engine is started.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 45

1A3--2 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS (Con t’d )
Application OM662LA OM661LA
Idle Speed (rpm) 720 -- 820 750 -- 850
Fuel Injection Pressure (bar) 135 -- 143 135 -- 143
Oil Capacity (liter) 8.0 -- 9.5 6.5 -- 8.0
Lubrication Type Forced by Gear Pump Forced by Gear Pump
Oil Filter Type Combined Full--Flow and Partial
Flow Filter
Fuel Diesel Diesel
Combined Full--Flow and Partial
Flow Filter
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 46

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A3--3
SECTIONAL VIEW
OM662L A ENGIN E
Front View
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 47

1A3--4 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
Side View
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 48

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A3--5
OM661L A ENGIN E
Front View
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 49

1A3--6 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
Side View
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 50

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A3--7
PERFORMANCE CURVE
OM662L A ENGIN E
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 51

1A3--8 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
OM661L A ENGIN E
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 52

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A3--9
SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOL S T AB LE
000 589 10 99 01
Torque Wrench
001 589 76 21 00
Compression Pressure
Tester
601 589 65 09 00
Socket
001 589 73 21 00
Hand Vacuum Pump
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 53

1A3--10 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
DIAGNOSIS
OIL LEAK DIAGNOSIS
Most fluid oil leaks are easily located and repaired by
visually finding the leak and replacing or repairing the
necessary parts. Onsome occasions a fluid leak may be
difficult to locate or repair. Thefollowingproceduresmay
help you in locating and repairing most leaks.
Finding the Leak
1. Identify the fluid. Determine whether it is engine oil,
automatic transmission fluid, power steering fluid,
etc.
2. Identify where the fluid is leaking from.
2.1 After running the vehicle at normal operating
temperature, park the vehicle over a large sheet
of paper.
2.2 Wai t a few minutes.
2.3 You should be able to find the approximate loca-
tion of the leak by the drippings on the paper.
3. Visually check around the suspected component.
Check around all the gasket mating surfaces for
leaks. A mirror is useful for finding leaks in areas that
are hard to reach.
4. If the leak still cannot be found, it may be necessary
to clean the suspected area with a degreaser, steam
or spray solvent.
4.1 Clean the area well.
4.2 Dry the area.
4.3 Operate the vehicle for several miles at normal
operating temperature and varying speeds.
4.4 After operating the vehicle, visually check the
suspected component.
4.5 If you still cannot locate the leak, try using the
powder or black light and dye method.
Powder Method
1. Clean the suspected area.
2. Apply an aerosol--type powder (such as foot powder)
to the suspected area.
3. Operate the vehicle under normal operating conditions.
4. Visually inspect the suspected component. You
should be able to trace the leak path over the white
powder surface to the source.
Black Light and Dye Method
A dye and light kit is available for finding leaks, Refer to
the manufacturer’s directions when using the kit.
1. Pour the specified amount of dye into theengine oil fill
tube.
2. Operate the vehicle normal operating conditions as
directed in the kit.
3. Direct the light toward the suspected area. The dyed
fluid will appear as a yellow path leading to the
source.
Repairing the Leak
Once the origin of the leak has been pinpoi nted and
traced back to its source, the cause of the leak must be
determinednorder for it to berepaired properly.If a gasket is replaced, but the sealing flange is bent, the new
gasket will not repair the leak. The bent flange must be
repaired also. Before attempting to repair a leak, check
for the following conditions and correct them as they
may cause a leak.
Gaskets
D The fluid level/pressure is too high.
D The crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
D The fasteners are tightened improperlyor the threads
are dirty or damaged.
D The flanges or the sealing surface is warped.
D There are scratches, burrs or other damage to the
sealing surface.
D The gasket is damaged or worn.
D There is cracking or porosity of the component.
D An improper seal was used (where applicable).
Seals
D The fluid level/pressure is too high.
D The crankcase ventilation system is malfunctioning.
D The seal bore is damaged (scratched, burred or
nicked).
D The seal is damaged or worn.
D Improper installation is evident.
D There are cracks in the components.
D The shaft surface is scratched, nicked or damaged.
D A loose or worn bearing is causing excess seal wear.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 54

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A3--11
COMPR ESSION PRESSUR E TEST
1 Test Adapter
2 Flexible Connector
3 Compression Pressure Recorder
Service Data
Normal Compression Pressure
Minimum Compression Pressure Approx.18bar
Permissible Pressure Difference Between Individual Cylinders Max. 3bar
DEngine at normal operating temperature of 80_C
Tools Required
000 589 65 09 00 Socket
001 589 73 21 00 Hand Vacuum Pump
28bar
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 55

1A3--12 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
Compression Pressure Measurement
Notice
Ensure that no gear is engaged and that the vehicle
is protected from rolling.
1. Run the engine to be the coolant temperature80_C.
2. Remove the fuel injection nozzle.
Socket Wrench Insert 001 589 65 09 00
3. Install the test adapter (1) and connect the flexible
connector (2) tothe compression pressure recorder.
Compression Pressure Recorder 001 589 76 21 00
4. Disconnect the vacuum line from the stop unit and
connect the hand vacuum pump to the stop unit.
5. Pump the hand vacuum pump and make the fuel in-
jection pump in stop position.
Operating Pressure Approx. 500bar
Hand Vacuum Pump 001 589 73 21 00
6. Using a starter motor, crank the engine 8 revolu-
tions.
7. Measure the remaining cylinder compression pres-
sure in the same manner and compare it with service data.
Notice
If out of standard, do cylinderpressure leakage test.
8. Remove the compression pressure recorder.
9. Install the fuel injection nozzle.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 56

GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION 1A3--13
CYLINDER PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
1 Connector
2 Connection Piece
3 Connection Hose
Permissible Pressure Leakage (Engine at Normal Operating Temperature of 80_C)
At Whole Engine
At Valve and Cylinder Head Gasket Max. 10 %
At Piston and Piston Ring Max. 20 %
Max. 25 %
Commercial T ools
Cylinder Pressure Leakage tester
Connection Piece BOSCH order no. 1 687 010 016
BOSCH, EFAW 210 A or SUN CLT 228
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 57

1A3--14 GENERAL ENGINE INFORMATION
Leakage Test
1. Run the engine to be the coolant temperature80_C.
2. Remove the fuel injection nozzle.
3. Open the coolant subtank cap.
4. Check the coolant level and replenish if necessary.
5. Open the oil filler cap.
6. Remove the air cleaner cover and element.
7. Position the piston at TDC.
8. Install the connector (1) and connection piece (2).
9. Calibrate the tester and connect the connection
hose (3)
10. Pressurize with compressed air and compare the
pressure changes with permissible pressure leakage.
11. If permissible pressure leakage is out of standard,
check followings :
-- Intake and exhaust lines.
-- Sounds in oil filler area.
-- Air bubbles in radiator coolant.
12. Do pressure leakage test for the remainingcylinders
according to the firing order.
D OM 662LA Engine : 1--2--4--5--3
D OM 661LA Engine : 1--3--4--2
13. Remove the tester.
14. Close the coolant pressure cap and oil filler cap.
15. Install the air cleaner element and cover.
16. Install the fuel injection nozzle.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 58

SECTION 1B1
M16 2 ENGINE MECHANICAL
CAUTION: Disconnect the negative battery cable before removing or installing any electrical unit or when a
tool or equipment could easily come in contact with exposed electrical terminals. Disconnecting this cable
will help prevent personal injury and damage to the vehicle. The ignition must also be in LOCK unless otherwise noted.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications 1B1--2............................
Fastener Tightening Specifications 1B1--2..........
Special T ools 1B1--4.............................
Special Tools Table 1B1--4.......................
Maintenance and Repair 1B1--7...................
On--Vehicle Service 1B1--7.........................
Engine Assembly 1B1--7.........................
Crankcase Ventilation System 1B1--14.............
Generator 1B1--16..............................
Engine Mount 1B1--17...........................
Poly V--Belt 1B1--18.............................
Tensioning Device 1B1--20.......................
Poly V--Belt Inspection 1B1--21...................
Cylinder Head Cover 1B1--24.....................
Cylinder Head Front Cover 1B1--26...............
Cylinder Head 1B1--28...........................
Ti ming Gear Case Cover 1B1--31.................
Crankshaft Sealing Rear Cover 1B1--33...........
Belt Pulley and Vibration Damper 1B1--35..........
Crankshaft Front Radial Seal 1B 1--38.............
Crankshaft Rear Radial Seal 1B1--40..............
Crankshaft 1B 1--41.............................
Flywheel / Driven Plate 1B1--47...................
Camshaft Adjuster 1B1--50.......................
Camshaft Sprocket Bolt 1B1--52..................
Camshaft 1B1--54..............................
Camshaft Timing Position 1B1--59................
Valve Spring 1B1--62............................
Valve Stem Seal 1B1--66........................
Chain Tensioner 1B1--67.........................
Ti ming Chain 1B1--70............................
Tensioning Rail 1B1--75..........................
Cylinder Head Guide Rail 1B1--76.................
Crankcase Guide Rail 1B1--77....................
Crankshaft Sprocket 1B1--78.....................
Piston 1B1--80..................................
Connecting Rod 1B1--83.........................
Piston Ring 1B1--85.............................
Engine Oil Specification 1B1--87..................
Oil Pan 1B1--88.................................
Engine Oil and Oil Filter Element 1B1--90..........
Oil Filter 1B1--92................................
Oil Pump 1B1--94...............................
Oil Pressure Relief Valve 1B1--96.................
Oil Non-Return V alve 1B1--97....................
Oil Dipstick Guide Tube 1B1--98..................
Unit Repair 1B1--99..............................
Oil Gallery in Crankcase 1B1--99..................
Oil Gallery in Cylinder Head 1B1--101..............
Core Plugs in Crankcase 1B1--104................
Cylinder Bore 1B1--106..........................
Crankcase Mating Surface 1B1--108..............
Cylinder Head Mating Surface 1B1--1 10...........
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 59

1B1 --2 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
g
SPECIFICATIONS
FASTEN ER TIGHTEN ING SPECIFICATIONS
Application NSm Lb-Ft Lb-In
Fuel Feed and Return Line 21 -- 25 15 -- 18 -Exhaust Manifold and Pipe 30 22 -Propeller Shaft to Transmission 81 -- 89 60 -- 66 -Engine Mounting Nuts 70 52 -Generator Carrier Bolts 25 18 -Tensioning Pulley Bolt 40.5 -- 49.5 29.9 -- 36.5 -Steering Pump Bolts 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -A/C Bracket Bolts 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -Intake Air Duct Mounting Nuts 9--11 -- 80 -- 97
Spark Plug Cover Bolts 9--11 -- 80 -- 97
Cylinder Head Cover Bolts 9--11 -- 80 -- 97
Magnetic Assembly Bolt 9--11 -- 80 -- 97
Cylinder Head Front Cover Bolt 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -Cylinder Head Bolts 55
+90°
+90°
Ti ming Gear Case Cover Bolts
Crankshaft Sealing Rear Cover Mounting Bolts 9--11 -- 80 -- 97
Vibration Damper Center Bolt 200 + 20
Connecting Rod Bearing Cap Bolts 40
Flywheel Mounting Bolt 45 + 5
Amarture Bolt 35 26 -Camshaft Adjuster Flange Bolts 18 -- 22
Intake Flange Shaft Bolts 18 -- 22
Exhaust Camshaft Sprocket Bolts 18 -- 22
Camshaft Bearing Cap Bolts 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -Chain Tensioner Screw Plug 40 30 -Chain Tensioner Assembly 72 -- 88 53 -- 65 -Oil Pump Sprocket Bolt 29 -- 35 21 -- 26 -Tensioning Device Bolts 26 -- 32 19 -- 24 -Water Pump Pulley Bolts 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -Upper Intake Manifold Bolt 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -Lower Intake Mainfold Bolt 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -Flange Bolt to Exhaust Mainfold 30 22 --
M8 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -M6 9--11 -- 80 -- 97
+90° +10°
+90°
+90° +10°
60°±5°
60°±5°
60°±5°
41
+90°
+90°
148 + 15
+90° +10°
30
+90°
33 + 3.7
+90° +10°
13 -- 16
60°±5°
13 -- 16
60°±5°
13 -- 16
60°±5°
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 60

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 3
g
FASTEN ER TIGHTEN ING SPECIFICATIONS (Cont’d )
Application NSm Lb-Ft Lb-In
Exhaust Mainfold Nut to Stud Bolt 26 -- 34 19 -- 25 -OilDrain Plug 25 18 -Oil Filter Cover 25 18 -Oil Filter Bolt 25 18 -Oil Pump Drive Sprocket Bolt 29 -- 35 21 -- 26 -Oil Pump Mounting Bolt 22.5 -- 27.5 16.6 -- 20.3 -Oil Strainer Bracket Bolt 9--11 -- 89 -- 97
Oil Pressure Relief Valve Screw Plug 50 37 -Oil Dipstick Guide Tube Bolt 9--11 -- 89 -- 97
Oil Gallery Screw Plug 15 11 -Torque Converter Mounting Bolts 42 31 -Crankshaft Bearing Cap Bolts 55/+90° 41/+90° -Oil Pan Mounting Bolts
M8 25 18 -M6 10 -- 89
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 61

1B1 --4 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
SPECIAL TOOLS
SPECIAL TOOL S T AB LE
000 589 58 43 00
Chain Assembly
111 589 01 59 00
Supporting Bar
111 589 18 61 00
Lever Pusher
103 589 02 09 00
Oil Filter Remover
DW110--120
Holding Pin
111 589 25 63 00
Thrust Piece
116 589 01 34 00
Threaded Pin
116 589 20 33 00
Sliding Hammer
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 62

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 5
Special Tools Table (Cont’d)
119 589 00 43 00
Drift
601 589 03 14 00
Crankshaft Front Seal
Installer
603 589 00 40 00
Fan Clutch Holder
601 589 03 43 00
Crankshaft Rear Seal
Installer
602 589 00 40 00
Engine Lock
617 589 00 10 00
Allen Wrench Socket
DAEW OO MY_2000
615 589 01 33 00
Crankshaft Sprocket
Puller
DW110 -- 090
Connecting Hose
Page 63

1B1 --6 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Special Tools Table (Cont’d)
DW110 -- 100
Valve Tappet Remover
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 64

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 7
MAINTENANCE AND REPAIR
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 65

1B1 --8 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative terminal of battery.
2. Remove the hood.
3. Remove the under cover.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 28 -- 47 NSm (21 -- 35 lb-ft)
4. Disconnect the mass air flow sensor meter connector.
5. Disconnect the mass air flow sensor meter from the
air filter housing.
6. Remove the intake air duct mounting nuts.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
7. Remove the air cleaner cover. Remove the mounting
bolts and air cleaner housing and element assembly.
8. Loosen the radiator drain cock and drain the coolant.
Notice: Open the coolant reservoir cap.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 66

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 9
9. Loosen the cylinder block drain plug and then drain
the coolant completely.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 30 NSm (22 lb-ft)
Notice: Replace the seal before installation of the drain
plug.
10. Remove the cooling fan shroud. Refer to Section
1D1, Engine Cooling.
11. Disconnect the each hose from radiator.
12. Remove the upper mounting bolts of radiator and
then remove the radiator.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 67

1B1 --10 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
13. Remove the hydraulic pipe of power steering.
Notice: Completely drain the oil.
14. Discharge the refrigerant from A/C system, and disconnect the discharge pipe and suction pipe from
the compressor. Refer to Section 7B, Manual Con-
trol Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning System.
15. Remove the fuel feed and return line.
Notice: Beforeremoving the fuel lines, release thepressure in the fuel system.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 21 -- 25 NSm (15 -- 18 lb-ft)
16. Disconnect the terminals from the generator.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 68

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 11
17. Disconnect the terminals from starter motor and remove the starter motor.
18. Disconnect the engine main harness ground.
19. Disconnect the engine ground wire.
20. Disconnect following sensors connector.
D HFM sensor.
D Coolant temperature sensor.
D 2 knock sensors.
D Camshaft and crankshaft sensors.
21. After removing the ignition coil cover, disconnect the
ignition coil connector.
22. Remove the harness cover and disconnect the 6 injection valve connectors. Disconnect the main harness.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 69

1B1 --12 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
23. Separate the hose toward engine from canister
purge solenoid valve.
24. Remove the canister. Refer to Section 1F1, Engine
Control.
25. Remove the automatic transmission oil cooler line
retaining bolts from the automatic transmission side
and oil pan side
26. Remove the automatic transmission oil cooler line
retaining bolts from engine side and oil pan side.
27. Separate the vacuum hose for brake booster.
28. Separate the other vacuum hoses.
29. By rotating the crankshaft from the front of engine,
remove the 6 torque converter mounting bolts from
the engine ring gear plate.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 42 NSm (31 lb-ft)
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 70

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 13
30. Remove the exhaust manifold and exhaust pipe.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 30 NSm (22 lb-ft)
31. Remove the t ransmission. Refer to Section 5A, Au-
tomatic Transmission.
32. Install a chain to the bracket of engine, by using a
hoist or crane.
33. Remove the engine mount nuts.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 70 NSm (52 lb-ft)
34. Carefullyseparate theengine assemblyfrom thevehicle.
35. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 71

1B1 --14 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
CRANKCASE VENTILATION SYSTEM
1 Crankcase
2 Air Admission Port in Crankcase
3 Oil Drain Port
4 Filter
5 Gasket
6 A/C Bracket
7 Oil Drain Pipe
8OilPan
9 Air Admission Line
10 Vent Line
11 Restriction Hole (Diameter = 2 mm)
12 Intake Manifold
13 Intake Air Duct (Cross Pipe)
14 Cylinder Head Cover
15 Oil Separator
16 Oil Separator
17 Air Admission and Vent Connection
18 Air Admission and Vent Connection
19 Throttle Valve
20 Vent Line
A Fresh Air
B Blowby Gas in Partial Load
C Blowby Gas in Full Load
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 72

Operation at Idling and Mid-Load
D It show that the throttle valve (19) is closed or very
partially opened and the vacuum pressure in intake
manifold is high.
The blowby gas in the crankcase in partial load flows
into the intake manifold through the vent line (20) after passing the air conditioner bracket (6) and the filter (4). The air reentered into the intake manifold will
be dilluted on the flowthrough the restriction hole(11)
in the vent line (10).
The circulated engine oil is separated at the air conditioner bracket (6) and then returns into the oil pan
through the drain pipe (7).
The vacuum pressure generated at the crankcase
sucks fresh air from intake air line (13) through the air
admission and vent connection (17,18).
The fresh air prevents engine oil from being contaminated and the air admission and vent connection
(17,18) is designed to control the rapid pressure
changes in intake air line (13).
Operation at Full-Load
D The throttle valve (19) is fully opened.
All the blowby gases flow into the intake air duct (13)
after passing through the oil separator (15,16) of the
cylinder head cover (14) when fully loaded. This dilluted air will be supplied to the combustion chamber
through the intake manifold (12).
M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 15
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 73

1B1 --16 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
GENERA T OR
1 Nut (M8) 22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).....
2 Bolt (M8 x 30, 3 pieces)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
3 Bolt (M8 x 40, 1 piece)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
4 Bolt (M8 x 70, 1 piece)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
5 Bolt (M8 x 75, 1 piece)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Remove the drive belt.
2. Remove the generator.
3. Unscrew the generator carrier bolts and remove the
carrier.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 25 NSm (18 lb-ft)
4. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 74

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 17
ENGINE MOUNT
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Unscrew the upper engine mount nuts and remove
the engine.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 70 NSm (52 lb-ft)
2. Unscrew the lower nuts.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 38 NSm (28 lb-ft)
3. Remove the hydraulic engine mounting insulator.
4. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 75

1B1 --18 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Preceding Work: Removal of cooling fan
POLY V -- BELT
1 Poly V--belt 2 Belt Tensioning Pulley
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Release the belt tension by turning the belt tensioning
pulley nut clockwise.
2. Remove the poly v--belt.
Notice: Check the belt for damage and tensioning
pulley bearing point for wear and replace them if necessary.
3. Install the belt by turning the nut of tensioning pulley
clockwise.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 76

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 19
Poly V- Belt Arrangement
1 Belt Tensioning Pulley
2 Crankshaft Belt Pulley
3 A/C Compressor Pulley
4 Cooling Fan Pulley
5 Generator Pulley
6 Idler
7 Power Steering Pump Pulley
8 Cooling Fan and Water Pump Pulley
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 77

1B1 --20 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
TENSIONIN G DEVICE
Preceding Work: Removal of poly v--belt
1 Belt (L = 2245)
2 Bolt Combi (M8 x 14, 3 pieces) + Washer
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
3 Water Pump Pulley
4Nut
5 Tensioning Pulley
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 78

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 21
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Remove the poly v--belt.
2. Remove the tensioning pulley by turning its mounting
nut counter clockwise as shown in figure.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque
3. Remove the 3 bolts (2) and remove the water pump
pulley (arrow).
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque
4. Remove the mounting bolts (M8 x30, 3 pieces) at the
tensioning device, and remove the tensioning device
(arrow).
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 26 -- 32 NSm (19 -- 24 lb-ft)
5. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
40.5 -- 49.5 NSm
(29.9 -- 36.5 lb-ft)
22.5 -- 27.5 NSm
(16.6 -- 20.3 lb-ft)
DAEW OO MY_2000
POLY V -- BELT INSPECTION
D Make marks on the belt with chalk.
D Rotate the engine and check the belt for damage.
Notice: If one of the following types of damages is
found, replace the belt.
Page 79

1B1 --22 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
1. Rubber lumps in the base of rib.
2. Dirt or grit ingrained.
3. Pointed rib.
4. Belt cord visible in the base of rib.
5. Cord torn out at the side.
6. Outer cords frayed.
7. Rib detached from the base of belt.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 80

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 23
8. Splits across the rib.
9. Sections of rib torn out.
10. Splits across several ribs.
11. Splits across the back of the belt.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 81

1B1 --24 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
CYLINDER HEAD COVER
1 Ignition Cable Dust Cover
2 Bolt (M6 x 65, 8 pieces)
3 Bolt (M6 x 50, 4 pieces)
4 Spacer Sleeve
5 Thrust Piece
6 Cylinder Head Cover
7 Gasket Replace...........................
9--11 NSm (80--97 lb-in).....................
9--11 NSm (80--97 lb-in).....................
8 Spart Plug Hole Seal Replace...............
9 Camshaft Seal Repl ace.....................
Composition of The Cylinder Head Cover
Bolts
A. M6 x 50, 4 Pieces -- Bolts + Washers
B. M6 x 65, 8 Pieces -- Bolts + Washers
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 82

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 25
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Remove the intake air duct.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
2. Remove the spark plug cover.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
Notice: Unscrew the seven (M6 x 60) bolts and remove
the spark plug cover.
3. Remove the spark plug connector and ignition cable.
4. Unscrew allthe bolts (2,3) and remove the head cover and the gasket.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
Notice: Replace the gasket witha newone if necessary.
5. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
6. Check for oil leaks by operating the engine.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 83

1B1 --26 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
CYLINDER HEAD FRONT COVER
Preceding Work: Removal of cylinder head cover
Removal of coolant connection fitting
1 Camshaft Position Sensor
2 Magnet Assembly
3 Upper Guide Rail
4 Bolt (M6 x 60, 3 pieces)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
5 Bolt (M8 x 80, 3 pieces)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
6 Front Cover
7 Rubber Gasket Replace....................
8 Bolt (M6 x 16, 3 pieces)
9--11 NSm (80--97 lb-in).....................
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 84

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 27
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Remove the magnet assembly.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
2. Remove the cylinder head front cover (6).
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque
22.5 -- 27.5 NSm
(16.6 -- 20.3 lb-ft)
Apply the sealant at the mating surface of the cylinder
head and the front cover.
3. Remove the upper guide rail pinand theguide rail(3).
Installation Notice
Install it while the chain tensioner is loose.
4. Remove the gasket (arrow).
Installation Notice
Replace the gasket with new one and apply the sealant.
5. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 85

1B1 --28 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
CYLINDER HEAD
Preceding Work: Removal of cylinder head cover
Removal of cylinder head front cover
Removal of upper intake manifold
1 Cylinder Head Bolt (14 pieces)
1st step 55 NSm (41lb-ft)...................
2nd step 90°
3rdstep90°
2 Washers (14 pieces)
3 Flange Bolts (3 pieces)
1ststep18--22NSm (13--16 lb-ft)............
2nd step 60°±5°
4 Exhaust Camshaft Sprocket
5 Cylinder Head
6 Gasket Replace...........................
7 Dowel Sleeve
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 86

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 29
TighteningTorqu
e
Tools Required
617589001000 AllenWrenchSocket
116 589 01 34 00 Threaded Pin
116 589 20 33 00 Sliding Hammer
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Rotate the crankshaft so that the piston of number 1
cylinder is at TDC.
Notice: Rotate the crankshaft in the normal engine direction.
2. Put the alignment marks (arrows) on the timing chain
and camshaft sprocket.
3. Drain the coolant from the crankcase.
4. Remove the three flange bolts in the exhaust camshaft sprocket.
Installation Notice
1st step: 18 -- 22 NSm
TighteningTorque
2nd step:60°±5°
(13 -- 16 lb-ft)
Do not reuse the removed bolts.
5. Separate the chain from the camshaft sprocket.
Notice: Be careful not to drop the chain into the timing
case.
6. Remove the guide rail fixing pin using threaded pin
116 589 01 34 00 (1) and sliding hammer 116 589 33
00 (2).
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 87

1B1 --30 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
L
th(L)
7. Remove the cylinder head bolts in numerical order
usingallenwrenchsocket617589001000.
Installation Notice
1st step: 55 NSm
(41 lb-ft)
Ti ghtening Torque
2nd step:90°
3rd step: 90°
8. Check the length of the cylinder head bolt.
Installation Notice
eng
New 160 ± 0.8 mm
Max. 162 ± 0.7 mm
D Replace the bolt if the measured length exceed
the max. length.
D Apply the oil to the thread surface of bolt.
9. Carefully remove the cylinder head and check the
mating surface.
10. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 88

TIMING GEAR CASE COVER
Preceding Work: Removal of cylinder head front cover
Removal of generator bracket
Removal of tensioning device
Removal of belt pulley and vibration damper
M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 31
1 Bolt (M8 x 60, 3 pieces)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
2 A/C Bracket
3 Bolt (M8 x 65, 3 pieces)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
4 Bolt (M8 x 40, 1 piece)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
DAEW OO MY_2000
5 Bolt (M8 x 60, 1 piece)
22.5--27.5 NSm (16.6--20.3 lb-ft).............
6Seal
7 Timing Gear Case Cover
8RollPin
9 Bolt (M6 x 22, 6 pieces)
9--11 NSm (80--97 lb-in).....................
Page 89

1B1 --32 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
T
igh
teningT
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Put the alignment marks (arrows) on the timing chain
and camshaft sprocket.
2. Unscrew the A/C bracket bolts (1) and remove the
bracket.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque
22.5 -- 27.5 NSm
(16.6 -- 20.3 lb-ft)
3. Remove the cooling fan and the viscous clutch. Unscrew the threebolts from the coolingfan bracket and
remove the bracket (arrows).
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque
22.5 -- 27.5 NSm
(16.6 -- 20.3 lb-ft)
4. Remove the timing gear case cover after unscrewing
the bolts (3) and (4) from the timing gear case cover
and the bolt (9) from the oil pan.
Notice: Be careful not to damage the oil pan gasket.
Installation Notice
Bolt (3, 4):22.5 -- 27.5 NSm
(16.6 -- 20.3 lb-ft)
orque
Bolt (9): 9 -- 11 NSm
(80 -- 97 lb-in)
D Apply the sealant after cleaning the timing gear
case cover surface.
D Be careful not to stain the oil chamber of chain
tensioner with the sealant.
5. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
6. Warm up the engine and check for oil leaks.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 90

CRANKSHAFT SEALING REAR COVER
Preceding Work: Removal of the automatic transmission drive plate
M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 33
1 Bolt (M6 x 20, 6 pieces)
2 Radial Shaft Seal
3 Rear Cover
4 Sleeve
9--11 NSm (80--97 lb-in).....................
5 Bolt (M6 x 85, 2 pieces)
9--11 NSm (80--97 lb-in).....................
6Washer
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 91

1B1 --34 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Tools Required
601 589 03 43 00 Crankshaft Rear Seal Installer
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Unscrew the bolts (1) and (5) and remove the closing
cover by pulling the rear cover lug (arrows).
Notice: Be careful not to damage the oil pan gasket.
2. Clean the sealing surface of the crankcase and the
rear sealing cover.
3. Checkthe radialshaft seal and replace it if necessary.
4. Apply the Loctite 573 to the rear cover sealing surface.
5. Apply the engine oil to the dust lip of the radial shaft
seal.
Notice: Do not use the grease.
6. Install the crankshaft rear radial seal and the crankshaft sealingrear cover, usingcrankshaft rear sealinstaller 601 589 03 43 00.
7. Install the crankshaft sealing rear cover mounting
bolts and remove the crankshaft rear seal installer
601 589 03 43 00.
Installation Notice
Ti ghtening Torque 9--11NSm (80 -- 97 lb-in)
8. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 92

BEL T PULLEY AND VIBRA TION DAMPER
Preceding Work: Removal of cooling fan and viscous clutch
Removal of fan shroud
Removal of drive belt
M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 35
1 Vibration Damper Center Bolt (M18 x 50)
1st step 200+20 NSm (148+15 lb-ft)..........
2nd step 90°+10°
2 Vibration Damper Disk
3 Bolt (M6 x 20, 6 pieces)
7.7--9.5 NSm (68.1--84.1 lb-in)...............
DAEW OO MY_2000
4 Vibration Damper Assembly
5 Woodruff Key
6 Bolt (M6 x 12, 4 pieces)
9--11 NSm (80--97 lb-in).....................
7 Cooling Fan Pulley
Page 93

1B1 --36 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
p
Components
1 Center Bolt (M18 x 50)
2 Center Bolt Washer
3 Vibration Damper and Pulley Assembly
4Key
5 Crankshaft Front Seal
6 Timing Gear Case Cover
ServiceDataStandard
Permissble Deviation of The Vibration Damper
7 Crankshaft Sprocket (Camshaft Driven)
8 Crankshaft Sprocket (Oil pump Driven)
9 Crankshaft
10 Oil Pan
11 Oil Pan Gasket
12 Oil Pan Mounting Bolt (M6 x 22)
Radial Runout 0.6 mm
Axial Runout 0.6 mm
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 94

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 37
TighteningTorqu
e
Tools Required
602589004000 EngineLock
Removal & Installation Procedure
1. Adjust the piston of number 1 cylinder to the TDC.
2. Remove the start motor and install the engine lock
602 589 00 40 00 to the flywheel ring gear.
3. Remove the vibration damper center bolt.
Installation Notice
1st step: 200 + 20 NSm
TighteningTorque
2nd step:90° +10°
(148 + 15 lb-ft)
4. Remove the vibration damper assembly using the
puller.
5. Installation should follow the removal procedure in
the reverse order.
Notice: If possible, don’t separate the vibration damper
and the pulley.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 95

1B1 --38 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
CRANKSHAFT FRONT RADIAL SEAL
Preceding Work: Removal of belt pulley and vibration damper
1 Center Bolt (M18 x 50)
1st step 200+20 NSm (148+15 lb-ft)..........
2nd step 90°+10°
2 Center Bolt Washer
3 Crankshaft Front Seal Installer
4 Crankshaft Front Seal
5Key
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 96

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 39
TighteningTorqu
e
Tools Required
601 589 03 14 00 Crankshaft Front Seal Installer
Replacement Procedure
1. Remove the radial seal with a screw driver.
Notice: Use a clean cloth not to damage the radialseal
mounting hole and the crankshaft.
2. Coat the radial sealing lip with engine oil.
3. Usingthe crankshaftfront sealinstaller 601 589 03 14
00, assemble the radial seal .
4. Align the sleeve groove and the woodruff key and
tighten the center bolt until the center bolt and the
damper disk stop in the movement.
Installation Notice
1st step: 200 + 20 NSm
TighteningTorque
2nd step:90° +10°
5. Remove the crankshaft front seal installer601 58903
14 00, and install the belt pulley and the vibration
damper.
6. Check for leaks while operating the engine.
(148 + 15 lb-ft)
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 97

1B1 --40 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
CRANKSHAFT REAR RADIAL SEAL
Preceding Work: Removal of flywheel or drive plate
1 Special T ool
2 Special T ool
3 Crankshaft Rear Seal
Tools Required
601 589 03 43 00 Crankshaft Rear Seal Installer
Replacement Procedure
1. Remove the radial seal with a screw driver.
Notice: Use a clean cloth not to damage the radialseal
mounting hole and the crankshaft.
2. Install the special tool (2) to the crankshaft.
3. Apply the engine oil on the special tool (2).
Notice: Do not use the grease.
4. Install the radial seal on the inner parts assembler.
5. Press in the special tool (1) until the radial seal is
stopped.
6. Check for leaks while operating the engine.
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 98

Preceding Work: Removal of engine assembly
Removal of timing gear case cover
Removal of cylinder head
Removal of oil pump
Removal of oil shield
M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 41
CRANKSHAFT
1 12--sided Stretch Bolt
55 NSm (41 lb-ft) + 90°, Iubricate............
2 Crank Shaft Bearing Cap
DAEW OO MY_2000
3 Crank Shaft Low Main Bearing
4 Lower Thrust Bearing
5 Crankshaft
Page 99

1B1 --42 M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL
Arrangement of the Thrust Bearing and the Main Bearing
1 Upper Main Bearing
2 Upper Thrust Bearing
3 Crankshaft
4 Lower Main Bearing
5 Lower Thrust Bearing
(1) -- (12) Weight Balance/Color Marking Point
j1 -- j7 Journal Main Bearing #1 -- #7
D Color Dot Marking
Thecolor dot marking are put on the(1), (2), (4), (6), (8),
(10), (12) and it indicates the diameter of crankshaft
journal by color as below.
A Crankcase Side
B Bearing Cap Side (Oil Pan Side)
C Axial Fit Bearing (Number 5 Bearing Point)
D Radial Bearing
DAEW OO MY_2000
Page 100

M162 ENGINE MECHANICAL 1B1-- 43
Color Dot
Marking
Blue 57.960 -- 57.965
Yellow 57.955 -- 57.960
Red 57.950 -- 57.955
White 57.945 -- 57.950
Violet 57.940 -- 57.945
Crankshaft Journal Diameter
(mm)
Selection of Crankshaft Main Bearing
1. Crankcase Side
There are seven punching marks on the mating sur-
face to oil pan. This mark is correspondent to the
bearing distinguished by color. Select the relevant
bearing according to the punching mark when repaired.
Punching
Mark
F Blue
FF Yellow
FFF Red
Bearing Color Selected
2. Crankshaft Bearing Cap Side
Select the crankshaft main bearing according to the
marking letter on the crankshaft main journal when
repaired.
Marking
Letter
B Blue
Y Yellow
R Red
W White
V Violet
Bearing Color Selected
Service Data Unit: mm
Crankshaft Stan-
dard and Repair
Size
Standard size 57.940--57.965 58 24.50--24.533 47.935--47.965 27.958--28.042
1st repair size 57.705--57.715 47.700--47.715
2nd repair size 57.450--57.465 47.450--47.465
3rd repair size 57.205--57.215
4th repair size 56.955--56.965 46.950--46.965
Crankshaft
Bearing Jour-
nal Diameter
Crankshaft
Bearing
Diameter
Crankshaft
Journal Width
at fit bearing
--
Connecting Rod
Bearing Journal
Diameter
47.200--47.215
Connecting Rod
Bearing Jourmal
Width
--
DAEW OO MY_2000
 Loading...
Loading...