BOSE 1201 Schematic

®
®
1201, 1401™ Series I and II
Direct Reflecting® Car Stereo
Speaker System
Model 1201
1401 Series I
1401 Series II
©1998 Bose Corporation |
Service Manual |
Part Number 122762 REV 01

Contents |
|
Electrostatic Discharge Sensitive (ESDS) Device Handling |
........................................................ 3 |
Specifications ................................................................................................................................ |
4-5 |
Technical Description ................................................................................................................. |
6 - 10 |
Figure 1. 1401 Block Diagram .......................................................................................................... |
9 |
Figure 2. 1401 II Block Diagram ..................................................................................................... |
10 |
Disassembly/Assembly Procedures ....................................................................................... |
11 - 12 |
Test Procedures ........................................................................................................................ |
13 - 15 |
Part List Notes ................................................................................................................................ |
16 |
PCB Identification .......................................................................................................................... |
16 |
Figure 3. 1401, 1401 II, and 1201 Exploded View ......................................................................... |
17 |
Figure 4. Main Part List Exploded View ......................................................................................... |
18 |
Main Part List .................................................................................................................................. |
19 |
Electrical Part List ..................................................................................................................... |
20 - 25 |
Speaker Part List ............................................................................................................................ |
26 |
Figure 5. Speaker Exploded View .................................................................................................. |
26 |
Technical Information .................................................................................................................... |
27 |
Technical Information .................................................................................................................... |
28 |
CAUTION: THE BOSE® 1201, 1401™ SERIES I AND II CONTAIN NO USER-SERVICE- ABLE PARTS. TO PREVENT WARRANTY INFRACTIONS, REFER SERVICE TO WARRANTY SERVICE STATIONS OR FACTORY SERVICE.
PROPRIETARY INFORMATION
THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OF
BOSE® CORPORATION WHICH IS BEING FURNISHED ONLY FOR
THE PURPOSE OF SERVICING THE IDENTIFIED BOSE PRODUCT
BY AN AUTHORIZED BOSE SERVICE CENTER OR OWNER OF THE
BOSE PRODUCT, AND SHALL NOT BE REPRODUCED OR USED
FOR ANY OTHER PURPOSE.
2
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE SENSITIVE (ESDS)
DEVICE HANDLING
This unit contains ESDS devices. We recommend the following precautions when repairing, replacing, or transporting ESDS devices:
•Perform work at an electrically grounded work station.
•Wear wrist straps that connect to the station or heel straps that connect to conductive floor mats.
•Avoid touching the leads or contacts of ESDS devices or PC boards even if properly grounded. Handle boards by the edges only.
•Transport or store ESDS devices in ESD protective bags, bins, or totes. Do not insert unprotected devices into materials such as plastic, polystyrene foam, clear plastic bags, bubble wrap or plastic trays.
3
SPECIFICATIONS
Power Output: 1401 four channels 1201 two channels
Individual Amplifiers:
IM Distortion:
Frequency Response:
Separation:
Signal to Noise Ratio:
Sensitivity:
Low Level Input:
High Level Input:
(1201 Input Level Adjustable)
Power On/Off: 1401 series I
1401 series II and 1201
Power Indicator: (1401 I and II only)
Low Frequency Control: (1401 I and II only)
Spatial Control™: (1401 I and II only)
Rear Panel Treble Switch: (1401 I and II only)
Rear Panel Switches and Controls: (1201 only)
100 Watts continuous into 0.45 Ohms
50 Watts continuous into 0.45 Ohms
25 Watts continuous into 0.45 Ohms resistive loads from 40 Hz to 17 kHz with less than .09% THD with 14.4 Volts DC
0.4% at 20 Watts output
± 1 dB from nominal equalization curve 40 Hz to 16 kHz with the bass control centered and the spatial control centered
Not less than 40 dB above 500 Hz, spatial slide control centered
Greater than 70 dB, "A" Weighted
250 mVrms for 25 Watts output at 1 kHz
2.75 Vrms for 25 Watts output at 1 kHz
Slide switch, controls power to booster and accessory power output line
Remote Turn-On Capability
Green LED
Slider, ± 8 dB relative to nominal position in two octave band, centered at approximately 170 Hz (refer to the response graphs)
Slider, providing front to back speaker balance adjustment above 200 Hz
Two position switch, 6 dB/octave relative attenuation on rear channels, beginning at 5 kHz
1 Speaker Select Switch
1 Input Level Select Switch
1 Input Level Adjustment Pot
4

|
SPECIFICATIONS |
|
Power Supply Tolerance: |
|
Will operate without noticeable |
|
||
|
|
performance defects between 10.5 and |
|
|
16.5 Volts DC |
Temperature Tolerance: |
|
-25° C (-13° F) to +60° C (+140° F) |
Dimensions: |
|
10" W x 5" D x 2 1/2 " H |
1401 I and II |
|
|
1201 |
|
8 1/8" W x 5 5/16" D x 1 3/4" H |
Weight: |
|
2.4 lbs |
1401 I and II |
|
|
1201 |
|
2 lbs |
Speakers: |
|
|
4 1/2" Driver |
|
2 or 4 full range drivers |
6" x 9" Driver |
|
1201 or 1401 II |
Impedance: |
|
.45 Ohms |
Maximum Power: |
|
25 Watts (1201 and 1401 II has short |
|
|
circuit protection) |
5
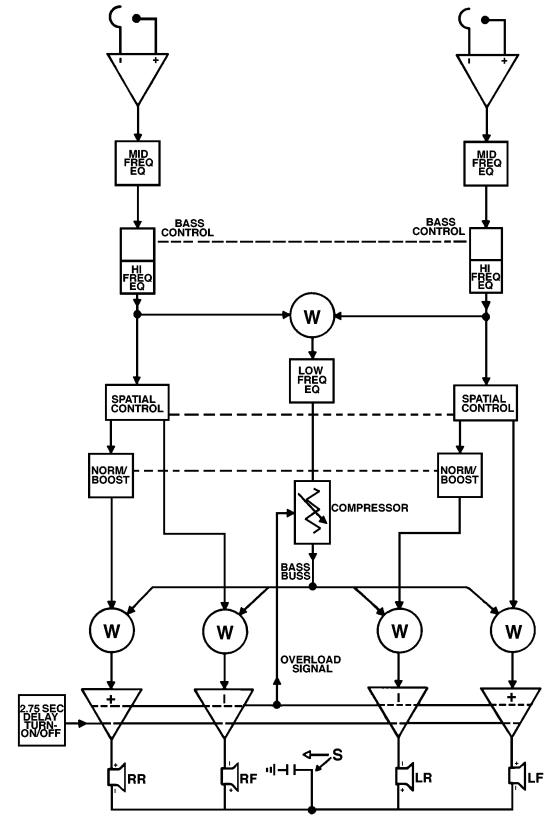
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
Note: The following description is based on the 1401 II. The 1401 I is very similar with the exception of the short circuit protection, remote turn-on circuitry, compressor, and any reference to the use of the 6"x 9" speakers.
The Bose® 1401™ II Booster/Equalizer incorporates unique circuitry that is different from other auto amplifier designs. We ask that you take the time to read this technical description before attempting to service the 1401, and 1401 series II, as it will aid you in the repair process.
The Booster/Equalizer contains a preamplifier, equalizer, short circuit protection circuitry, remote turn on/off circuitry, Spatial Control™, and two or four power amplifiers, each delivering 25 watts of power into 0.45 ohms.
The 1401, and 1401 II are compatible with all front end radio/tape or tape player auto units having their own amplifier, or preamplifier outputs. Low level inputs connect to the output of a front end unit having preamplifier outputs. The booster will produce full output with 250 mVrms applied to the low level input connections. If the front end has only speaker outputs, the high level inputs are utilized. The input signal is reduced by the 100k resistors R52, 53, 72, 73 and then fed to the same differential amplifier as the low level input signal. The high level inputs produce full output with a 2.75 volt input signal.
A differential amplifier U51 is used at the input to minimize sensitivity to alternator whine and other electrical noise. The differential amplifier feeds the equalizer. The equalization curve of the booster has been designed specifically for the drivers supplied with the units.
The first section of the equalizer adjusts the mid frequencies. The signals are then fed to the network driven by U52, 53, (pins 5 and 10) which provides both high frequency equalization and the bass slide control. This control provides boost or cut by approximately 8 dB centered at 170 Hz.
The signal then takes two paths. One is the low frequency path. The signals from the left and right channels are summed and fed through a lowpass filter. This signal is fed to U53 (pin 12), the bass equalization circuitry. The output of the U53 (pin 14), becomes a common bass buss, which feeds the low frequency information to all four power amplifiers.
The second signal path is for the mid and high frequencies, which pass thorough the Spatial Control™. The slider is a front to back balance control for the mid and high frequencies. This is not a fader control. The slider maintains constant and total acoustic power for any spatial setting. The spatial control allows you to shift the mid and high frequency sound image between the front and rear speakers, with the sum of the power delivered to the front or rear speakers remaining the same. This allows great flexibility in compensating for the acoustic properties of various autos, vans, and trucks in which the system may be used. Also a switchable lowpass filter, S1 (located on the rear of the unit) is in the second signal path. This control only affects the signal going to the rear speakers. In position I, the high frequencies going to the rear speakers are cut 6 dB/octave, starting at 5 kHz. In position II, the filter is disconnected. This control compensates for different speaker placement. For example: if the rear speakers were mounted higher than the front speakers, the high frequencies from the rear speakers might sound too bright relative to the front speakers, thus the lowpass filter attenuating circuit would than be used.
6
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The 1401™II has four separate power amplifiers. Each power amplifier receives a summed signal from the common bass buss, and the mid and high frequency information from the Spatial Control™ slider. Using all four speakers to reproduce the bass frequencies provides full rich bass response while directing the other frequencies to the appropriate, left/right/front/back speakers, to maintain proper spatial characteristics.
Each power amplifier uses a high slew rate operational amplifier (U11 left front, U21 left rear, U31 right front, U41 right rear). These ICs are the low level stage for each of the power amplifiers. Pins 4 and 7 of the ICs provide out-of-phase signals to the driver transistors. The voltage across the 47 Ohm resistor attached to pin 6 of each IC is proportional to the current flowing into the driver transistors.
The bias current of the driver transistors is device dependent. The emitter resistor voltage (R11, 12, 21, 22, 31, 32, 41, 42) divided by .47 Ohms will give you the bias current of that transistor. The bias current should typically be 20-60 mA, with a maximum of 140 mA.
The output transistors are unbiased. Therefore, the output waveform will show crossover distortion. "Glitches" will be visible at higher frequencies when driving a load. The distortion from these "glitches" is well above the range of human hearing.
Power is supplied to the 1401 from the vehicle's fuse block. This is fed directly to the output transistors. A network composed of R111 and C91 filters the 14.4 Vdc for all of the ICs in the unit. An 18V zener diode (D55) provides over voltage switching transient and load dump protection. U53, C92, R112, and R113 create a stable voltage that is 1/2 Vcc which is used as a "0" Volt reference for the audio signal.
The turn on/off transient eliminator circuit works in conjunction with the remote turn on and over current protection circuit. When power is applied to the 1401, the output of U52 goes high, which turns on Q63. This turns on Q15, 16, 25, 26 for the left amplifiers and Q35, 36, 45, 46 for the right amplifiers which prevents the driver and power transistors of each amplifier from turning on. This eliminates a turn on "thump" as the amplifiers stabilize during power up. U52's output will go low after approximately three seconds, turning off Q63, which turns off Q15, 16, 25, 26, 35, 36, 45, 46 which, in turn enables the driver and output transistors in the circuit to operate.
The turn off detector is Q51 and Q52. When the 1401 is turned off, Q51 turns off, turning on Q52. This makes the gate of SCR Q62 go high, turning on the SCR. This pulls the voltage of pin 6, U52 low, causing U52 to go high, turning on the transistors Q15, 16, 25, 26, 35, 36, 45, 46, which shuts off the driver and output transistors, eliminating any transients. In addition, whenQ52 goes high, it turns on Q61 And Q80 which discharges C53, the signal return capacitor through R142.
The remote turn on detector is Q53. When voltage is applied to the remote sense line, Q53 shuts off. This makes the gate of SCR Q62 go low, turning off the SCR. This allows C52 to charge, which brings the voltage of pin 6, U52 up, causing U52 to go low, turning on the driver and output transistors. Also, when Q53 shuts off, Q61 and Q80 shuts off, allowing C53 to charge.
7
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The over-current protection network is Q54 and Q55. If the unit draws substantial current across either or both R137 or R139 the voltage approaches .6 volts, creating the same chain of events as previously mentioned in the turn off section. The over-current protection circuit will attempt to recycle a turn on approximately every three seconds. If the over-current conditions are still present, the unit will not turn on.
The 1401™ series I has a compressor circuit. This circuit contains two sections. IC U53, (pins 5, 6, and 7) is the clipping detector, and Z50, is used as a variable attenuator. The compressor affects only the common bass buss signal. Pin 6 of each of the differential amplifiers is tied to an overload signal buss, which is fed to Pin 5 of IC U53. Pins 5, 6, and 7 of IC U53 comprise a voltage comparator network. The voltage at Pin 6 of U53 is the threshold voltage of the comparator. When the voltage at Pin 5 goes negative with respect to Pin 6, due to any amplifier being over driven, the voltage of pin 7 will go negative, with respect to speaker reference (SR). When the voltage of pin 7 goes negative, it turns on the LED, which is inside Z50, its resistance goes down, which attenuates the bass signal. In effect, if any amplifier begins to be over driven, the compressor circuitry is activated and will reduce the amount of common bass signal to the power amplifiers, thereby reducing the bass gain, preventing the amplifier from clipping, reducing potential distortion.
1201 Technical Description
The Bose® 1201 Booster/Equalizer is a two speaker system similar to the 1401™ II. In general, the same troubleshooting rules apply to both units. The RCA and high level inputs are the same, as well as the connectors for the power and speakers. The 1201 also has mute and short circuit protection circuits.
The 1201 has two amplifiers instead of four. The system has switchable equalization for the 4.5" driver or the new 6"x 9" speakers. The equalizer attenuates frequencies above 1kHz in the 4.5" position and turns off the bass equalization in the 6"x 9" position. The 1201 does not have Spatial Control™ or frequency controls.
A new feature for the 1201 is an input level control that provides the ability to interface with a variety of front ends. The input level control adjusts the amp gain for a power sensitivity of approximately 100-1000 mV (low level) and 1-10 Volts (high level) to produce 25 Watts of power per channel at full output at 1 kHz.
Also new in the 1201 amplifier is a compressor circuit. The compressor monitors the power amplifiers and reduces the input gain when the power amplifier begins to clip. Comprised of 1/2 of U1 and U3, U3 acts as a current controlled resistor across R109/209 whose equivalent resistance is inversely proportional to the current into pins 3/6. With no control current, U3 looks like an open circuit. As the current into pins 3/6 increases, the net resistance of R109/ 209 goes down and reduces the compressor amp gain. Control current is provided by detector/driver circuit of Q601-603. The outputs of the power amps (U4, U5, pin 6) pulses when the amp begins to clip. These pulses are detected by Q602, 603 and is filtered. The DC voltage is converted to control currents by R302, 402.
The mute circuit is different than in the 1401 II. It contains two comparators that serve as voltage and time delay sensors. U6, pins 1-3, senses the ANT SW control voltage and goes low if the ANT SW input or supply falls below 9-10 Volts. When U6, pin 1, goes high, C510 charges through R516. When C510's voltage exceeds that of U6, pin 6, (after approximately 2.5 seconds) pin 7 goes high and unmutes the amplifier. If U6, pin 1 goes low, C510 discharges immediately through D501 and mutes the amplifier. During short-circuit conditions, Q503 turns on and pulls U6, pin 2, high causing pin 1 to go low, starting the mute cycle.
8
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
Figure 1. 1401 Block Diagram
9
 Loading...
Loading...