AMD SEMPRON 10 User Manual

AMD SempronTM
Processor Model 10
with 256K L2 Cache
Data Sheet
Publication # 31994 Rev. A-1
Issue Date: August 2004
©2004 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
The contents of this document are provided in connection with Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (“AMD”) products. AMD makes no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this publication and reserves the right to make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time without notice. No license, whether express, implied, arising by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this publication. Except as set forth in AMD’s Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale, AMD assumes no liability whatsoever, and disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to its products including, but not limited to, the implied warranty of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, or infringement of any intellectual property right.
AMD’s products are not designed, intended, authorized or warranted for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or in other applications intended to support or sustain life, or in any other application in which the failure of AMD’s product could create a situation where personal injury, death, or severe property or environmental damage may occur. AMD reserves the right to discontinue or make changes to its products at any time without notice.
Trademarks
AMD, the AMD Arrow logo, AMD Athlon, AMD Duron, AMD Sempron, and combinations thereof, QuantiSpeed, and 3DNow! are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
HyperTransport is a licensed trademark of the HyperTransport Technology Consortium.
MMX is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Other product names used in this publication are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective companies.

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
Table of Contents
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.1 QuantiSpeed™ Architecture Summary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.2 Signaling Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.3 Push-Pull (PP) Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.4 AMD Athlon™ System Bus Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3 Logic Symbol Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4 Power Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.1 Power Management States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Working State. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Halt State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Stop Grant States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Probe State. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.2 Connect and Disconnect Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Connect Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Connect State Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.3 Clock Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5 CPUID Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6 333 FSB AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with
256K L2 Cache Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6.1Electrical and Thermal Specifications for the AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 with
256K L2 Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6.2333 FSB AMD Sempron Processor Model 10
SYSCLK and SYSCLK# AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
6.3333 FSB AMD Athlon System Bus AC Characteristics . . . . . 23
6.4333 FSB AMD Athlon System Bus DC Characteristics . . . . . 24
7 Electrical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
7.1 |
Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
25 |
7.2 |
Interface Signal Groupings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
25 |
7.3 |
Voltage Identification (VID[4:0]) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
26 |
7.4 |
Frequency Identification (FID[3:0]) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
27 |
7.5 |
VCCA AC and DC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
27 |
7.6 |
Decoupling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
27 |
7.7 |
VCC_CORE Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
28 |
7.8 |
Absolute Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
30 |
Table of Contents |
|
iii |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
7.9 SYSCLK and SYSCLK# DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
7.10 General AC and DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
7.11 Open Drain Test Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.12 Thermal Diode Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Thermal Diode Electrical Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Thermal Protection Characterization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.13 APIC Pins AC and DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
8 Signal and Power-Up Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.1 Power-Up Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Signal Sequence and Timing Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Clock Multiplier Selection (FID[3:0]) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.2 Processor Warm Reset Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Northbridge Reset Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
9 Mechanical Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.1 Die Loading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
9.2AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 Part Number
27488 OPGA Package Dimensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.3AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 Part Number
27493 OPGA Package Dimensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
10 Pin Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
10.1 Pin Diagram and Pin Name Abbreviations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
10.2 Pin List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
10.3 Detailed Pin Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
A20M# Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
AMD Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
AMD Athlon System Bus Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Analog Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
APIC Pins, PICCLK, PICD[1:0]# . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
CLKFWDRST Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
CLKIN, RSTCLK (SYSCLK) Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
CONNECT Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
COREFB and COREFB# Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
CPU_PRESENCE# Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
DBRDY and DBREQ# Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
FERR Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
FID[3:0] Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
FSB_Sense[1:0] Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
FLUSH# Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
IGNNE# Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
INIT# Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
INTR Pin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
JTAG Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
K7CLKOUT and K7CLKOUT# Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Key Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
NC Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
iv |
Table of Contents |

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
NMI Pin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
PGA Orientation Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
PLL Bypass and Test Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
PWROK Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
SADDIN[1:0]# and SADDOUT[1:0]# Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Scan Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
SMI# Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
STPCLK# Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
SYSCLK and SYSCLK#. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
THERMDA and THERMDC Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
VCCA Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
VID[4:0] Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
VREFSYS Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
ZN and ZP Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
11 Ordering Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Standard AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 Products . . . . . . . . . . 77
Appendix A Thermal Diode Calculations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Ideal Diode Equation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Temperature Offset Correction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Appendix B Conventions and Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Signals and Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Data Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Abbreviations and Acronyms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Related Publications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Table of Contents |
v |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
vi |
Table of Contents |

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
|
List of Figures |
|
|
Figure 1. Typical AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 System |
|
|
|
Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 4 |
Figure 2. Logic Symbol Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 7 |
|
Figure 3. AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 Power |
|
|
|
Management States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 9 |
Figure 4. AMD Athlon™ System Bus Disconnect Sequence in |
|
|
|
the Stop Grant State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
14 |
Figure 5. Exiting the Stop Grant State and Bus Connect Sequence . . . . . |
15 |
|
Figure 6. Northbridge Connect State Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
16 |
|
Figure 7. Processor Connect State Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
17 |
|
Figure 8. |
SYSCLK Waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
22 |
Figure 9. |
VCC_CORE Voltage Waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
29 |
Figure 10. SYSCLK and SYSCLK# Differential Clock Signals . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 11. General ATE Open-Drain Test Circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 12. Signal Relationship Requirements During Power-Up
Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 13. AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 Part Number
27488 OPGA Package Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 14. AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 Part Number
27493 OPGA Package Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 15. AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 Pin Diagram—
Topside View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 16. AMD Sempron Processor Model 10 Pin Diagram—
Bottomside View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Figure 17. OPN Example for the AMD Sempron Processor
Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
List of Figures |
vii |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
viii |
List of Figures |

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
|
List of Tables |
|
|
Table 1. |
Electrical and Thermal Specifications for the |
|
|
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache . . . . |
21 |
Table 2. |
333 FSB SYSCLK and SYSCLK# AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . |
22 |
Table 3. |
333 FSB AMD Athlon™ System Bus AC Characteristics . . . . . . |
23 |
Table 4. |
333 FSB AMD Athlon System Bus DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . |
24 |
Table 5. |
Interface Signal Groupings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
25 |
Table 6. |
VID[4:0] DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
26 |
Table 7. |
FID[3:0] DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
27 |
Table 8. |
VCCA AC and DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
27 |
Table 9. |
VCC_CORE AC and DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
28 |
Table 10. |
Absolute Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
30 |
Table 11. |
SYSCLK and SYSCLK# DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
31 |
Table 12. |
General AC and DC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
32 |
Table 13. |
Thermal Diode Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
35 |
Table 14. |
Guidelines for Platform Thermal Protection of the |
|
|
Processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
37 |
Table 15. |
APIC Pin AC and DC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
37 |
Table 16. |
Mechanical Loading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
43 |
Table 17. |
Dimensions for the AMD Sempron Processor |
|
|
Model 10 Part Number 27488 OPGA Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
44 |
Table 18. |
Dimensions for the AMD Sempron Processor |
|
|
Model 10 Part Number 27493 OPGA Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
46 |
Table 19. |
Pin Name Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
52 |
Table 20. |
Cross-Reference by Pin Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
60 |
Table 21. |
FID[3:0] Clock Multiplier Encodings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
70 |
Table 22. |
Front-Side Bus Sense Truth Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
71 |
Table 23. |
VID[4:0] Code to Voltage Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
74 |
Table 24. |
Constants and Variables for the Ideal Diode Equation . . . . . . . |
79 |
Table 25. |
Constants and Variables Used in Temperature Offset |
|
|
Equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
80 |
Table 26. |
Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
85 |
Table 27. |
Acronyms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
86 |
List of Tables |
ix |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
x |
List of Tables |

31994A—1August 2004 AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet
Revision History
Date |
Rev |
|
Description |
|
|
|
|
August 2004 |
A-1 |
■ |
Initial release of the AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 Data Sheet |
|
|
|
|
Revision History |
xi |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
xii |
Revision History |

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
1 Overview
The AMD Sempron™ processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache, the new value brand for every-day computing, performs at the top of its class. Using QuantiSpeed™ architecture, this processor is designed to power over 60,000 home and business applications, and it is compatible with various operating systems including Linux and all existing Windows® operating systems.
The AMD Sempron™ processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache, based on proven 0.13 micron technology, integrates the innovative design with the manufacturing expertise of AMD. The processor delivers excellent performance and low power, while maximizing system value and maintaining the stable and compatible Socket A infrastructure of the AMD Sempron processor. The 4-digit model(+) numbering system helps identify overall software performance—the higher the number the better the performance. Detailed technical documentation and performance benchmarks are available at www.amd.com. Visit the AMD Sempron processor product comparison site for more production information.
Delivered in an OPGA package, the AMD Sempron processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache has full-featured capabilities that deliver the integer, floating-point, and 3D multimedia performance for highly demanding applications running on x86 system platforms. The AMD Sempron processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache delivers compelling performance for over 60,000 cutting-edge software applications that include:
■high-speed, smooth stream Internet capability
■digital content creation
■digital photo editing and digital video
■image compression
■video encoding for streaming over the Internet
■soft DVD
■commercial 3D modeling
■workstation-class computer-aided design (CAD)
■commercial desktop publishing
■speech recognition
Chapter 1 |
Overview |
1 |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
The AMD Sempron processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache is binary-compatible with existing x86 software and backwards compatible with applications optimized for MMX™, SSE, and 3DNow!™ technology. Using a data format and single-instruction multiple-data (SIMD) operation based on the MMX instruction model, the AMD Sempron processor model 10 can produce as many as four, 32-bit, single-precision floating-point results per clock cycle. The 3DNow! Professional technology implemented in the AMD Sempron processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache includes integer multimedia instructions and software-directed data movement instructions for optimizing such applications as digital content creation and streaming video for the internet, as well as instructions for digital signal processing (DSP) and communications applications.
The AMD Sempron processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache features a seventh-generation microarchitecture with an integrated, exclusive L2 cache, which supports the growing processor and system bandwidth requirements of emerging software, graphics, I/O, and memory technologies. The high-speed execution core of the AMD Sempron processor model 10 includes multiple x86 instruction decoders, a dual-ported 128-Kbyte split level-one (L1) cache, an exclusive 256-Kbyte L2 cache, three independent integer pipelines, three address calculation pipelines, and a superscalar, pipelined, out-of-order, three-way floating-point engine. The floating-point engine is capable of delivering top-of-the-class performance on numerically complex applications.
The AMD Sempron processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache also includes QuantiSpeed™ architecture, a 333-MHz, 2.7-Gigabyte per second AMD Athlon™ system bus, and 3DNow! Professional technology. The AMD Athlon system bus combines the latest technological advances, such as point-to-point topology, source-synchronous packet-based transfers, and low-voltage signaling to provide an extremely powerful, scalable bus for an x86 processor.
2 |
Overview |
Chapter 1 |

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
1.1QuantiSpeed™ Architecture Summary
The following design features summarize the QuantiSpeed architecture of the AMD Sempron processor model 10 with 256K of L2 cache:
■A nine-issue, superpipelined, superscalar x86 processor microarchitecture designed for increased instructions per cycle (IPC) and high clock frequencies
■Pipelined floating-point unit that executes all x87 (floating-point), MMX, SSE and 3DNow! instructions
■Hardware data pre-fetch that increases and optimizes performance on high-end software applications utilizing high-bandwidth system capabilities
■Advanced two-level translation look-aside buffer (TLB) structures for both enhanced data and instruction address translation. The AMD Sempron processor model 10 with QuantiSpeed architecture incorporates three TLB optimizations: the L1 DTLB increases from 32 to 40 entries, the L2 ITLB and L2 DTLB both use exclusive architecture, and the TLB entries can be speculatively loaded.
The AMD Sempron processor model 10 delivers excellent system performance in a cost-effective, industry-standard form factor. The AMD Sempron processor model 10 is compatible with motherboards based on Socket A.
Figure 1 on page 4 shows a typical AMD Sempron processor model 10 with 256K L2 cache system block diagram.
Chapter 1 |
Overview |
3 |
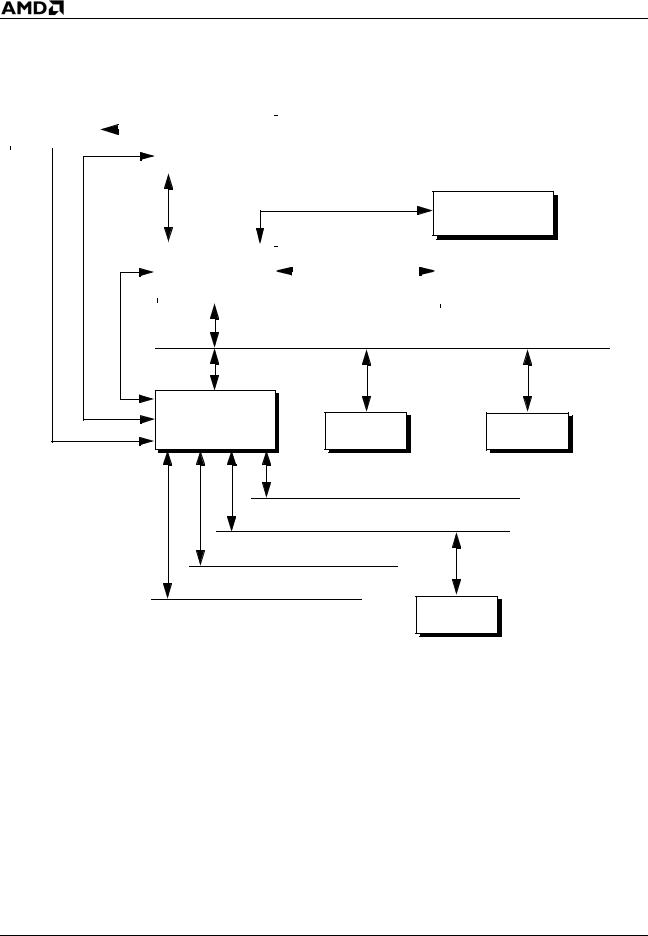
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
|
Thermal Monitor |
|
|
|
|
AMD Sempron™ Proces- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
sor Model 10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMD Athlon™ System Bus
AGP
AGP Bus
|
System Controller |
|
Memory Bus |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SDRAM or DDR |
|||
|
(Northbridge) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCI Bus
Peripheral Bus Con- |
|
|
troller |
LAN |
SCSI |
(Southbridge) |
Modem / Audio
LPC Bus
USB
Dual EIDE
BIOS
Figure 1. Typical AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 System Block Diagram
4 |
Overview |
Chapter 1 |

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
2 Interface Signals
This section describes the interface signals utilized by the
AMD Sempron™ processor model 10.
2.1Overview
The AMD Athlon system bus architecture is designed to deliver excellent data movement bandwidth for next-generation x86 platforms as well as the high-performance required by enterprise-class application software. The system bus architecture consists of three high-speed channels (a unidirectional processor request channel, a unidirectional probe channel, and a 64-bit bidirectional data channel), source-synchronous clocking, and a packet-based protocol. In addition, the system bus supports several control, clock, and legacy signals. The interface signals use an impedance controlled push-pull, low-voltage, swing-signaling technology contained within the Socket A socket.
For more information, see “AMD Athlon™ System Bus Signals” on page 6, Chapter 10, “Pin Descriptions” on page 49, and the
AMD Athlon™ and AMD Duron™ System Bus Specification, order# 21902.
2.2Signaling Technology
The AMD Athlon system bus uses a low-voltage, swing-signaling technology, that has been enhanced to provide larger noise margins, reduced ringing, and variable voltage levels. The signals are push-pull and impedance compensated. The signal inputs use differential receivers that require a reference voltage (VREF). The reference signal is used by the receivers to determine if a signal is asserted or deasserted by the source. Termination resistors are not needed because the driver is impedance-matched to the motherboard and a high impedance reflection is used at the receiver to bring the signal past the input threshold.
For more information about pins and signals, see Chapter 10, “Pin Descriptions” on page 49.
Chapter 2 |
Interface Signals |
5 |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
2.3Push-Pull (PP) Drivers
The AMD Sempron processor model 10 supports push-pull (PP) drivers. The system logic configures the processor with the configuration parameter called SysPushPull (1=PP). The impedance of the PP drivers is set to match the impedance of the motherboard by two external resistors connected to the ZN and ZP pins.
See “ZN and ZP Pins” on page 75 for more information.
2.4AMD Athlon™ System Bus Signals
The AMD Athlon system bus is a clock-forwarded, point-to- point interface with the following three point-to-point channels:
■A 13-bit unidirectional output address/command channel
■A 13-bit unidirectional input address/command channel
■A 72-bit bidirectional data channel
For more information, see Chapter 6, “333 FSB AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Specifications” on page 21, Chapter 7, “Electrical Data” on page 25, and the AMD Athlon™ and AMD Duron™ System Bus Specification, order# 21902.
6 |
Interface Signals |
Chapter 2 |
31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
3 Logic Symbol Diagram
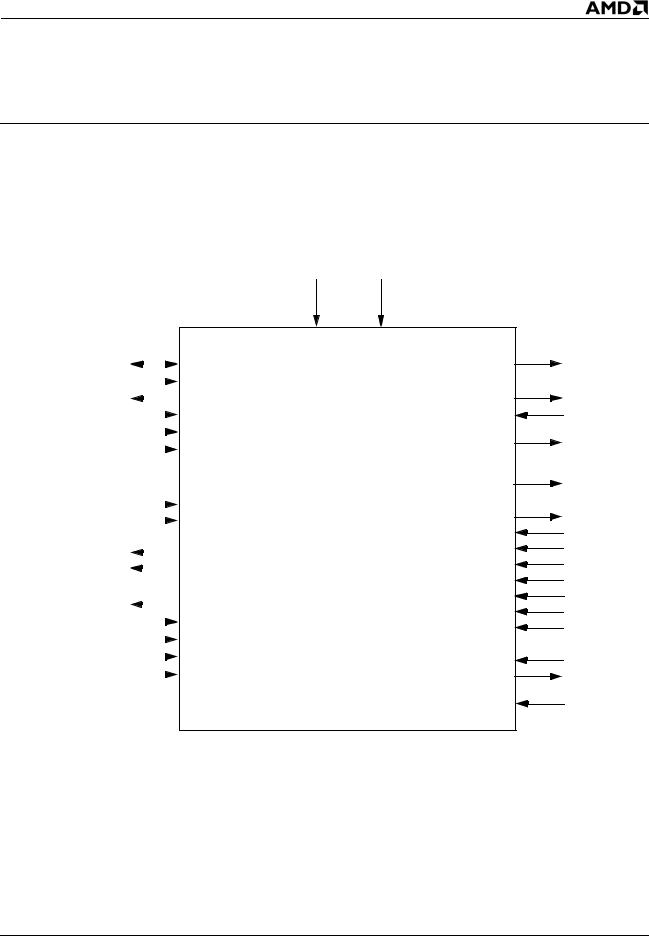
Figure 2 is the logic symbol diagram of the processor. This diagram shows the logical grouping of the input and output signals.
Clock
{
|
{ |
|
|
|
|
SYSCLK |
SYSCLK# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SDATA[63:0]# |
|
|
VID[4:0] |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
SDATAINCLK[3:0]# |
|
|
COREFB |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Data |
|
|
|
SDATAOUTCLK[3:0]# |
|
|
COREFB# |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
SDATAINVALID# |
|
|
PWROK |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
SDATAOUTVALID# |
|
|
FID[3:0] |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
SFILLVALID# |
|
|
FSB_SENSE[1:0] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Probe/SysCMD { |
|
|
|
SADDIN[14:2]# |
AMD Sempron™ |
FERR |
|||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
SADDINCLK# |
||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Processor Model 10 |
IGNNE# |
|
Request { |
|
|
SADDOUT[14:2]# |
|
|
INIT# |
|||
|
|
|
|
INTR |
|||||
|
|
SADDOUTCLK# |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NMI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PROCRDY |
|
|
A20M# |
Power |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SMI# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CLKFWDRST |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FLUSH# |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
and ManagementInitialization { |
|
|
|
|
STPCLK#CONNECT |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
THERMDA |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
RESET# |
|
|
THERMDC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
 {Voltage Control
{Voltage Control
Frequency
Control
Front-Side Bus
Autodetect
{ |
||
|
Legacy |
|
{ |
Thermal |
|
Diode |
||
|
||
PICCLK PICD[1:0]
{
APIC
Figure 2. Logic Symbol Diagram
Chapter 3 |
Logic Symbol Diagram |
7 |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
8 |
Logic Symbol Diagram |
Chapter 3 |

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
4 Power Management
This chapter describes the power management control system of the AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10. The power management features of the processor are compliant with the ACPI 1.0b and ACPI 2.0 specifications.
4.1Power Management States
The AMD Sempron processor model 10 supports low-power Halt and Stop Grant states. These states are used by advanced configuration and power interface (ACPI) enabled operating systems for processor power management.
Figure 3 shows the power management states of the processor. The figure includes the ACPI “Cx” naming convention for these states.
C1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Execute HLT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
C0 |
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Halt |
|
|
SMI#, INTR, NMI, INIT#, RESET# |
|
|
|
Working4 |
|||||||||||||||||||
ProbeIncoming |
|
P |
|
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
throttling)or |
registerPLVL2(Read |
|
assertedSTPCLK# |
|
deassertedSTPCLK# |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
o |
|
|
|
|
T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
K |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S |
|
|
S |
|
|
|
|
|
|
# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
T |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
r |
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
v |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
K |
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
i |
|
|
|
|
|
|
# |
|
|
|
|
|
|
r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
d |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
r |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Incoming Probe |
|
|
|
|
C2 |
|
|
|||||||||||
Probe |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Probe Serviced |
|
|
Stop Grant |
||||||||||||||||
State1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cache Snoopable |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Note: |
The AMD AthlonTM System Bus is connected during the following states: |
1)The Probe state
2)During transitions between the Halt state and the C2 Stop Grant state
3)During transitions between the C2 Stop Grant state and the Halt state
4)C0 Working state
|
S |
|
|
|
|
T |
|
|
|
|
P |
|
|
|
|
C |
|
|
|
|
L |
|
|
|
|
K |
|
|
|
S |
# |
|
|
|
|
d |
|
|
|
T |
e |
|
|
|
P |
a |
|
|
|
|
C |
s |
||
|
L |
s |
||
|
K |
|
e |
|
|
|
r |
||
|
# |
|
t |
|
|
|
e |
||
|
a |
|
d |
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
s |
|
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
r |
|
|
|
|
t |
|
|
|
|
e |
|
|
|
|
d |
|
|
|
|
|
S1 |
|
|
|
|
Stop Grant |
|
|
|
|
Cache Not Snoopable |
|
|
|
|
Sleep |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Legend |
|
|
|
Hardware transitions |
|
||
|
Software transitions |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 3. AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 Power Management States
Chapter 4 |
Power Management |
9 |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
|
The following sections provide an overview of the power |
|
management states. For more details, refer to the |
|
AMD Athlon™ and AMD Duron™ System Bus Specification, |
|
order# 21902. |
|
Note: In all power management states that the processor is |
|
powered, the system must not stop the system clock |
|
(SYSCLK/SYSCLK#) to the processor. |
Working State |
The Working state is the state in which the processor is |
|
executing instructions. |
Halt State |
When the processor executes the HLT instruction, the processor |
|
enters the Halt state and issues a Halt special cycle to the |
|
AMD Athlon system bus. The processor only enters the low |
|
power state dictated by the CLK_Ctl MSR if the system |
|
controller (Northbridge) disconnects the AMD Athlon system |
|
bus in response to the Halt special cycle. |
|
If STPCLK# is asserted, the processor will exit the Halt state |
|
and enter the Stop Grant state. The processor will initiate a |
|
system bus connect, if it is disconnected, then issue a Stop |
|
Grant special cycle. When STPCLK# is deasserted, the |
|
processor will exit the Stop Grant state and re-enter the Halt |
|
state. The processor will issue a Halt special cycle when |
|
re-entering the Halt state. |
|
The Halt state is exited when the processor detects the |
|
assertion of INIT#, RESET#, SMI#, or an interrupt via the INTR |
|
or NMI pins, or via a local APIC interrupt message. When the |
|
Halt state is exited, the processor will initiate an AMD Athlon |
|
system bus connect if it is disconnected. |
Stop Grant States The processor enters the Stop Grant state upon recognition of assertion of STPCLK# input. After entering the Stop Grant state, the processor issues a Stop Grant special bus cycle on the AMD Athlon system bus. The processor is not in a low-power state at this time, because the AMD Athlon system bus is still connected. After the Northbridge disconnects the AMD Athlon system bus in response to the Stop Grant special bus cycle, the processor enters a low-power state dictated by the CLK_Ctl MSR. If the Northbridge needs to probe the processor during the Stop Grant state while the system bus is disconnected, it
10 |
Power Management |
Chapter 4 |

31994A—1August 2004 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
must first connect the system bus. Connecting the system bus places the processor into the higher power probe state. After the Northbridge has completed all probes of the processor, the Northbridge must disconnect the AMD Athlon system bus again so that the processor can return to the low-power state. During the Stop Grant states, the processor latches INIT#, INTR, NMI, SMI#, or a local APIC interrupt message, if they are asserted.
The Stop Grant state is exited upon the deassertion of STPCLK# or the assertion of RESET#. When STPCLK# is deasserted, the processor initiates a connect of the AMD Athlon system bus if it is disconnected. After the processor enters the Working state, any pending interrupts are recognized and serviced and the processor resumes execution at the instruction boundary where STPCLK# was initially recognized. If RESET# is sampled asserted during the Stop Grant state, the processor exits the Stop Grant state and the reset process begins.
There are two mechanisms for asserting STPCLK#—hardware and software.
The Southbridge can force STPCLK# assertion for throttling to protect the processor from exceeding its maximum case temperature. This is accomplished by asserting the THERM# input to the Southbridge. Throttling asserts STPCLK# for a percentage of a predefined throttling period: STPCLK# is repetitively asserted and deasserted until THERM# is deasserted.
Software can force the processor into the Stop Grant state by accessing ACPI-defined registers typically located in the Southbridge.
The operating system places the processor into the C2 Stop
Grant state by reading the P_LVL2 register in the Southbridge.
If an ACPI Thermal Zone is defined for the processor, the operating system can initiate throttling with STPCLK# using the ACPI defined P_CNT register in the Southbridge. The Northbridge connects the AMD Athlon system bus, and the processor enters the Probe state to service cache snoops during Stop Grant for C2 or throttling.
Chapter 4 |
Power Management |
11 |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
In C2, probes are allowed, as shown in Figure 3 on page 9
|
The Stop Grant state is also entered for the S1, Powered On |
|
Suspend, system sleep state based on a write to the SLP_TYP |
|
and SLP_EN fields in the ACPI-defined Power Management 1 |
|
control register in the Southbridge. During the S1 Sleep state, |
|
system software ensures no bus master or probe activity occurs. |
|
The Southbridge deasserts STPCLK# and brings the processor |
|
out of the S1 Stop Grant state when any enabled resume event |
|
occurs. |
Probe State |
The Probe state is entered when the Northbridge connects the |
|
AMD Athlon system bus to probe the processor (for example, to |
|
snoop the processor caches) when the processor is in the Halt or |
|
Stop Grant state. When in the Probe state, the processor |
|
responds to a probe cycle in the same manner as when it is in |
|
the Working state. When the probe has been serviced, the |
|
processor returns to the same state as when it entered the |
|
Probe state (Halt or Stop Grant state). When probe activity is |
|
completed the processor only returns to a low-power state after |
|
the Northbridge disconnects the AMD Athlon system bus again. |
4.2 |
Connect and Disconnect Protocol |
|
|
|
|
Significant power savings of the processor only occur if the |
|
|
|
processor is disconnected from the system bus by the |
|
|
|
Northbridge while in the Halt or Stop Grant state. The |
|
|
|
Northbridge can optionally initiate a bus disconnect upon the |
|
|
|
receipt of a Halt or Stop Grant special cycle. The option of |
|
|
|
disconnecting is controlled by an enable bit in the Northbridge. |
|
|
|
If the Northbridge requires the processor to service a probe |
|
|
|
after the system bus has been disconnected, it must first |
|
|
|
initiate a system bus connect. |
|
Connect Protocol |
In addition to the legacy STPCLK# signal and the Halt and Stop |
||
|
|
Grant special cycles, the AMD Athlon system bus connect |
|
|
|
protocol includes the CONNECT, PROCRDY, and CLKFWDRST |
|
|
|
signals and a Connect special cycle. |
|
|
|
AMD Athlon system bus disconnects are initiated by the |
|
|
|
Northbridge in response to the receipt of a Halt or Stop Grant. |
|
|
|
Reconnect is initiated by the processor in response to an |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
|
Power Management |
Chapter 4 |

31994A—1August 2004
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet
interrupt for Halt or STPCLK# deassertion. Reconnect is initiated by the Northbridge to probe the processor.
The Northbridge contains BIOS programmable registers to enable the system bus disconnect in response to Halt and Stop Grant special cycles. When the Northbridge receives the Halt or Stop Grant special cycle from the processor and, if there are no outstanding probes or data movements, the Northbridge deasserts CONNECT a minimum of eight SYSCLK periods after the last command sent to the processor. The processor detects the deassertion of CONNECT on a rising edge of SYSCLK and deasserts PROCRDY to the Northbridge. In return, the Northbridge asserts CLKFWDRST in anticipation of reestablishing a connection at some later point.
Note: The Northbridge must disconnect the processor from the AMD Athlon system bus before issuing the Stop Grant special cycle to the PCI bus or passing the Stop Grant special cycle to the Southbridge for systems that connect to the Southbridge with HyperTransport™ technology.
This note applies to current chipset implementation— alternate chipset implementations that do not require this are possible.
Note: In response to Halt special cycles, the Northbridge passes the Halt special cycle to the PCI bus or Southbridge immediately.
The processor can receive an interrupt after it sends a Halt special cycle, or STPCLK# deassertion after it sends a Stop Grant special cycle to the Northbridge but before the disconnect actually occurs. In this case, the processor sends the Connect special cycle to the Northbridge, rather than continuing with the disconnect sequence. In response to the Connect special cycle, the Northbridge cancels the disconnect request.
The system is required to assert the CONNECT signal before returning the C-bit for the connect special cycle (assuming CONNECT has been deasserted).
For more information, see the AMD Athlon™ and AMD Duron™ System Bus Specification, order# 21902 for the definition of the C-bit and the Connect special cycle.
Chapter 4 |
Power Management |
13 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
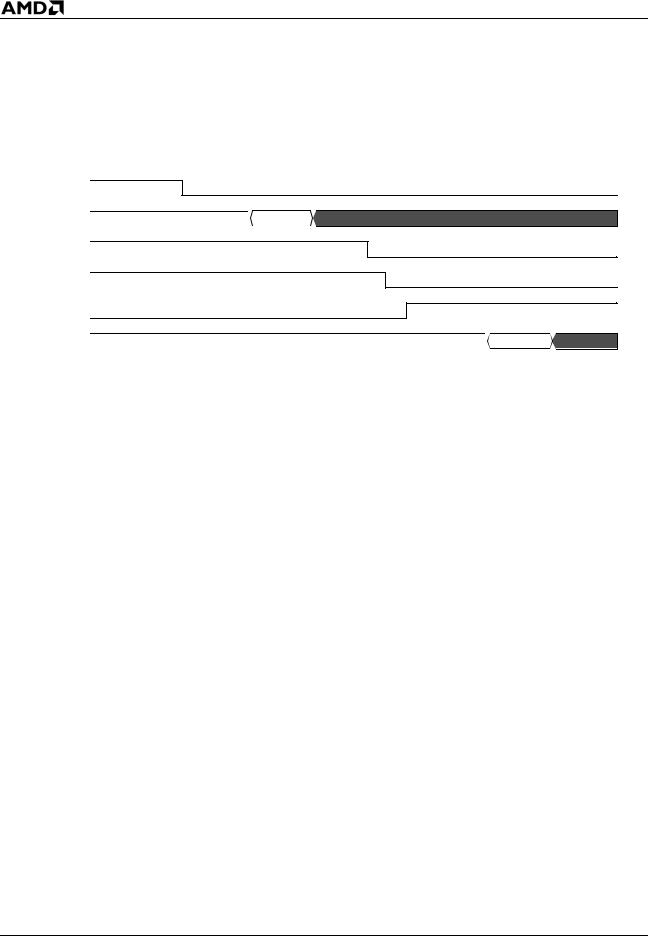
Figure 4 shows STPCLK# assertion resulting in the processor in the Stop Grant state and the AMD Athlon system bus disconnected.
STPCLK#
AMD Athlon™
System Bus  Stop Grant
Stop Grant 
CONNECT
PROCRDY
CLKFWDRST
PCI Bus  Stop Grant
Stop Grant
Figure 4. AMD Athlon™ System Bus Disconnect Sequence in the Stop Grant State
An example of the AMD Athlon system bus disconnect sequence is as follows:
1.The peripheral controller (Southbridge) asserts STPCLK# to place the processor in the Stop Grant state.
2.When the processor recognizes STPCLK# asserted, it enters the Stop Grant state and then issues a Stop Grant special cycle.
3.When the special cycle is received by the Northbridge, it deasserts CONNECT, assuming no probes are pending, initiating a bus disconnect to the processor.
4.The processor responds to the Northbridge by deasserting PROCRDY.
5.The Northbridge asserts CLKFWDRST to complete the bus disconnect sequence.
6.After the processor is disconnected from the bus, the processor enters a low-power state. The Northbridge passes the Stop Grant special cycle along to the Southbridge.
14 |
Power Management |
Chapter 4 |

31994A—1August 2004
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet
Figure 5 shows the signal sequence of events that takes the processor out of the Stop Grant state, connects the processor to the AMD Athlon system bus, and puts the processor into the Working state.
Figure 5. Exiting the Stop Grant State and Bus Connect Sequence
The following sequence of events removes the processor from the Stop Grant state and connects it to the system bus:
1.The Southbridge deasserts STPCLK#, informing the processor of a wake event.
2.When the processor recognizes STPCLK# deassertion, it exits the low-power state and asserts PROCRDY, notifying the Northbridge to connect to the bus.
3.The Northbridge asserts CONNECT.
4.The Northbridge deasserts CLKFWDRST, synchronizing the forwarded clocks between the processor and the Northbridge.
5.The processor issues a Connect special cycle on the system bus and resumes operating system and application code execution.
Chapter 4 |
Power Management |
15 |
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
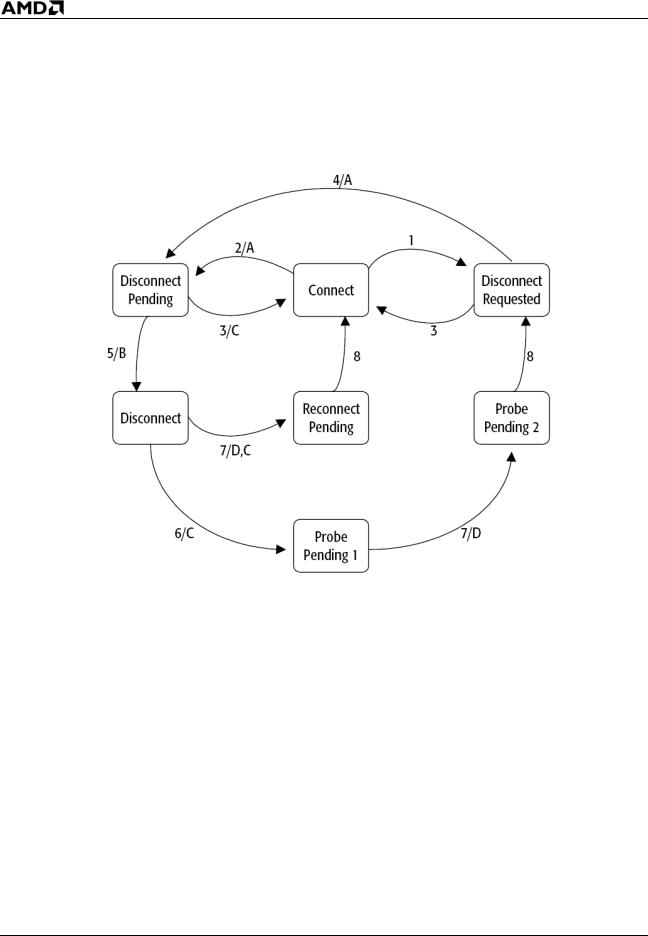
Connect State |
Figure 6 below and Figure 7 on page 17 show the Northbridge |
Diagram |
and processor connect state diagrams, respectively. |
. |
|
|
Condition |
|
|
1 |
A disconnect is requested and probes are still pending. |
|
|
2 |
A disconnect is requested and no probes are pending. |
|
|
3 |
A Connect special cycle from the processor. |
|
|
4 |
No probes are pending. |
|
|
5 |
PROCRDY is deasserted. |
|
|
6 |
A probe needs service. |
|
|
7 |
PROCRDY is asserted. |
|
|
|
Three SYSCLK periods after CLKFWDRST is deasserted. |
8 |
Although reconnected to the system interface, the |
Northbridge must not issue any non-NOP SysDC |
|
|
commands for a minimum of four SYSCLK periods after |
|
deasserting CLKFWDRST. |
|
|
|
Action |
|
|
|
|
A |
Deassert CONNECT eight SYSCLK periods |
|
after last SysDC sent. |
||
|
||
|
|
|
B |
Assert CLKFWDRST. |
|
|
|
|
C |
Assert CONNECT. |
|
|
|
|
D |
Deassert CLKFWDRST. |
|
|
|
Figure 6. Northbridge Connect State Diagram
16 |
Power Management |
Chapter 4 |
31994A—1August 2004
AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet
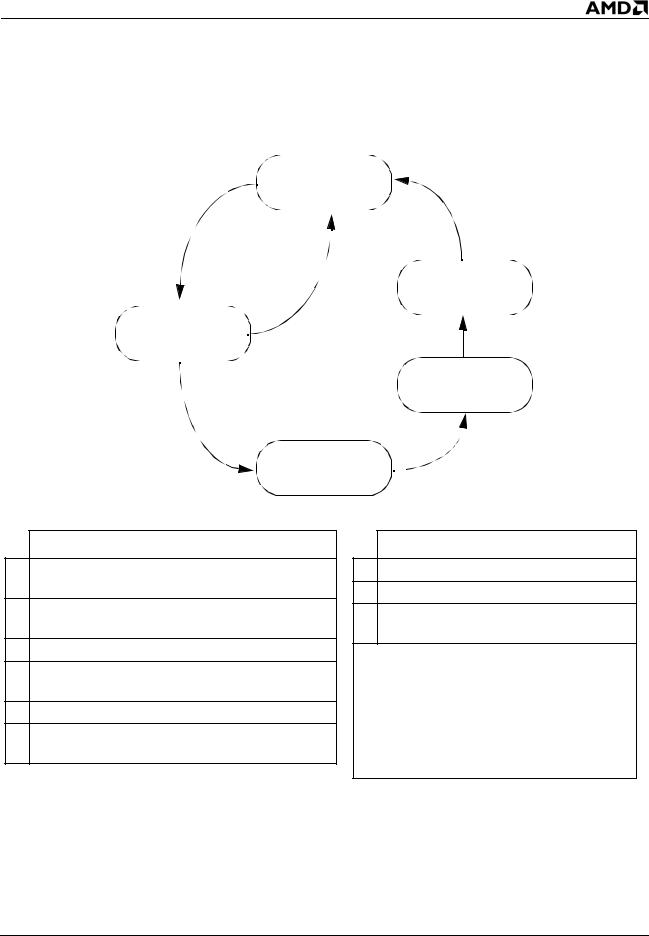
Connect
6/B
1
2/B
Connect
Pending 2
Disconnect |
5 |
Pending |
Connect
Pending 1
3/A
Disconnect  4/C
4/C
Condition
1
CONNECT is deasserted by the Northbridge (for a previously sent Halt or Stop Grant special cycle).
2
Processor receives a wake-up event and must cancel the disconnect request.
3 Deassert PROCRDY and slow down internal clocks.
4
Processor wake-up event or CONNECT asserted by Northbridge.
5 CLKFWDRST is deasserted by the Northbridge.
6
Forward clocks start three SYSCLK periods after CLKFWDRST is deasserted.
Action
ACLKFWDRST is asserted by the Northbridge.
BIssue a Connect special cycle.*
C
Return internal clocks to full speed and assert PROCRDY.
Note:
*The Connect special cycle is only issued after a processor wake-up event (interrupt or STPCLK# deassertion) occurs. If the AMD Athlon™ system bus is connected so the Northbridge can probe the processor, a Connect special cycle is not issued at that time (it is only issued after a subsequent processor wake-up event).
Figure 7. Processor Connect State Diagram
Chapter 4 |
Power Management |
17 |

AMD Sempron™ Processor Model 10 with 256K L2 Cache Data Sheet |
31994A—1August 2004 |
4.3Clock Control
The processor implements a Clock Control (CLK_Ctl) MSR (address C001_001Bh) that determines the internal clock divisor when the AMD Athlon system bus is disconnected.
Refer to the AMD Athlon™ and AMD Duron™ Processors BIOS, Software, and Debug Developers Guide, order# 21656, for more details on the CLK_Ctl register.
18 |
Power Management |
Chapter 4 |
 Loading...
Loading...