Abit AT7 User Manual

Copyright and Warranty Notice
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on part of the vendor, who assumes no liability or responsibility for any errors that may appear in this manual.
No warranty or representation, either expressed or implied, is made with respect to the quality, accuracy or fitness for any particular part of this document. In no event shall the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages arising from any defect or error in this manual or product.
Product names appearing in this manual are for identification purpose only and trademarks and product names or brand names appearing in this document are the property of their respective owners.
This document contains materials protected under International Copyright Laws. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced, transmitted or transcribed without the expressed written permission of the manufacturer and authors of this manual.
If you do not properly set the motherboard settings, causing the motherboard to malfunction or fail, we cannot guarantee any responsibility.


AT7/AT7E Motherboard User’s Manual
|
|
|
Index |
|
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION OF AT7/AT7E FEATURES ................. |
1-1 |
|
||
1-1. |
FEATURES OF AT7/AT7E MOTHERBOARD ........................................................... |
1-1 |
|
|
1-2. |
SPECIFICATIONS.................................................................................................... |
1-2 |
|
|
1-3. |
ITEM CHECKLIST .................................................................................................. |
1-4 |
|
|
1-4. |
LAYOUT DIAGRAM FOR AT7/AT7E...................................................................... |
1-5 |
|
|
CHAPTER 2. INSTALLING THE MOTHERBOARD.............................. |
2-1 |
|
||
2-1. |
INSTALLATION OF THE AMD ATHLON™ XP, ATHLON™ AND DURON™ CPU ......... |
2-2 |
|
|
2-2. |
INSTALLING THE MOTHERBOARD TO THE CHASSIS ................................................ |
2-5 |
|
|
2-3. |
INSTALLING SYSTEM MEMORY ............................................................................. |
2-6 |
|
|
2-4. |
CONNECTORS, HEADERS AND SWITCHES............................................................... |
2-7 |
|
|
CHAPTER 3. INTRODUCING THE BIOS ................................................ |
3-1 |
|
||
3-1. |
CPU SETUP [SOFT MENU™ III]......................................................................... |
3-3 |
|
|
3-2. |
STANDARD CMOS FEATURES SETUP MENU ......................................................... |
3-6 |
|
|
3-3. |
ADVANCED BIOS FEATURES SETUP MENU......................................................... |
3-10 |
|
|
3-4. |
ADVANCED CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP MENU..................................................... |
3-14 |
|
|
3-5. |
INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS ................................................................................. |
3-22 |
|
|
3-6. |
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP MENU .................................................................. |
3-25 |
|
|
3-7. |
PNP/PCI CONFIGURATIONS SETUP MENU........................................................... |
3-31 |
|
|
3-8. |
PC HEALTH STATUS........................................................................................... |
3-34 |
|
|
3-9. |
LOAD FAIL-SAFE DEFAULTS............................................................................... |
3-35 |
|
|
3-10. |
LOAD OPTIMIZED DEFAULTS .............................................................................. |
3-35 |
|
|
3-11. |
SET PASSWORD................................................................................................... |
3-35 |
|
|
3-12. |
SAVE & EXIT SETUP ........................................................................................... |
3-36 |
|
|
3-13. |
EXIT WITHOUT SAVING ...................................................................................... |
3-36 |
|
|
CHAPTER 4. RAID SETTING GUIDE ...................................................... |
4-1 |
|
||
4-1. |
THE FEATURES OF RAID ON THE AT7 .................................................................. |
4-1 |
|
|
4-2. |
RAID SETUP ON THE AT7.................................................................................. |
4-1 |
|
|
4-3. |
THE BIOS SETTING MENU ................................................................................... |
4-2 |
|
|
CHAPTER 5. HPT 374 DRIVER INSTALLATION .................................. |
5-1 |
|
||
5-1. |
DOS® |
................................................................................................................... |
5-1 |
|
5-2. |
WINDOWS® 2000.................................................................................................. |
5-1 |
|
|
CHAPTER 6. |
HPT 374 RAID MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE |
|
|
|
|
........... |
INSTALLATION GUIDE FOR WINDOWS ® 2000 |
6-1 |
|
APPENDIX A. |
VIA 4 IN 1 DRIVERS INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS ® |
|||
|
........................................................................................ |
2000 |
A-1 |
|
APPENDIX B. |
AUDIO DRIVERS INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS ® 2000 |
|||
|
................................................................................................ |
|
B-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4200-0283-02 |
|
Rev. 1.00 |
||

APPENDIX C. |
LAN DRIVERS INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS® 2000 C-1 |
|
APPENDIX D. |
USB 2.0 DRIVERS INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS® 2000 |
|
|
................................................................................................ |
D-1 |
APPENDIX E. |
INSTALLING THE WINBOND HARDWARE MONITOR |
|
|
SOFTWARE........................................................................... |
E-1 |
APPENDIX F. |
BIOS UPDATE GUIDE ........................................................ |
F-1 |
APPENDIX G. |
TROUBLESHOOTING (NEED ASSISTANCE?) ............... |
G-1 |
APPENDIX H. |
HOW TO GET TECHNICAL SUPPORT............................. |
H-1 |
AT7/AT7E

Introduction of AT7/AT7E Features |
1-1 |
|
|
Chapter 1. Introduction of AT7/AT7E Features
1-1. Features of AT7/AT7E Motherboard
This motherboard is designed for AMD Socket A Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ processors. It supports the AMD Socket-A structure, with up to 3 GB (Unbuffered) or 3.5 GB (Registered) of memory, super I/O, USB 2.0, IEEE 1394 (For AT7 Full Version Only) and Green PC functions.
The AT7/AT7E uses the VIA KT333 and VT8233A chipsets to make the evolutionary move from PC 100/PC 133 SDRAM to PC 1600/PC 2100/PC 2700 DDR SDRAM, increasing the speed of the system and memory buses from 100 MHz to 166 MHz. Its 200/266/333 MHz memory interface supports a wide range of PC 1600/PC 2100/PC 2700 DDR SDRAM memory devices now on the market.
VIA KT333 is a system bus controller, or northbridge, that houses the high-speed system elements critical to overall system performance while also containing the system interface to the processor. The key functions of the KT333 System Controller include the 266 MHz Athlon System Bus, the 333 MHz DDR Memory Subsystem, the AGP 4X/2X/1X modes Graphics Interface (AGP 2.0 Compliant) and the 33 MHz/32-bit PCI Bus Interface (PCI 2.2 Compliant), including arbiter.
DDR SDRAM is the newest memory standard. It provides the maximum translation bandwith and also greatly improves data transaction delays. This feature improves system performance and speed, especially with multimedia environment applications.
The AT7/AT7E has a built in Ultra DMA 133 function. This means that it provides speedier HDD throughput boosting overall system performance. Ultra DMA 133 is the newest standard for IDE devices. It enhances existing Ultra DMA 33 technology by increasing both performance and data integrity. This new high-speed interface almost doubles the Ultra DMA 66 burst data transfer rate to 133 Mbytes/sec. The result is maximum disc performance using the current PCI local bus environment. Another benefit is the ability to connect four IDE devices to your system, either through Ultra DMA 66, Ultra DMA 100 or Ultra DMA 133. With this, you will have more flexibility to expand your computer system.
AT7‘s built-in HighPoint HPT 374 chipset gives you the capability to support Ultra DMA 133. Ultra DMA 133 is the newest standard for IDE devices. It provides four IDE channels (IDE3, IDE4, IDE5, IDE6) that also support Ultra DMA 133 specifications, and it allows for four additional IDE devices in your computer system. It can give you high performance and efficiency data transfer rate through the IDE channels. This also means that your computer, in total, can connect up to twelve IDE devices (IDE1 ~ IDE6). This allows for maximum expandability for future hardware demands. This chipset also supports IDE RAID, inlcuding RAID 0, RAID 1 and RAID 0+1. This feature enables you to maximize your data storage performance and security. (For AT7 Full Version Only)
AT7/AT7E provides high flexibility to users building AMD Socket A Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ systems. It provides the option of 133MHz/133MHz CPU and memory bus combinations. The AT7/AT7E has built-in hardware monitoring functions (refer to Appendix E for detailed information) to ensure a safe computing environment.
Part of the MAX Motherboard Series
The AT7/AT7E is part of the MAX Series of motherboard products, offering advanced features and extraordinary value. With its legacy-free operation, ABIT’s MAX Series frees up system resources to offer users a robust, high-performance computing platform. Moreover, expanded connectivity via USB and Firewire ports gives users an easy way to connect to today’s hottest audio and video peripherals. On-board 10/100 LAN provides high-speed networking capabililites, and built in 6-channel audio delivers a rich multimedia experience. Highly integrated with the latest technologies, ABIT’s MAX Series looks
User’s Manual

1-2 |
Chapter 1 |
|
|
to the future, giving users a new level of system longevity and flexibility.
1-2. Specifications
1.Processor
!Supports AMD Athlon™ XP 1500+ ~ 2200+ or future Socket A processors based on 200 MHz/266 MHz (100 MHz/133 MHz Double Data Rate)
!Supports AMD Athlon™ 700 MHz ~ 1.4 GHz or future Socket A processors based on 200 MHz/266 MHz (100 MHz/133 MHz Double Data Rate)
!Supports AMD Duron™ 600 MHz ~ 1.2 GHz or future Socket A processors based on 200 MHz (100 MHz Double Data Rate)
!Supports 200 MHz Alpha EV6 bus for the AMD Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ processors
2.Chipset (VIA KT333 and VT8233A):
!Supports Ultra DMA 33, Ultra DMA 66, Ultra DMA 100 and Ultra DMA 133 IDE protocol
!Supports Advanced Configuration and Power Management Interface (ACPI)
!Accelerated Graphics Port connector supports AGP 2X (3.3V) and 4X (1.5V) mode (Sideband) device
!Supports 200 MHz/266 MHz/333 MHz (100 MHz/133 MHz/166 MHz Double Data Rate) memory bus settings
3.Ultra DMA 133/RAID (For AT7 Full Version Only)
!HighPoint HPT 374 IDE controller
!Supports Ultra DMA 133MB/sec data transfer rate
!Supports RAID0 (Stripping mode for boosting performance) mode
!Supports RAID1 (Mirroring mode for data security) mode
!Supports RAID 0+1 (Stripping and Mirroring) mode
4.Memory (System Memory)
!Four 184-pin DIMM slots support PC 1600, PC 2100 and PC 2700 DDR SDRAM modules
!Supports 6 banks up to 3 GB DRAMs for unbuffered DDR/SDRAM modules. (64, 128, 256, 512 MB and 1 GB DDR SDRAM). For PC 2700 DDR SDRAM modules, it supports 4 banks up to 2 GB DRAMs for unbuffered DDR/SDR modules. (64, 128, 256, 512 MB and 1 GB DDR SDRAM).
!Supports 8 banks up to 3.5 GB DRAMs for registered DDR/SDRAM modules. (64, 128, 256, 512 MB and 1 GB DDR SDRAM). For PC 2700 DDR SDRAM modules, it supports 6 banks up to 3 GB DRAMs for registered DDR/SDRAM modules. (64, 128, 256, 512 MB and 1 GB DDR SDRAM).
5.System BIOS
!SOFT MENU™ III technology, can easily set the processor parameters
!Award PnP (Plug and Play) BIOS supports APM and DMI (Desktop Management Interface)
!Supports ACPI (Advanced Configuration Power Interface)
!Write-Protect Anti-Virus function by AWARD BIOS
AT7/AT7E

Introduction of AT7/AT7E Features |
1-3 |
|
|
6.Audio
!Realtek ALC650 (AC-Link)
!Supports 6 CH DAC for AC3 5.1 CH purpose
!Professional digital audio interface supporting 24-bit S/PDIF OUT
7.LAN
!Onboard Realtek 8100B single chip Ethernet controller interface
!10/100 Mb Operation
!User friendly driver included
8. ABIT Media XP (Optional)
! Supports memory card (MS, SD, CF and MicroDrive) interface ! Supports LPC (Low Pin Count) bus
! Supports SONY MS (Memory Stick) interface/SD (Secure Digital) memory card interface ! Supports CF (Compact Flash) ROM interface (Both Type I & Type II)
9. Multi I/O Functions
!Two channels of bus master IDE ports supporting up to four Ultra DMA 33/66/100/133 devices (IDE1 & IDE2)
!Four channels (IDE3, IDE4, IDE5 and IDE6) of bus master IDE ports supporting up to eight Ultra DMA 33/66/100/133 (RAID 0/1/0+1) specifications HDD devices (For AT7 full version only)
!One floppy port connector (up to 2.88MB)
!Four USB 1.1 connectors (Located at USB1 and USB2 connectors)
!One USB header (USB 3) for two extra USB channels (USB 1.1)
!Onboard VIA VT6202 chipset, provide two USB 2.0 connectors (Located at U30 connector)
!Onboard VIA VT6202 chipset, provide one USB 2.0 header (USB4) for two extra USB 2.0 channels
!Two IEEE 1394 connectors (For AT7 full version only)
!One S/PDIF-Out connector (OPT1)
!One 10/100 Mb port connector (Located on U30 connector)
!Two sets of audio connectors (included Mic-In, Line-In, Front Right+Left, Rear Right+Left and Center+Subwoofer connectors)
10. Miscellaneous
!ATX form factor
!One AGP slot, three PCI slots
!Built-in Wake on LAN header
!Built-in Wake on Ring header
!One built-in SM-Bus header
!One built-in IEEE 1394 header (For AT7 full version only)
!One CD audio input connector
!One AUX audio input connector
!One ABIT front panel Media XP header for analog and digital signal connection to computer chassis front panel (ABIT Media XP is optional accessory designed by ABIT)
!Hardware monitoring Included fan speed, voltages, CPU and system environment temperature
!Board size: 305 * 245mm
User’s Manual

1-4 |
Chapter 1 |
|
|
#Supports Wake On LAN, Modem, but your ATX power supply 5V standby power must be able to provide at least a 720mA current capacity. Otherwise, the functions may not work normally.
#HPT 374 IDE controller is designed to support high-speed and high performance mass storage devices. Thus we suggest that you don’t connect non-disk devices that use ATA/ATAPI interfaces, such as CD-ROM to HPT 374 IDE connector (IDE3, IDE4, IDE5 and IDE6). (For AT7 full version only)
#This motherboard supports the standard bus speeds of 66 MHz/100 MHz/133 MHz that are used by specific PCI, processor and chipset specifications. Exceeding these standard bus speeds is not guaranteed due to the specific component specifications.
#Specifications and information contained in this manual are subject to change without notice.
Note
All brand names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1-3. Item Checklist
Check that your package is complete. If you discover any damaged or missing items, please contact your retailer or dealer.
One ABIT AT7 or AT7E motherboard
Three 80-wire/40-pin ribbon cable for master and slave Ultra DMA 133, Ultra DMA 100, Ultra DMA 66 or Ultra DMA 33 IDE devices
One ribbon cable for 3.5” floppy disk devices
One compact disc for support drivers and utilities
One USB cable (For USB 1.1 used)
One DIY bag
One user’s manual for the motherboard
One floppy disk of HPT 374 drivers (AT7 Full Version Only)
One I/O shield
AT7/AT7E
Introduction of AT7/AT7E Features |
1-5 |
|
|
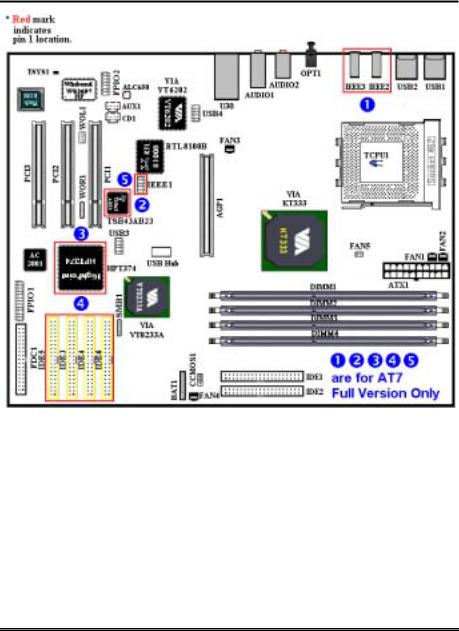
1-4. Layout Diagram for AT7/AT7E
Figure 1-1. AT7/AT7E motherboard component location
User’s Manual

1-6 |
Chapter 1 |
|
|
AT7/AT7E
Installing the Motherboard |
2-1 |
|
|
Chapter 2. Installing the Motherboard
This AT7/AT7E motherboard not only provides all standard equipment for classic personal computers, but also provides great flexibility for meeting future upgrade demands. This chapter will introduce step by step all of the standard equipment and will also present, as completely as possible, future upgrade capabilities. This motherboard is able to supports all AMD Socket A Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ processors now on the market. (For details, see specifications in Chapter 1.)
This chapter is organized according the following features:
1.Installation of the AMD Socket A Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ CPU
2.Installing the Motherboard to the Chassis
3.Installing System Memory
4.Connectors, Headers and Switches
%%%% Before Proceeding with the Installation %%%%
Before you install or unplug any connectors or add-on cards, please remember to turn the ATX power supply switch off (fully turn the +5V standby power off), or take the power cord off. Otherwise, you may cause the motherboard components or add-on cards to malfunction or be damaged.
&
User Friendly Instructions
Please read our instructions carefully and follow them step-by-step. Our objective is to enable the novice computer user to perform the installation by himself. We have attempted to write this document in a very clear, concise and descriptive manner to help overcome any obstacles you may face during installation.
Diagram and Photos
This chapter contains many color drawings, diagrams and photos, we strongly recommend you read this chapter use the PDF file that is stored on the CD-Title. Color improves the clarity and quality of the diagrams. For the downloadable edition, as files larger than 3 MB are difficult to download, we will cut the graphics and photo resolution to reduce the manual file size. In such this case, if your manual is downloaded from our WEB site and not from a CD-ROM, enlarging graphics or photos will distort the image.
User’s Manual
2-2 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
2-1. Installation of the AMD Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™
CPU
Note
!Installing a heatsink and cooling fan is necessary for heat to dissipate from your processor. Failing to install these items may result in overheating and processor damage.
!The AMD Socket A processor will produce a lot of heat while operating, so you need to use a large heat sink that is especially designed for the AMD socket A processor. Otherwise, it may result in overheating and processor damage.
!If your processor fan and its power cable are not installed properly, never plug the ATX power cable into the motherboard. This can prevent possible processor damage.
!Please refer to your processor installation manual or other documentation with your processor for detailed installation instructions.
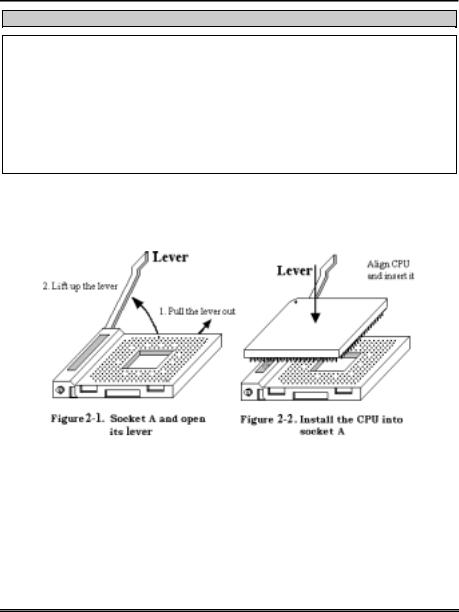
The AMD Socket A Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ processor installation is easy, like Socket 7 Pentium® processors before. Because it uses the “Socket A” ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) socket, you can easily fix the processor firmly into position. Figure 2-1 shows you what the socket A looks like, and how to open the lever. The socket A has more pins than the socket 7. Therefore, a Pentium® level processor cannot be inserted into a socket A.
When you raise the lever, you have to loosen the socket lock. Please raise the lever to the end, and prepare to insert the processor. Next, you need to align the processor pin 1 to the socket pin 1. If you put it in the wrong direction, you will not be able to insert the processor easily, and processor pins will not fully go into the socket. If this is the case, please change the direction, until it easily and fully inserts into the socket A. See Figure 2-2. At the same time check the processor temperature detection thermistor height (if your motherboard has this component), then you can slowly insert the processor into the Scoket A. Finally, you need to check that the processor edge and the Socket A edge is parallel. It should be parallel and not tilted.
When you finish the above, push the lever down to its original position, you should feel the lever lock the socket A. You have then finished the processor installation.
AT7/AT7E
Installing the Motherboard |
2-3 |
|
|
Heatsink Installation Hints
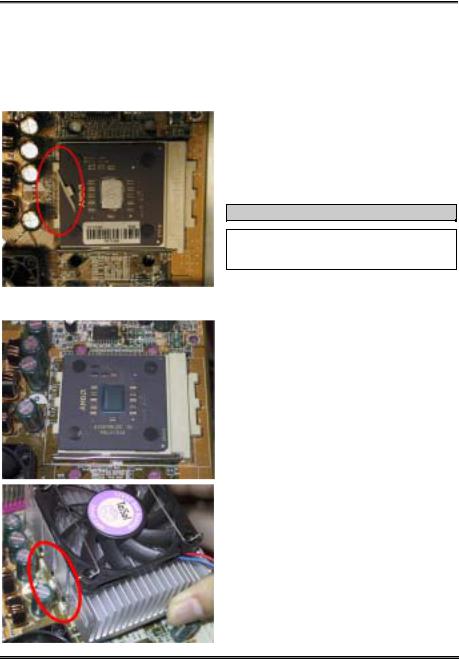
Because the processor will produce a lot of heat while operating, we suggest you use a heatsink approved by AMD to be safe and to keep the processor temperature within normal operation temperatures. The heatsink will be large and heavy, so the fixing plate has a strong tension. When you install the heatsink on to the processor and its socket, you have to very carefully fix the fixing plate to the processor socket hook on both sides. If you do not pay attention to this, you may make the fixing plate scratch the PCB surface and cause circuit damage, break socket hooks or damage the die on the top of processor.
Please follow the sequence metioned below, Do Not inverse the sequence. Otherwise, you may have a situation like the photo on the left. Because of the design of the CPU socket, the left side hooks are not as strong as the right side hooks. If you follow our suggestions you will prevent your processor and socket from damage.
Note
Considering the chassis structure problem, please always take off the motherboard from chassis, before adding or removing a heatsink kit.
The proper procedure to install the heatsink kit:
First, install the processor into the processor socket.
Insert the heatsink left side fix plate into the processor socket left side fix hooks. Make sure the fit is very tight. Check the photo on the left.
User’s Manual

2-4 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
Insert a flat screwdriver into the middle slot of the right side fix plate and push down. Then you can push the fix plate over the socket hooks on the right side. Check the photo on the left.
Check the photo on the left. You have finished the heatsink installation.
Now hold the whole heatsink and slightly shake it, make sure the buttom right side of the heaksink does not contact the right side of the Socket (see bottom picture). Otherwise, the processor die does not have proper contact with the heatsink. This situation may cause processor damage.
Remember to install the heatsink fan power cable to the CPU fan header on the motherboard.
Now you can reinstall the motherboard back into the chassis.
When all above procedures done, you can connect the ATX power cable to the motherboard.
If you have different types of heatsink kit, please refer to the manual that came with the heatsink kit. The left photo shows another type of heatsink fix plate design. The install sequences are still the same, from right side to left side. Just remember that.
We strongly recommand you to buy a heatsink with three holes in the fix plate. This will provide the best stabability and won’t cause the Socket fix hooks to be broken or damaged.
The left photo shows the bottom right side of the heaksink in contact with the right side of the Socket. In this situation, the processor die does not properly contact the heatsink. If you start the computer at this monent, it will immediately cause the processor damage. Always check this place when you finish the heatsink installation.
AT7/AT7E
Installing the Motherboard |
2-5 |
|
|
2-2. Installing the Motherboard to the Chassis
After you install the processor to the motherboard, you can start to fix the motherboard into the chassis. Most computer chassis will have a base on which there will be many mounting holes that allows the motherboard to be securely attached and at the same time, prevents short circuits. There are two ways to attach the motherboard to the base of chassis:
!With studs
!With spacers
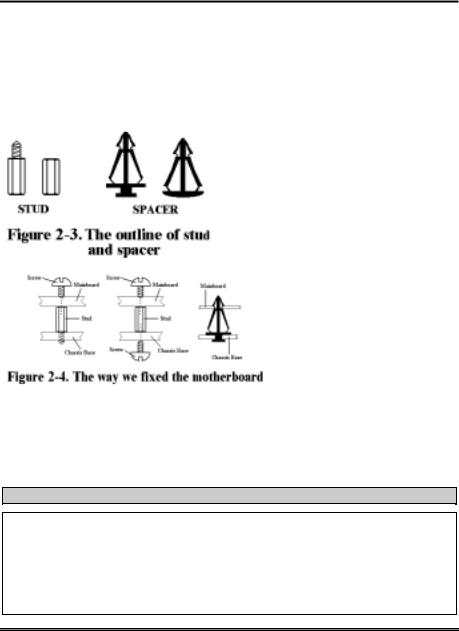
Please refer to figure 2-3, which shows the studs and spacers. There may be several types, but all look like the figures below:
In principle, the best way to attach the motherboard is with studs. Only if you are unable to do this should you attach the board with spacers. Take a careful look at the motherboard and you will see many mounting holes on it. Line these holes up with the mounting holes on the base. If the holes line up and there are screw holes this means you can attach the motherboard with studs. If the holes line up and there are only slots, this means you can only attach the motherboard with spacers. Take the tip of the spacers and insert them into the slots. After doing this to all the slots, you can slide the motherboard into position aligned with the slots. After the motherboard has been positioned, check to make sure everything is OK before putting the casing back on.
Figure 2-4 shows you the way to affix the
motherboard using studs or spacers.
Note
If the motherboard has mounting holes, but they don’t line up with the holes on the base and there are no slots to attach the spacers, don’t worry, you can still attach the spacers to the mounting holes. Just cut the bottom portion of spacers (the spacer they may be a little hard to cut, so be careful with your hands). In this way you can still attach the motherboard to the base without worrying about short circuits. Sometimes you may need to use the plastic springs to isolate the screw from the motherboard PCB surface, because the circuit wire may be near by the hole. Be careful, don’t let the screw contact any the printed circuit wire or parts on the PCB that are near the fixing hole, otherwise it may damage the board or cause board malfunctioning.
User’s Manual

2-6 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
2-3. Installing System Memory
This motherboard provides four 184-pin DDR DIMM sites for memory expansion. The DDR SDRAM DIMM sockets support 8 M x 64 (64 MB), 16M x 64 (128 MB), 32 M x 64 (256 MB), 64 M x 64 (512 MB) and 128 M x 64 (1024 MB) or double density DDR SDRAM DIMM modules. Minimum memory is 64 MB and the maximum memory is 3 GB (Unbuffered, PC 1600 and PC 2100) / 2GB (Unbuffered, PC 2700) or 3.5 GB (Registered, PC 1600 and PC 2100) / 3 GB (Registered, PC 2700) DDR SDRAM. There are four memory module sockets on the system board (for a total of eight banks). In order to create a memory array, following rules must be followed.
! Supports single and double density DDR DIMMs.
Table 2-1. Valid Memory Configurations
Bank |
|
Memory Module |
Total Memory |
Bank 0, 1 |
|
64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB, |
64 MB ~ 1 GB |
(DDR DIMM1) |
|
512 MB, 1024 MB |
|
Bank 2, 3 |
|
64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB, |
64 MB ~ 1 GB |
(DDR DIMM2) |
|
512 MB, 1024 MB |
|
Bank 4, 5 |
|
64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB, |
64 MB ~ 1 GB |
(DDR DIMM3) |
|
512 MB, 1024 MB |
|
Bank 6, 7 |
|
64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB, |
64 MB ~ 1 GB |
(DDR DIMM4) |
|
512 MB, 1024 MB |
|
Total System Memory for Unbuffered DDR DIMM |
64 MB ~ 3 GB |
||
|
(PC 1600/PC 2100) |
|
|
Total System Memory for Registered DDR DIMM |
64 MB ~ 3.5 GB |
||
|
(PC 1600/PC 2100) |
|
|
Total System Memory for Unbuffered DDR DIMM |
64 MB ~ 2 GB |
||
|
|
(PC 2700) |
|
Total System Memory for Registered DDR DIMM |
64 MB ~ 3 GB |
||
|
|
(PC 2700) |
|
|
|
Generally, installing DDR SDRAM modules to your |
|
|
|
motherboard is an easy thing to do. You can refer to |
|
|
|
Figure 2-5 to see what a 184-pin PC 1600, PC 2100 |
|
|
|
and PC 2700 DDR SDRAM module looks like. |
|
Unlike installing SIMMs, DIMMs may be “snapped” directly into the socket. Note: Certain
DDR DIMM sockets have minor physical differences. If your module doesn't seem to fit, please do not force it into the socket as you may damaged your memory module or DDR DIMM socket.
The following procedure will show you how to install a DDR DIMM module into a DDR DIMM socket.
Step 1. Before you install the memory module, please place the computer power switch in the off position and disconnect the AC power cord from your computer.
Step 2. Remove the computer’s chassis cover.
AT7/AT7E
Installing the Motherboard |
2-7 |
|
|
Step 3. Before touching any electronic components, make sure you first touch an unpainted, grounded metal object to discharge any static electricity stored on your clothing or body.
Step 4. Locate your computer’s 184-pin memory expansion DDR DIMM socket.
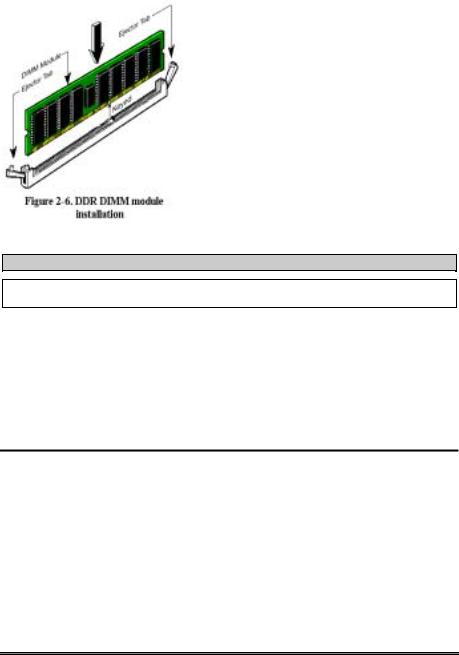
Step 5. Insert the DDR DIMM module into the expansion socket as shown in the illustration. Note how the module is keyed to the socket. You can refer to Figure 2-6 for the details. This insures the DDR DIMM module will be plugged into the socket in one way only. Firmly press the DDR DIMM module into DDR DIMM socket, making certain the module is completely seated in the DDR DIMM socket.
Step 6. Once the DDR DIMM module has been installed, the installation is complete and the computer’s
cover can be replaced. Or you can continue to install other devices and add-on cards that are mentioned in the following section.
Note
When you install a DDR DIMM module fully into the DDR DIMM socket, the eject tab should be locked into the DDR DIMM module very firmly and fit into its indention on the both sides.
It is difficult to differentiate between the PC 1600, PC 2100 and PC 2700 DDR SDRAM modules from the exterior. The only way you can identify them is to look at the sticker on the DDR SDRAM module. The sticker will tell you which kind of structure module the DDR SDRAM is.
2-4. Connectors, Headers and Switches
Inside the case of any computer several cables and plugs have to be connected. These cables and plugs are usually connected one-by-one to connectors located on the motherboard. You need to carefully pay attention to any connection orientation the cables may have and, if any, notice the position of the first pin of the connector. In the explanations that follow, we will describe the significance of the first pin.
We will show you all of the connectors, headers and switches here, and tell you how to connect them. Please pay attention and read the entire section for necessary information before attempting to finish all of the hardware installation inside the computer chassis.
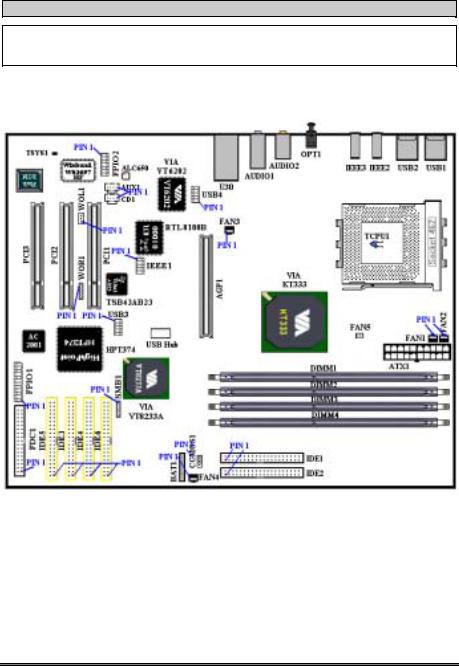
Figure 2-7 shows you all of the connectors and headers that we’ll discuss in the next section, you can use this diagram to visually locate each connector and header we describe.
User’s Manual
2-8 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
Note
This components diagram will be slightly different because there are a number of models. We’ll use the AT7 full version motherboard as standard; all descriptions of connector and header will be based on the AT7 full version motherboard.
All connectors, headers and switches mentioned here, will depend on your system configuration. Some features you may (or may not) have and need to connect or configure depending on the peripheral. If your system doesn't have such add-on cards or switches you can ignore some special feature connectors.
Figure 2-7. All connectors and headers for the AT7
First, Let’s see the headers that AT7 uses, and what their functions are. We will show you all the connectors and headers.
AT7/AT7E

Installing the Motherboard |
2-9 |
|
|
(1). ATX1: ATX Power Input Connector
Attach the connector from the power supply to the ATX1 connector here. Remember you have to push the connector from the ATX power supply firmly to the end with the ATX1 connector, insuring that you have a good connection.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation.
Caution
If the power supply connectors are not properly attached to the ATX power supply, the power supply or add-on cards may be damaged.
One end of AC power core connects to ATX power supply, and the other end (AC plug) will plug into the wall outlet. Be aware that when facing the wall outlet, the round hole is in the middle. The right side slot is called ground wire slot. It has a longer slot length than the left side slot. The left side slot is called the live wire slot. You can use an electroscope to detect its polarity or you can use a voltage meter to measure the voltage of both slot sides. If you insert an electroscope into the live wire slot, the electroscope will light up. Using a voltage meter, you will find that the live wire slot will register a higher voltage.
If you reverse the polarity of AC plug, it may affect the life of computer equipment, or cause an electric shock when you touch the computer chassis. We suggest that you plug the computer AC plug to a three-hole wall outlet for better safety and to avoid electric shock.
User’s Manual
2-10 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
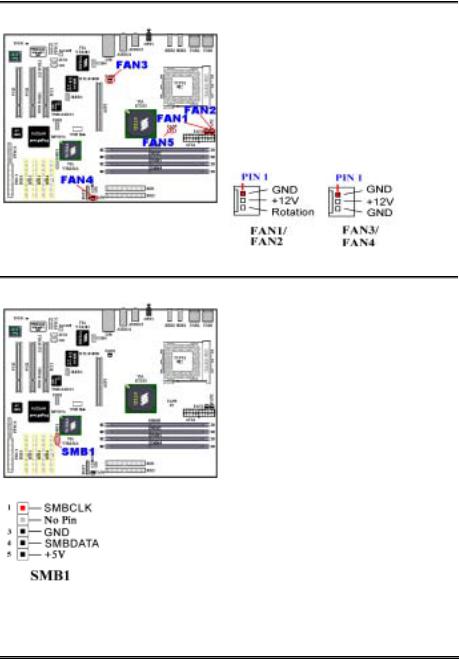
(2). FAN1, FAN2, FAN3, FAN4 and FAN5 Headers
Attach the connector from the processor fan to the header named FAN1 or FAN2 and connector from the front chassis fan to the header FAN4. Attach the connector from the power fan or back chassis fan to FAN3 header and attache the connector from northbridge fan to the header named FAN5. You must attach the processor fan to the processor, or your processor will work abnormally or may be damaged by overheating. To prevent the computer chassis internal temperature from getting too high, also connect the chassis fan.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
(3). SMB1: System Management Bus (SM-Bus) Header
This header is reserved for the system management bus (SM-Bus). The SM-Bus is a specific implementation of an I2C bus. I2C is a multi-master bus, this means that multiple chips can be connected to the same bus and each one can act as a master by initiating a data transfer. If more than one master simultaneously tries to control the bus, an arbitration procedure decides which master gets priority. You can connect the devices which utilizes the SM-Bus.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
AT7/AT7E
Installing the Motherboard |
2-11 |
|
|
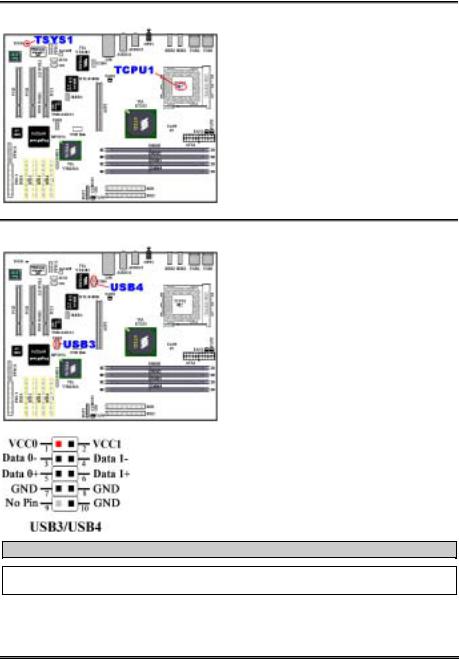
(4). TCPU1 & TSYS1: Temperature Thermistor
The TCPU1 is used to detect the CPU temperature. The TSYS1 is used to detect the system environment temperature. You can see the readings in the BIOS or in the hardware monitoring application main screen.
(5). USB3 and USB4 Headers: Additional USB Plugs Header
Thess headers are for connecting the additional USB port plugs. Each connector can provides two additional USB plugs. Which means, total you can get two additional USB plugs from each connector. You can use the special USB port expansion cable to connect it (the cable come with the metal plate can fixed on the back panel of computer chassis).
The USB3 is for USB 1.1 devices connection, and
USB4 is for USB 2.0 devices connection.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
Note
The USB4 header supports USB 2.0 specification function, please use the special USB cable design for USB 2.0 specifications. Otherwise, it may cause not stable or signal error situation.
User’s Manual
2-12 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
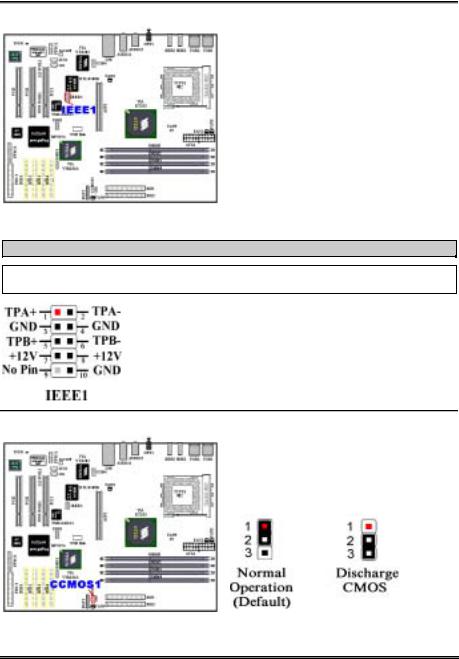
(6). IEEE1 Header: IEEE 1394 Header (For AT7 Full Version Only)
This header is reserved for connection to the ABIT Media XP product (Optional). The Media XP can provide the total solution for the front panel connections. It provided a various function, like a: SD/MS/CF card reader, USB 2.0/IEEE 1394 connectors, S/PDIF-Out connector and MIC/Earphone connectors. They all designed on one 5.25” diskette size panel, can fit on the chasses front panel 5.25” diskette slot.
For detailed information of ABIT Media XP, please see its user’s manual.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
Note
You don’t need to install any additional drivers for IEEE 1394 devices. The newest operation system will fully support this feature. For example: Windows® 2000, Windows® XP, etc.
(7). CCMOS1 Header: CMOS Discharge Jumper
Jumper CCMOS1 used to discharge CMOS memory. When you install the motherboard, make sure this jumper is set for normal operation (pin 1 and 2 shorted). See figure below.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
AT7/AT7E
Installing the Motherboard |
2-13 |
|
|
Note
Before you clear the CMOS, you have to first turn the power off (including the +5V standby power). Otherwise, your system may work abnormally.
After updating your BIOS and before boot up, please clear the CMOS first. Then put the jumper to its default position. After that, you can reboot your system and ensure that your system is working fine.
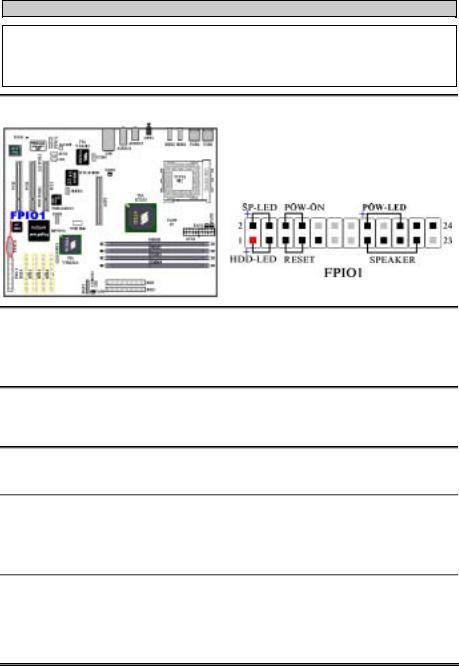
(8). FPIO1 Headers: The Headers for Chassis’s Front Panel Indicators and Switches
FPIO1 are for switches and indicators for the chassis’s front panel, there are several functions that come from this header. You have to watch the pin position and the orientation, or you may cause LED do not light up. Figure below shows you the FPIO1 functions of the pins.
FPIO1 (Pin 1 & 3): HDD LED Header
Attach the cable from the case’s front panel HDD LED to this header. If you install it in the wrong direction, the LED light will not illuminate correctly.
Note: Watch the HDD LED pin position and the orientation.
FPIO1 (Pin 5 & 7): Hardware Reset Switch Header
Attach the cable from the case’s front panel Reset switch to this header. Press and hold the reset button for at least one second to reset the system.
FPIO1 (Pin 15-17-19-21): Speaker Header
Attach the cable from the system speaker to this header.
FPIO1 (Pin 2 & 4): Suspend LED Header
Insert the two-threaded suspend LED cable into this header. If you install it in the wrong direction, the LED light will not illuminate correctly.
Note: Watch the Suspend LED pin position and the orientation.
FPIO1 (Pin 6 & 8): Power On Switch Header
Attach the cable from the case’s front panel power on switch to this header.
User’s Manual

2-14 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
FPIO1 (Pin 16-18-20): Power On LED Headers
There is a specific orientation for pins 1 through 3. Insert the three-threaded power on LED cable to this header. Check to make sure the correct pins go to the correct connectors on the motherboard. If you install them in the wrong direction, the power LED light will not illuminate correctly.
Note: Watch the power LED pin position and orientation.
For the PN1 and PN2 pin’s count-name list, please refer to table 2-2.
Table 2-2. FPIO1 pin count name list
|
PIN Name |
Significance of signal |
PIN Name |
Significance of signal |
|
||
|
|
PIN 1 |
HDD LED (+) |
|
PIN 2 |
SP-LED (+) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIN 3 |
HDD LED (-) |
|
PIN 4 |
SP-LED (-) |
|
|
|
PIN 5 |
Reset SW (-) |
|
PIN 6 |
PWR-ON (+) |
|
|
|
PIN 7 |
Reset SW (+) |
|
PIN 8 |
PWR-ON (-) |
|
|
|
PIN 9 |
No Connection |
|
PIN 10 |
No Pin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FPIO1 |
PIN 11 |
No Pin |
FPIO1 |
PIN 12 |
No Pin |
|
|
|
PIN 13 |
No Pin |
|
PIN 14 |
No Pin |
|
|
|
PIN 15 |
Speaker (+5V) |
|
PIN 16 |
PWR LED (+) |
|
|
|
PIN 17 |
Speaker (GND) |
|
PIN 18 |
No Pin |
|
|
|
PIN 19 |
Speaker (GND) |
|
PIN 20 |
PWR LED (-) |
|
|
|
PIN 21 |
Speaker (Driver) |
|
PIN 22 |
No Connection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIN 23 |
No Pin |
|
PIN 24 |
No Connection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(9). FPIO2 Header: Front Panel Input/Output Signals Header
You’ll see this header on AT7/AT7E motherboard. This header is designed to connect the ABIT Media XP product. This header can provide the analog audio output signals for front right and front left channel. It also provides one digital S/PDIF output connector.
Note: Watching the pin position and the orientation
AT7/AT7E

Installing the Motherboard |
2-15 |
|
|
(10). WOR1: Wake On Ring Header
If you have an internal modem adapter that supports this feature, then you can connect the specific cable from the internal modem adapter to this header. This feature lets you wake up your computer via remote control through the modem.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
(11). WOL1: Wake on LAN Header
If you have a network adapter that supports this feature, then you can connect the specific cable from the network adapter to this header. This feature lets you wake up your computer via remote control through a local area network. You may need a specific utility to control the wake up event, like using the PCnet Magic Packet utility or other similar utilities.
There are three types of WOL, “Remote Wake-Up high (RWU-high)”, “Remote Wake-Up low (RWU-low)”, and “Power Management Event (PME)”. This motherboard supports the type of “Remote Wake-Up low (RWU-low)” only.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
User’s Manual
2-16 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
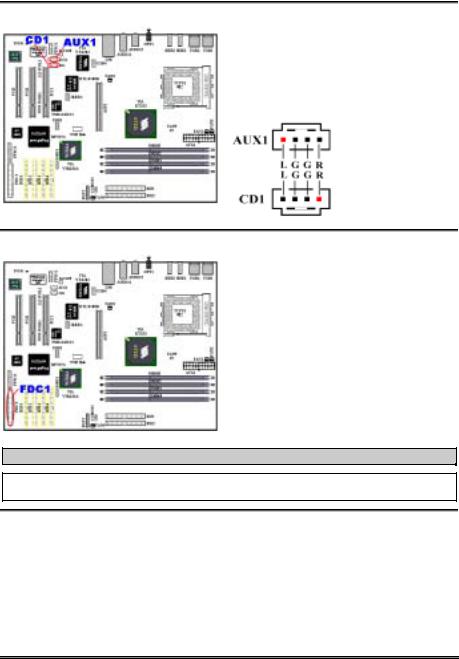
(12). CD1 and AUX1 Headers: CD Audio and Auxiliary audio signal input headers
These connectors connect to the audio output of internal CD-ROM drive or add-on card.
(13). FDC1 Connector
This 34-pin connector is called the “floppy disk drive connector”. You can connect a 360K, 5.25”, 1.2M, 5.25”, 720K, 3.5’’, 1.44M, 3.5” or 2.88M, 3.5” floppy disk drive.
A floppy disk drive ribbon cable has 34 wires and two connectors to provide the connection of two floppy disk drives. After connecting the single end to the FDD1, connect the two connectors on the other end to the floppy disk drives. In general, people only install one floppy disk drive on their computer system.
Note
A red mark on a wire typically designates the location of pin 1. You need to align the wire pin 1 to the FDC1 connector pin 1, then insert the wire connector into the FDC1 connector.
(14). IDE1, IDE2, IDE3, IDE4, IDE5 and IDE6 Connectors
This motherboard provides two IDE ports (IDE1 & IDE2) to connect up to four IDE devices in Ultra DMA 133 mode by Ultra DMA 66 ribbon cables. Each cable has 40-pin 80-conductor and three connectors, providing two hard drive connections with the motherboard. Connect the single end (blue connector) at the longer length of ribbon cable to the IDE port on motherboard, and the other two ends (gray and black connector) at the shorter length of the ribbon cable to the connectors on hard drives.
AT7’s built-in HighPoint HPT 374 chipset gives you the capability to support Ultra DMA 133. It provides four IDE channels (IDE3, IDE4, IDE5 & IDE6) that also support Ultra DMA 133 specifications, and it allows for eight additional IDE devices in your computer system. Especially, if you want to connect
AT7/AT7E

Installing the Motherboard |
2-17 |
|
|
two or four HDDs to get RAID functions, it is very convenient for you to install the HDDs to IDE3, IDE4, IDE5 or IDE6. See the Chapter 4 for detailed information about RAID settings. (For AT7 Full Version Only)
If you want to connect two hard drives together through one IDE channel, you must configure the second drive to Slave mode after the first Master drive. Please refer to the HDD documentation for jumper settings. The first drive connected to IDE1 is usually referred to as “Primary Master”, and the second drive as “Primary Slave”. The first drive connected to IDE2 is referred to as “Secondary Master” and the second drive as “Secondary Slave”.
Keep away from connecting one legacy slow speed device, like CD-ROM, together with another hard drive on the same IDE channel, this will decrease your integral system performance.
Figure 2-8. Ultra DMA 66
Ribbon Cable Outline
Note
!The Master or Slave status of the hard disk drive is set on the hard disk itself. Please refer to the hard disk drive user’s manual.
!To connect Ultra DMA 100 & Ultra DMA 133 devices on IDE1 to IDE6, an Ultra DMA 66 cable is required.
!A red mark on a wire typically designates the location of pin 1. You need to align the wire pin 1 to the IDE connector pin 1, before inserting the wire connector into the IDE connector.
!HPT 374 IDE controller is designed to support high-speed and high performance mass storage devices. Thus, we suggest that you don’t connect non-disk devices that use ATA/ATAPI interfaces, such as a CD-ROM, to HPT 374 IDE connector (IDE3 ~ IDE6). (AT7 Full Version Only)
User’s Manual
2-18 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
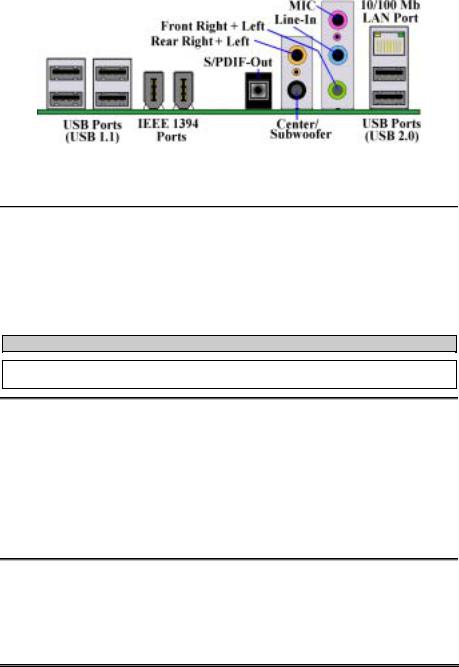
Figure 2-9. AT7 back panel connectors
Figure 2-9 shows the AT7 back panel connectors, these connectors are for connection to outside devices to the motherboard. We will describe which devices will attach to these connectors below.
(15). USB Ports Connectors
This motherboard provides six USB ports (on back panel of motherboard). Four are complient with USB 1.1 specifications, and two are complient with USB 2.0 specification. Attach the USB cable connector from the individual device to these connectors.
You can attach USB devices such as a, keyboard, mouse, printer, portable HDD, scanner, digital speakers, monitor, hub, digital camera, joystick etc. to one of each USB connector. You must make sure your operating system supports this feature and you may need to install an additional driver for individual devices. Please refer to your device user’s manual for detailed information.
Note
Please use the special USB cable designed for USB 2.0 specifications. Otherwise, it may cause not stable or signal error situation.
(16). IEEE 1394 Ports (For AT7 Full Version Only)
These two ports supports IEEE 1394 specifications. Attach the IEEE 1394 cable connector from the individual device to these connectors.
The IEEE 1394 high-speed serial bus provides enhanced PC connectivity for consumer electronics audio/video (A/V) appliances, storage peripherals, other PCs, and portable devices. Such as DV recoder, DVD recording, etc.
IEEE 1394 provides a Plug and Play-compatible expansion interface for the PC. The 100 Mbps, 200 Mbps and 400 Mbps transfer rates currently specified in IEEE 1394.a and the enhancements in
IEEE 1394.b are well suited to multi-streaming I/O requirements. The Microsoft® Windows® operating system offers strong built-in support for IEEE 1394.
(17). OPT2 S/PDIF-Out Connector
This connector can let you using the optical cable to connection the device, and transfer the digital data through it. You can connect this signal to the digital decoder to decode and transfer the digital signal to the analog signal.
AT7/AT7E

Installing the Motherboard |
2-19 |
|
|
(18). Audio1 and Audio2 Connectors
Audio1 and Audio2 connectors are audio connectors for analog audio signal in or out.
Mic In Connector: You can connect the plug from the microphone to this connector. Do not connect other audio (or signal) sources to this connector.
Line In Connector: You can connect the TV adapter audio output signal, or external audio sources, like a CD walkman, video camcorder, VHS recorder audio output signal plug to this connector. Your audio software can control the input level for the line-in signal.
Front Right + Left Channel Connector: You can connect the plug from the front channel speakers or front channel amplifier to this connector. Please make sure you are connect to the front channel speakers or front channel amplifier correctly, otherwise you may get the wrong sound positioning.
Rear Right + Left Channel Connector: You can connect the plug from the rear channel speakers or rear channel amplifier to this connector. Please make sure you are connect to the rear channel speakers or rear channel amplifier correctly, otherwise you may get the wrong sound positioning.
Center + Subwoofer Channel Connector: You can connect the plug from the center/subwoofer channel speakers or center/subwoofer channel amplifier to this connector. Please make sure you are connect to the center/subwoofer channel speakers or center/subwoofer channel amplifier correctly, otherwise you may get the wrong sound positioning.
(19). 10/100 Mb LAN Port Connector
This motherboard provides one built-in 10/100 Mb LAN port, this jack is for connecting the RJ-45 cable from the local area network hub to your computer. We suggest you use the category 5 UPT (Unshielded Twisted Pair) or STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) cable to make this connection. The connection length from the hub to the computer is best to be kept under 100 meter.
The green LED shows the connection situation. If the network active well, this LED will light on. The yellow LED shows if the data is active or not. If the computer is translating or receiving data from the network, this LED will flicker.
Note
This chapter contains many color drawing diagram and photos, we strongly recommend you to read this chapter use the PDF file we gave you that store in the CD-Title. It will provide you the better look and clearly color identify.
User’s Manual

2-20 |
Chapter 2 |
|
|
AT7/AT7E
 Loading...
Loading...