Planet Technology SGSW-2402 User Manual

10/100/1000Mbps
Intelligent Stackable Switch
SGSW-2402
User’s Manual
Trademarks
Copyright PLANET Technology Corp. 2002. Contents subject to revision without prior notice.
PLANET is a registered trademark of PLANET Technology Corp. All other trademarks belong to their respective owners.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications, and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose.
PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User’s Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability for any inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User’s Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User’s Manual. PLANET makes no commitment to update or keep current the information in this User’s Manual, and reserves the right to make improvements to this User’s Manual and/or to the products described in this User’s Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your comments and suggestions.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the Instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Revision
PLANET Intelligent Stackable Switch User's Manual
FOR MODEL: SGSW-2402
REVISION: 2.0
Part No.: EM-SGSW2402V2
|
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
|
1. INTRODUCTION........................................................................................................................................ |
1 |
|
1.1 |
CHECKLIST ............................................................................................................................................. |
1 |
1.2 |
ABOUT THE SWITCH ................................................................................................................................ |
1 |
1.3 |
FEATURES .............................................................................................................................................. |
1 |
1.4 |
SPECIFICATION ....................................................................................................................................... |
2 |
2. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION .................................................................................................................... |
4 |
|
2.1 |
FRONT PANEL......................................................................................................................................... |
4 |
2.2 REAR PANEL........................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
|
2.3 |
HARDWARE INSTALLATION ....................................................................................................................... |
5 |
2.4 |
TERMINAL SETUP .................................................................................................................................... |
5 |
2.5 |
IP CONFIGURATION................................................................................................................................. |
6 |
3.WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT................................................................................................................... |
8 |
|
3.1 |
CONFIGURATION ..................................................................................................................................... |
8 |
3.2 WEB PAGES ........................................................................................................................................... |
9 |
|
3.3 PORT CONFIG ......................................................................................................................................... |
9 |
|
3.4 VLAN CONFIG...................................................................................................................................... |
11 |
|
3.5 |
TRUNK CONFIG...................................................................................................................................... |
12 |
3.6 ADVANCED CONFIGURATION .................................................................................................................. |
13 |
|
3.7 STP CONFIG ........................................................................................................................................ |
13 |
|
3.7.1 STP Port....................................................................................................................................... |
13 |
|
3.7.2 STP Bridge................................................................................................................................... |
14 |
|
3.8 IGMP................................................................................................................................................... |
15 |
|
3.8.1 IGMP Management...................................................................................................................... |
15 |
|
3.8.2 Definition on IGMP v1.0 and v2.0 ................................................................................................ |
15 |
|
3.9 |
STACK .................................................................................................................................................. |
16 |
3.10 SNMP................................................................................................................................................ |
18 |
|
3.11 RMON STATISTICS............................................................................................................................. |
19 |
|
3.12 PORT SECURITY.................................................................................................................................. |
20 |
|
3.12.1 Setting Up Procedures............................................................................................................... |
21 |
|
3.12.2 Delete MAC Address ................................................................................................................. |
21 |
|
3.13 MIRROR PORT .................................................................................................................................... |
21 |
|
3.13.1 Using Mirror Port to Monitor Traffic............................................................................................ |
21 |
|
3.13.2 Setup Procedures ...................................................................................................................... |
22 |
|
3.14 AGING CONTROL................................................................................................................................. |
22 |
|
3.15 ADDRESS SEARCH .............................................................................................................................. |
23 |
|
3.15.1 Host Searching Procedures....................................................................................................... |
24 |
|
3.15.2 MAC Address Search ................................................................................................................ |
25 |
|
3.16 SYSTEM TOOLS................................................................................................................................... |
26 |
|
3.17 SYSTEM CONFIG ................................................................................................................................. |
26 |
|
3.18 SYSTEM INFORMATION......................................................................................................................... |
27 |
|
3.19 CHANGE PASSWORD ........................................................................................................................... |
28 |
|
3.20 FIRMWARE UPGRADE .......................................................................................................................... |
30 |
|
3.21 SAVE & REBOOT................................................................................................................................. |
32 |
|
3.21.1 Save ........................................................................................................................................... |
33 |
|
3.21.2 Backup ....................................................................................................................................... |
33 |
|
3.21.3 Restore....................................................................................................................................... |
35 |
|
3.21.4 Clear and Reset ......................................................................................................................... |
36 |
|
3.22 MESSAGE WINDOWS ........................................................................................................................... |
37 |
|
3.23 REBOOT SWITCH................................................................................................................................. |
38 |
|
3.24 LOGOUT ............................................................................................................................................. |
38 |
|
4 CONSOLE INTERFACE........................................................................................................................... |
40 |
|
4.1 CONNECT TO PC .............................................................................................................................. |
40 |
|
4.2 |
LOGGING ON TO THE SWITCH ................................................................................................................. |
41 |
4.2.1. sys--System Management Commands....................................................................................... |
43 |
|
4.2.2 sys show info................................................................................................................................ |
44 |
|
4.2.3. sys show IP ................................................................................................................................. |
44 |
4.2.4. sys show Ethernet address........................................................................................................ |
45 |
4.2.5. sys set ip <IP Address> <Subnet Mask> <Default Gateway>.................................................... |
45 |
4.2.6. sys set name "string"................................................................................................................... |
46 |
4.2.7. sys set contact "string"................................................................................................................ |
46 |
4.2.8. sys set location "string" ............................................................................................................... |
47 |
4.2.9. sys set password ........................................................................................................................ |
47 |
4.2.10. sys set link_info <on|off> .......................................................................................................... |
48 |
4.2.11. sys reset system ....................................................................................................................... |
48 |
4.2.12. sys reset config ......................................................................................................................... |
49 |
4.2.13. sys save config ......................................................................................................................... |
49 |
4.2.14. logout ........................................................................................................................................ |
50 |
4.2.15. port--Port Management Commands ......................................................................................... |
50 |
4.2.16. port show................................................................................................................................... |
51 |
4.2.17. port set enable <port number> [-h|-f] [-10|-100|-1000] [-A]....................................................... |
51 |
4.2.18. port set disable <port number>................................................................................................. |
52 |
4.2.19. port set flw <port number> <on|off>.......................................................................................... |
52 |
4.2.20. port set bck <port number> <on|off> ........................................................................................ |
52 |
4.2.22. port set vid <port number> <-v vid>.......................................................................................... |
53 |
4.2.23. vlan--VLAN Management Commands ...................................................................................... |
54 |
4.2.24. vlan show .................................................................................................................................. |
54 |
4.2.25. vlan build <vid> <-u untags> <-t tags> <-p priority>................................................................. |
55 |
4.2.26. vlan delete <vid>....................................................................................................................... |
55 |
4.2.27. vlan set pri <vid> <-p priority> .................................................................................................. |
55 |
4.2.28. trunk--TRUNK Management Commands.................................................................................. |
56 |
4.2.29. trunk show................................................................................................................................. |
56 |
4.2.30. trunk set <port1> [port2] [port3] [port4] ..................................................................................... |
57 |
4.2.31. stp--STP Management Commands .......................................................................................... |
57 |
4.2.32. snmp--SNMP Management Commands................................................................................... |
57 |
4.2.33. stack--STACK Management Commands.................................................................................. |
58 |
APPENDIX A NETWORKING CONNECTION............................................................................................ |
59 |

1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Checklist
Check the contents of your package for following parts:
SGSW-2402. User's manual CD. Power cord.
19” rack mounting kit. RS-232 cable.
Quick Installation Guide.
If any of these pieces are missing or damaged, please contact your dealer immediately, if possible, retain the carton including the original packing material, and use them against to repack the product in case there is a need to return it to us for repair.
1.2 About the Switch
The SGSW-2402 Intelligent stackable Switch is designed to provide your network with Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet connectivity over twisted pair and fiber optic cabling.
Two expansion slots on the front panel of the SGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch further add to the flexibility of the systems.
The SGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch is a combination of 24x10/100M Ethernet RJ-45 ports and 2 optional module slots.
The two optional modules can be 1-Port 100 Base-FX Intelligent Fiber Module, Gigabit 1000Base-T Intelligent Switch Modules, and Gigabit 1000Base-SX/LX Intelligent Fiber Modules.
With its build-in Web-based Management, managing and configuring the SGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch becomes easier.
From cabinet management to port-level control and monitoring, you can visually configure and manage your network via Web Browser, just click your mouse instead of typing cryptic command strings. However, the SGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch can also be managed via Console, or third-party SNMP Management.
1.3Features
--Complies with the IEEE802.3 Ethernet, IEEE802.3u Fast Ethernet , IEEE802.3z and IEEE802.3ab Gigabit Ethernet standard
--Provide 2 module slots for 100Mbps-FX, 1000Mbps-T or 1000Mbps-SX/LX option of modules
--Features Store-and-Forward mode with wire-speed filtering and forwarding rates
--Auto-negotiation & Full-duplex/Half-duplex
--Automatic source address learning and aging
--Support up to 4K MAC address
--Support IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
--IEEE802.3x compliant full-duplex flow control
--Broadcast storm control, runt and CRC Filtering eliminates erroneous packets to optimize the network bandwidth
--Support to handle up to 1522 bytes packet
--Stack up to 8 units
1

|
VLAN |
802.1Q VLAN, up to 32 VLANs supported |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QoS |
IEEE 802.1p QoS support with 2 priority queue using WFQ (Weighted Fair |
|
|
|
|
Queueing) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IGMP Multicast Filtering |
Passive snooping on IGMP Query/Report messages |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port trunking |
Up to 4 ports can be combined into a fat pipe |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Port Mirroring |
1 mirroring port to monitor several mirrored ports |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standards Conformance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Regulation Compliance |
FCC Part 15 Class A, CE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standards Compliance |
IEEE 802.3 (Ethernet) |
RFC 768 UDP |
|
|
|
IEEE 802.3u (Fast Ethernet), |
RFC 783 TFTP RFC 791 IP |
|
|
|
IEEE 802.3z (1000Base-SX/LX), |
RFC 792 ICMP |
|
|
|
IEEE 802.3ab(1000Base-T), |
RFC 826 ARP |
|
|
|
IEEE 802.1D (STP), |
RFC 1122 Host Requirements |
|
|
|
IEEE 802.3x (full-duplex flow control), |
RFC 2068 HTTP |
|
|
|
IEEE 802.1p (QoS), |
RFC 2236 IGMP v2 |
|
|
|
IEEE 802.1Q (VLANs) |
RFC 1157 SNMP v1/v2 |
|
|
|
|
RFC 1213 MIB II |
|
|
|
|
RFC 1643 Ethernet MIB |
|
|
|
|
RFC 1757 RMON group 1, statistics |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
2. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
This product series provide three different running speed – 10Mbps, 100Mbps, and 1000Mbps in the same switch and automatically distinguish the speed of incoming connection.
This section describes the hardware features of these Switches. For easier management and control of the switch, familiarize yourself with its display indicators, and ports. Front panel illustrations in this chapter display the unit LED indicators. Before connecting any network device to the switch, read this chapter carefully
There are following option module for expansion:
1-Port 100 Base-FX Intelligent Fiber Module
1-Port Gigabit 1000Base-T Intelligent Switch Module 1-Port Gigabit 1000Base-SX/LX Intelligent Fiber Module
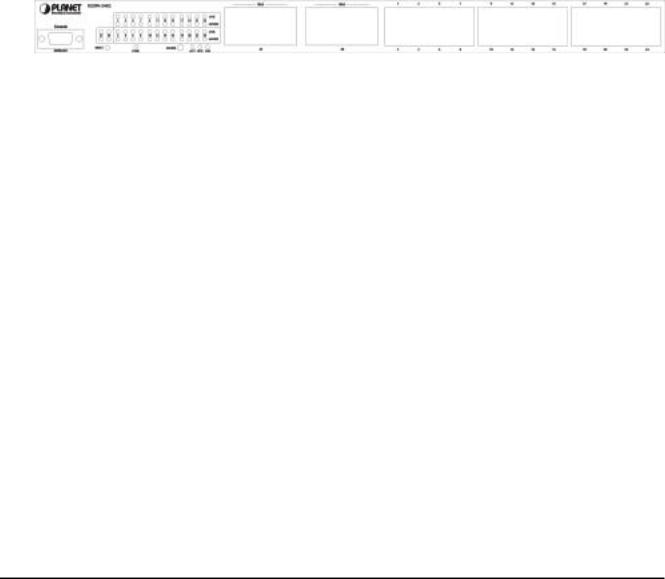
2.1 Front Panel
The Front Panel of the SGSW-2402 Intelligent Switch consists of 24x auto-sensing 10/100Mbps Ethernet RJ-45 Ports, two optional expansion slots, and Console port. The LED Indicators are also located on the front panel of the Switch.
|
|
|
SGSW-2402 Switch front panel |
2.1.1 LED indicators |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SGSW-2402 |
|
|
|
PWR |
Green |
Lit on: Power on |
|
|
|
Lit off: power off |
|
Link |
Green |
Lit on: the connection is good |
|
|
|
Lit off: the port is disabled or not detecting a link |
|
Mode: (could be three kinds of meaning, varies with the Mode button) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
ACT |
Green |
Lit on: the connection is good. |
|
|
|
Blink: The port is receiving or transmitting data |
|
FDX |
Green |
Lit on: the port run at full-duplex |
|
|
|
Blink: Half-Duplex/ Collision |
|
|
|
Off: Half-duplex or not connected |
|
100 |
Green |
Lit on: run at 100Mbps |
|
|
|
Lit off: run at 10Mbps or not connected |
2.1.2 Buttons indicators |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
SGSW-2402 |
|
|
|
RESET |
When press this button, Switch will reboot |
|
|
MODE |
Hold the button for at lease 5 seconds and release, the LED will turns to the |
|
|
|
next LED in cycle. (ACT FDX Speed ACT) |
|
4

2.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Switch indicates an AC inlet power socket which accepts input power from 100 to 240VAC, 50-60Hz.
SGSW-2402 Switch rear panel
Power Notice:
1.The device is a power-required device, it means, it will not work till it is powered. If your networks should active all the time, please consider using UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply) for your device. It will prevent you from network data loss or network downtime.
2.In some area, installing a surge suppression device may also help to protect your switch from being damaged by unregulated surge or current to the Switch or the power adapter.
2.3Hardware Installation
2.3.1 Connecting end node or hub or switch
1.Place the Switch on a smooth surface or fasten the mounting brackets with the provided screws in a standard 19” rack.
2.Connect switch or PC to one port of the Switch using Category 3/4/5 UTP/STP cabling.
3.Connect another switch or PC to the other port of Switch by following the same process as described in Step2.
Notice:
Cable distance for Switch
The cable distance between Ethernet Switch and hub/PC should not exceed 100 meter for UTP/STP cable, 2km for 62.5/125 and 50/125 fiber cable on 100Base-FX module, 220m for 62.5/125 fiber cable and 500m for 50/125 fiber cable on 1000Base-SX module, 550m for 62.5/125 and 50/125 fiber cable and 10km for 9/125 fiber cable on 1000Base-LX module.
Make sure the wiring is correct
It can be used Category 3/4/5 cable in 10 Mbps operation. To reliably operate your network at 100Mbps and 1000Mbps, you must use an Unshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP) Category 5 cable, or better Data Grade cabling. While a Category 3 or 4 cable may initially seem to work, it will soon cause data loss.
2.3.2 Connecting to Network Backbone or Server
Connect to the Gigabit Ethernet ports with Category 5 copper cable or fiber optic cable for uplinking to a network backbone or network server. These ports operate at 1000Mbps in full-duplex mode. A valid connection is indicated when the Link LED is light.
2.4 Terminal Setup
To configure the system, connect a serial cable to a COM port on a PC or notebook computer and to serial (console) port of the device. The console port of the device is DCE already, so that you can connect the console port directly through PC without the need of Null Modem.
A terminal program is required to make the software connection to the device. Windows’ Hyper Terminal program may be a good choice. It can be accessed from the Start menu. Click START, then Programs, Accessories and then Hyper Terminal.
MS-DOS based terminal program such as PC-PLUS, PROCOMM, can also make the connection with the device built-in software. The COM port should be configured as:
5

♦ Baud |
: 38400 |
♦ Parity |
: None |
♦ Data bits |
: 8 |
♦ Stop bits |
: 1 |
♦ Flow Control: none
Once the terminal has connected to the device, power on the device. The terminal will display that it is loading the firmware. Then, the screen as below will show up:
Press “Enter” and input the password. The default password is “admin”.
2.5 IP Configuration
Once log on to the console, the “Command>” prompt will be shown. You can type “help” for all available commands.
6

To setup the IP address, please use “sys set ip” command in the following format: sys set ip <IP Address> <Subnet Mask> <Default Gateway>
For example, to configure the switch with the following IP settings: IP Address: 192.168.0.2
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway: 192.168.0.254
Press input the following command and press <Enter> button: sys set ip 192.168.0.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.254
If the IP is successful configured, the switch will automatically restart as the following window. You can then configure the switch through its web interface.
7

3.WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT
3.1 Configuration
As well as the menu-driven system configuration program, the agent module provides an embedded HTTP Web agent. This agent can be accessed by any computer on the network using a standard Web browser (Internet Explorer 5.0 or above, or Netscape Navigator 4.5 or above).
Using the Web browser management interface you can configure a switch and view statistics to monitor network activity. The Web interface also provides access to a range of SNMP management functions with access to the switch's MIB and RMON database.
Prior to accessing the switch from a Web browser, be sure you have first performed the following tasks:
Configure it with a valid IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway using an out-of-band serial connection.
For Internet Explorer 5.0 or later version user, please check the Java setting below before startup.
1.Click on Tools
2.Pick Internet Options
3.Select the Security tab
4.Select Local Intranet (click on the icon)
5.Click on Sites, click Advanced and add the IP address of the switch to the zone
6.Click on Custom Level
7.Scroll down and set Java Permissions to Custom
8.Press the Java Custom Settings button
9.Select the Edit Permissions tab
10.Set Run Unsigned Content to Enable
11.Press OK for all open dialog windows
For IE5.0 or later version, if you can not find the Java option in point 7, please make sure your
Ethernet Explorer is installed with “Microsoft VM” JAVA virtual-machine plug-in.
NOTE
8
3.2 Web Pages
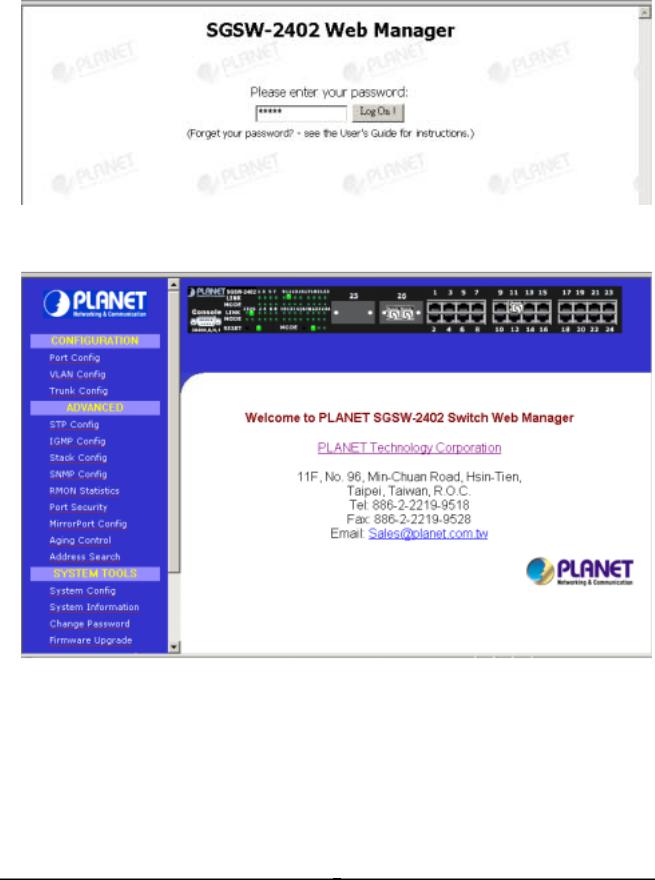
To access the Web-browser interface you must first enter the password. The default password is "admin" You will see the following screen comes out on the Web browser program:
Figure 3-1 : Password Screen
After the password is entered you will see the main menu screen.
Figure 3-2: The start up screen of SGSW-2402 Web Page
3.3 Port Config
This section allows you to have an easy access in configuring the ports of the management Switch. Notice that the “Link state” option indicates “Up”. This shows that the port is connected to the network. It can either be in “Up” (Connected) or “Down” (No connection) state.
9
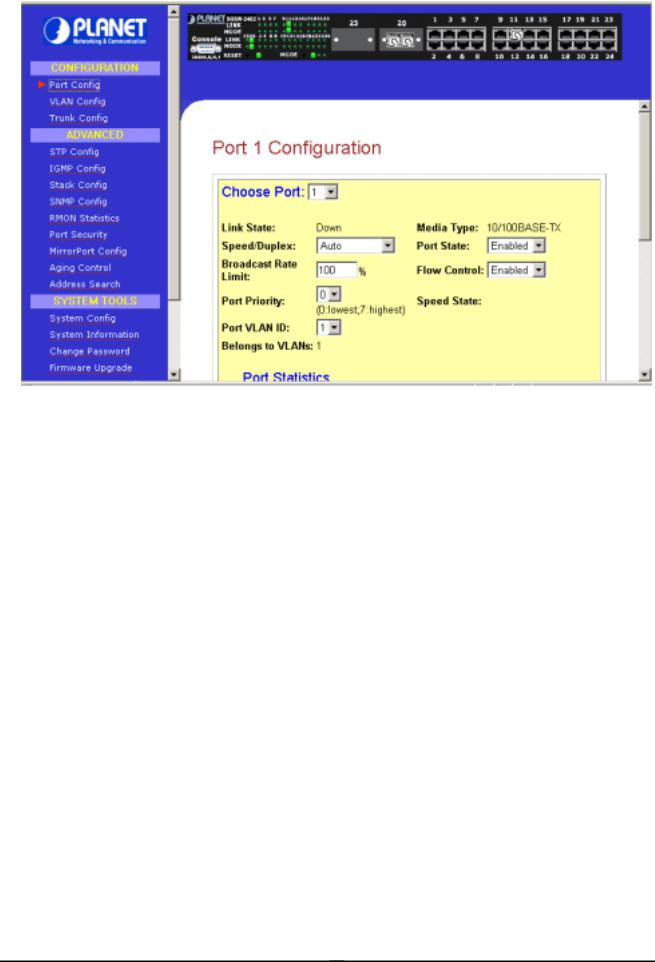
Figure 3-3 The Port Config screen
Choose Port
You can choose a port either by clicking on the picture or by selecting it at the “Choose Port” field.
Speed/ Duplex
Speed/ Duplex is to select the operation mode of chosen port. The options are as: ‘Auto’: Auto negotiation
‘10Mbps HD’: 10 Base-T Half Duplex ‘10Mpbs FD’: 10Base-T Full Duplex ‘100Mpbs HD’: 100Base-TX Half Duplex ‘100Mbps FD’: 100Base-TX Full Duplex
Broadcast Rate Limit
This function sets broadcast limit to the desired rate for the specified port. It controls the reception of broadcasting packets. The ranging for Broadcast rate limit varies from 0% to 100%. The higher the rate is, the more broadcast packets can pass through the port. Rate is the percent of the traffic to allow before throttling. That is, if you configure this value to 10% and current connected speed is 100M, Only 10M broadcast data can pass through the port.
Port Priority
In a tagged VLAN application, you can specify the VLAN priority to expedite the VLAN traffic. There are 8 levels of priority, namely ‘0’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’ and ‘7’ in ascending priority.
Port VLAN ID
VLAN ID is the sequence number of a VLAN. The setting of the VLAN ID depends on ‘Belongs to VLANs’ option. Thus, you should first configure the VLAN table through “VLAN config” option and then specify this value.
Port State
Port state is for enabling or disabling the switch operation of the chosen port. If it is ‘enabled’, the chosen port will receive and forward the packets, and learns the respective source MAC Addresses. If it is ‘disable’, the chosen port will not receive or forward any packets or learn source MAC Addresses.
It should be noted that if the cpu port (i.e. the switch port connected to the management workstation) is disabled, without doubt, the communication link between user and the switch will not proceed further. It
10
is recommended to locate the link your PC used before disable the port state.
Flow Control
This feature enables or disables the Flow Control function of the port. Flow control can eliminate frame loss by "blocking" traffic from end stations or segments connected directly to the switch when its buffers fill. IEEE 802.3x flow control is used for full duplex. Note that flow control should not be used if a port is connected to a hub.
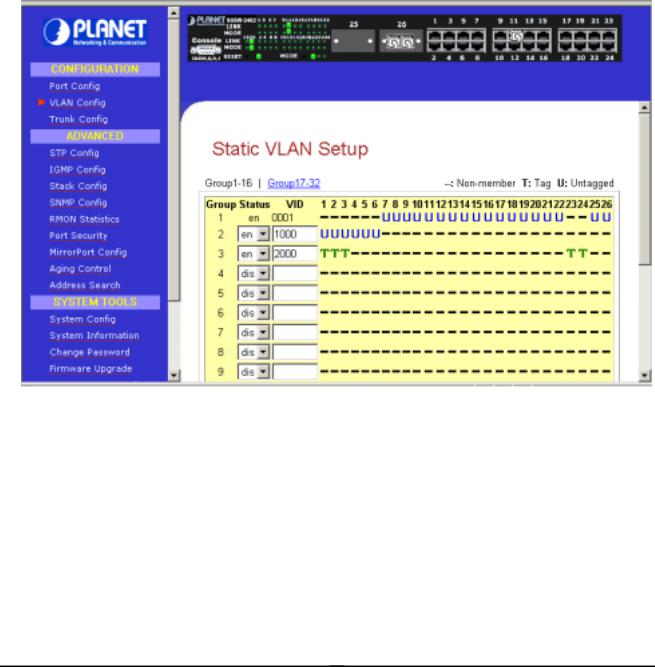
3.4 VLAN Config
The management switch supports Virtual LAN, which logically group the connection into VLANs for traffic isolation and security purposes. Both tagged and untagged based VLAN are supported with a total maximum of 32 groups. Each VLAN group only forwards traffic within its member ports. For tagged VLAN, each port can be a member of more than one VLAN group and it also supports priority with eight levels. There is also provision for creating an untagged VLAN which support a connection with a legacy untagged port. The VLAN configuration feature also allows you to build, delete and view tagged / untagged VLAN groups and setting priority for tagged VLANs. The range of VID starts from 2 to 4094, as VID 001 is the default for Group 1.
Figure 3-4 The VLAN config Page
Setup Procedures
Step 1: Decide which Group you want to set for monitoring using mirror port. Click status column for that particular group and key in the VLAN ID.
Step 2: Next, click on the dashed line’-‘ to select either “T” for Tagged or “U” for Untagged.
Step 3: Hit on “Apply” button after you satisfied with the setup. Click “Save” button to update the latest configuration.
11
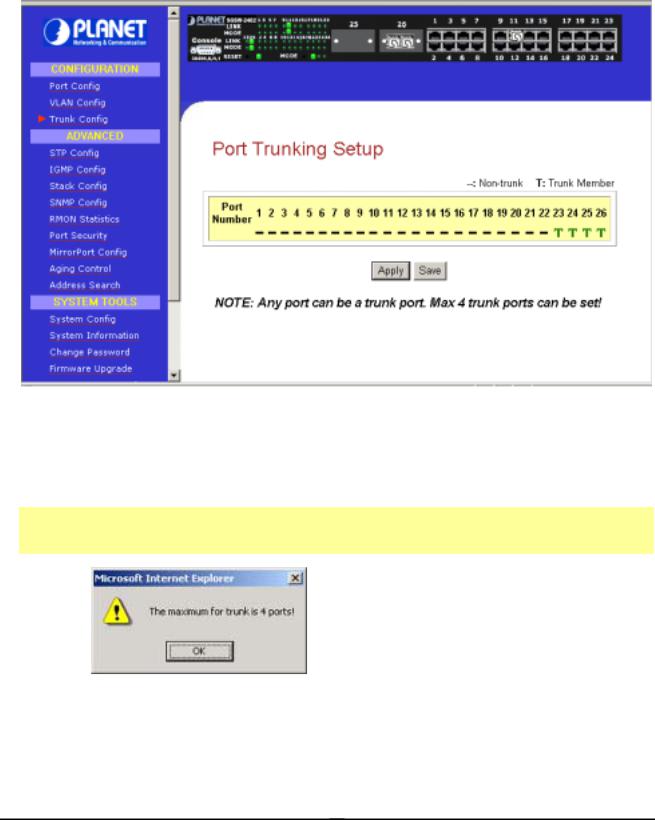
3.5 Trunk config
Port Trunking is the ability to group together several switch ports to increase the bandwidth between the management switch and other switch. This is an inexpensive method to increase throughput between switches (or to servers). We define the Port Trunking as the ability to group a set of ports into a single logical link. The port trunk acts as single link between switches. It doesn’t create a loop even though it is physically connected as such.
Figure 3-5 The Port Trunk config Page
Port Trunking Setup Procedures
Step 1: You can choose up to 4-port for Trunking by selecting ‘-‘ as “T”
Step 2: Click on “Apply” button to make the configuration effective.
Step 3: Click “Save” button to save the latest setting.
If you select more than 4 ports for trunking, the following error message will appear:
NOTE
Click “OK” button and select the ports again
12

3.6 Advanced Configuration
The available options in “Advanced menu” are:
STP Config |
The Spanning Tree Setup Screen |
|
|
IGMP Config |
The IGMP Setup Screen |
|
|
Stack Config |
The Stack Setup Screen |
|
|
SNMP Config |
The SNMP Setup Screen |
|
|
RMON Statistics |
Show RMON statistics information |
|
|
Port Security |
The Port Security Setup Screen |
|
|
MirrorPort Config |
The Mirror Port Setup Screen |
|
|
Aging Control |
The Aging Control Setup Screen |
|
|
Address Search |
The Address Search Setup Screen |
|
|
3.7 STP Config
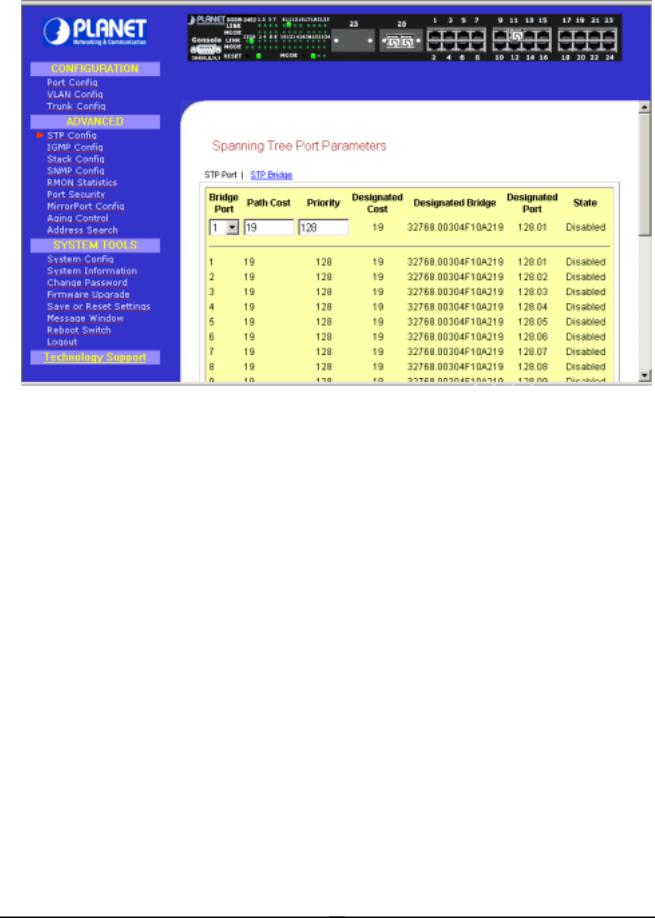
STP Config provides two menu page to configure: STP Port and STP Bridge
3.7.1 STP Port
Bridge Port
This option shows the port of the bridge that connects to the root bridge.
Path Cost
This parameter is used by the STA algorithm to determine the best path between devices. Therefore, lower values should be assigned to ports attached to faster media, and higher values assigned to ports with slower media. (Path cost takes precedence over port priority.)
The default and recommended range is: Ethernet: 100 (50~600) Fast Ethernet: 19 (10~60) Gigabit Ethernet: 4 (3~10). The allowed range is 0 - 65535.
Priority
Defines the priority for the use of a port in the Spanning Tree algorithm. If the path cost for all ports on a switch are the same, the port with the highest priority (i.e., lowest value) will be configured as an active link in the Spanning Tree. Where more than one port is assigned the highest priority, the port with lowest numeric identifier will be enabled. The range is 0 - 255.
Setup Procedures
Step 1: Select any one of the ports, from 1 to 26, to connect to the root bridge.
Step 2: Key in the value for Path Cost.
Step 3: Set the priority level.
13
3.7.2 STP Bridge
This page lets you to have a clearer view in Spanning Tree parameters for whole switch.
Figure 3-6 The Spanning Tree Screen
Description of Parameters
STP State
When STP is enabled, it will dynamically detect network looping owing to mis-configuration of the network topology. The redundant connectors will be disabled to avoid looping of packets. Looping would often result in flooding of broadcast packets, halting the normal traffic.
Root Priority
Device priority is used in selecting the root device, root port, and designated port. The device with the highest priority becomes the STA root device. However, if all devices have the same priority, the device with the lowest MAC address will then become the root device.
Hello Time
The Hello time of the Spanning Tree field shows the number of seconds between the transmissions of Spanning Tree protocol configuration messages.
Forward Delay
The Forward Delay field shows the number of seconds a port waits before changing from its Spanning Tree Protocol learning and listening states to the forwarding state. This waiting is necessary so that other switches on the network ensure no loop is formed before they allow other port to forward packets.
Max Age
The maximum age time of the Spanning Tree shows the number of seconds the bridge waits without receiving Spanning Tree Protocol configuration message before attempting a reconfiguration.
Setup Procedures
Step 1: Select Spanning Tree state option, either to enable or disable it.
Step 2: Set Root Priority from 0 s – 65535 s, and Hello Time from 1 s – 10 s.
Step 3: Key in the Forward Delay Time, Maximum Age and Hello Time.
14
Step 4:
NOTE
Click “Apply” button and save it if everything is OK.
The screen is divided into two sections. Current Spanning Tree Root section displays the read-only Spanning Tree settings for the current root switch and the parameters this switch is to use when it becomes the root switch.
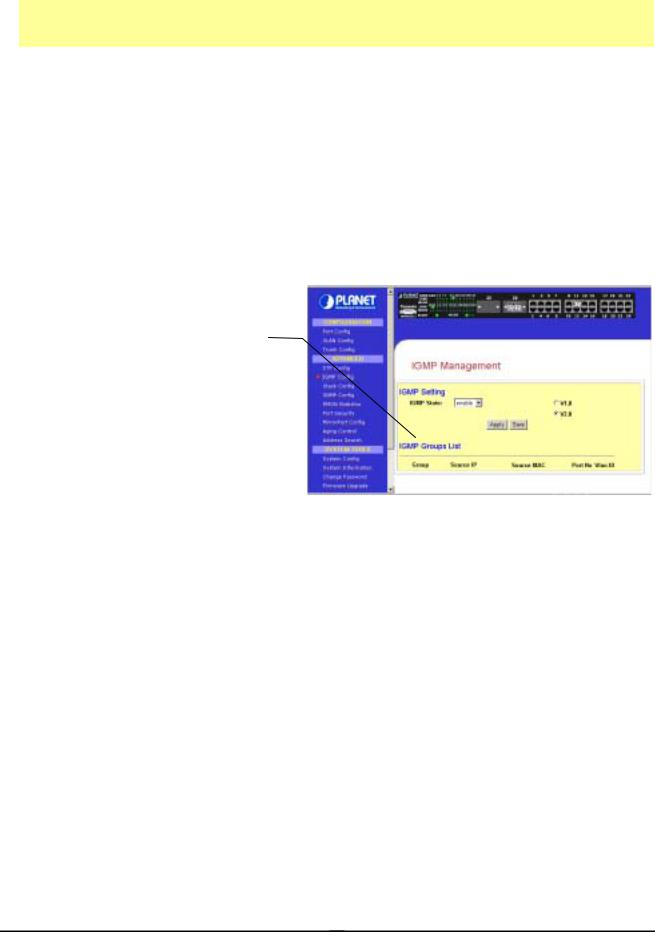
3.8 IGMP
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an Internet protocol that provides a way for an Internet computer to report its multicast group membership to adjacent routers. It allows the management switch to forward multicast traffic intelligently. The switch "snoops" the IGMP query and report messages and forwards traffic to only the ports that request the multicast traffic. This prevents
|
the switch from broadcasting the traffic to all ports and |
Host Group Addresses |
possibly affecting network performance. |
Host groups are identified by class D IP |
The membership of a host group is dynamic - hosts may join |
addresses, i.e., those with "1110" as their |
and leave groups at any time. There is no restriction on the |
high-order four bits. Class D IP addresses, |
|
i.e., those with "1111" as their high-order |
location or number of members in a host group. A host may |
four bits, are reserved for future addressing |
be a member of more than one group at a time. A host need |
modes. |
not be a member of a group to send datagrams to it. |
In Internet standard "dotted decimal" |
|
notation, host group addresses range from |
|
224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The address |
|
224.0.0.0 is guaranteed not to be assigned |
|
to any group, and 224.0.0.1 is assigned to |
|
the permanent group of all IP hosts |
|
(including gateways). This is used to |
|
address all multicast hosts on the directly |
|
connected network. There is no multicast |
|
address (or any other IP address) for all |
|
hosts on the total Internet. The addresses of |
|
other well-known, permanent groups are to |
|
be published in "Assigned Numbers". |
|
|
|
Figure 3-7 The IGMP Screen page
3.8.1 IGMP Management
To activate IGMP function,
Step 1: Select “enabled” in the IGMP state field.
Step 2: Click on the radio button to select the version for IGMP.
Step 3: Hit on the “Apply” button and save your setting.
3.8.2 Definition on IGMP v1.0 and v2.0
For IGMP v1.0,
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP v1.0) is used by IP hosts to report their host group memberships to any immediately neighboring multicast routers. IGMP is an asymmetric protocol and is specified here from the point of view of a host, rather than a multicast router.
|
IGMPv1 has no leave mechanism. If a host no longer wants to receive the traffic, it simply |
NOTE |
quits. If it is the last, the router will not have any answers to its query and will delete the GDA |
for that subnet. |
For IGMP v2.0,
IGMP v2.0 allows group membership termination to be quickly reported to the routing protocol, which is important for high-bandwidth multicast groups and/or subnets with highly volatile group membership.
15
 Loading...
Loading...