Nortel Networks DMS-MSL-100 User Manual

297-2183-912
Nortel Networks Symposium Call Center
Server
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide
Product release 5.0 |
Standard 1.0 |
April 2004 |
|
|
|
|
|
|

Nortel Networks Symposium Call Center Server
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide
Publication number: |
297-2183-912 |
Product release: |
5.0 |
Document release: |
Standard 1.0 |
Date: |
April 2004 |
|
|
Copyright © 2004 Nortel Networks, All Rights Reserved
Information is subject to change without notice. Nortel Networks reserves the right to make changes in design or components as progress in engineering and manufacturing may warrant.
The process of transmitting data and call messaging between the Meridian 1 and Symposium Call Center Server is proprietary to Nortel Networks. Any other use of the data and the transmission process is a violation of the user license unless specifically authorized in writing by Nortel Networks prior to such use. Violations of the license by alternative usage of any portion of this process or the related hardware constitutes grounds for an immediate termination of the license and Nortel Networks reserves the right to seek all allowable remedies for such breach.
*Nortel Networks, the Nortel Networks logo, the Globemark, DMS, DMS-100, IVR, MAP, Meridian, Meridian 1, and Symposium are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
CALLPATH is a trademark of Genesys Telecommunications Laboratories, Inc.
CRYSTAL REPORTS is a trademark of Crystal Decisions, Inc.
MICROSOFT, MS-DOS, POWERPOINT, WINDOWS, and WINDOWS NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
PCANYWHERE is a trademark of Symantec Corporation.

Publication history
April 2004 |
The Standard 1.0 version of the Nortel Networks Symposium |
|
Call Center Server Symposium and |
|
DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide Release 5.0, is released. |
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
v |

Publication history |
Standard 1.0 |
vi |
Symposium Call Center Server |

Contents
1 Getting started |
9 |
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 Skills you need . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 What’s new in Release 5.0? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 How Symposium Call Center Server communicates with the switch . . . . . . 19 Support for switch features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24 Preinstallation checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31 Configuration tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
2 |
Configuring the switch |
35 |
|
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
36 |
|
Section A: Configuring the ICM link parameters |
37 |
Overview of configuring the server logon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38 Configuring SCAICOMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43 Configuring BGDATA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44 Configuring SCAIGRP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46 Configuring SCAISSRV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47 Configuring SCAIPROF. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49 Configuring CUSTNTWK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Section B: Configuring switch resources |
53 |
Overview of configuring switch resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54 Configuring RAN and music routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56 Configuring ACD groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57 Configuring ACD subgroups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65 Configuring DNs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66 Configuring agent phonesets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69 Configuring supervisor phonesets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74 Configuring logon IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Section C: Checking the server configuration |
79 |
Overview of server configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80 Checking the server configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81 Relationship of server configuration and switch datafill . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
vii |

Contents |
|
Standard 1.0 |
3 |
Verifying the configuration |
87 |
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Verifying that the server can log on to the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89 Verifying ACD groups and subgroups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91 Verifying that phonesets are correctly configured . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92 Verifying that agents are correctly configured . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94 Verifying that the CDNs are correctly configured . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95 Verifying that music and RAN routes are correctly configured . . . . . . . . . . . 97 Verifying that DNISs are correctly configured. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4 Troubleshooting |
101 |
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102 Subsystem link problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103 Resource configuration problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
A Preinstallation checklist |
111 |
Preinstallation checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. 112 |
Glossary |
115 |
Index |
137 |
viii |
Symposium Call Center Server |

C h a p t e r 1
Getting started
In this chapter
Overview |
10 |
Skills you need |
11 |
What’s new in Release 5.0? |
12 |
Components |
13 |
How Symposium Call Center Server communicates with the switch |
19 |
Support for switch features |
24 |
Preinstallation checklist |
31 |
Configuration tasks |
32 |
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
9 |

Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
Overview
Throughout this guide, the term DMS switch applies to the following switch types:
!
!
!
!
DMS Switch
MLS-100
Succession 2000
Nortel Networks Communication Server 2100
Symposium Call Center Server works in conjunction with other systems to ensure that calls entering your call center are successfully routed to agents qualified to handle the calls. To enable the features of your Symposium Call Center Server, you must configure the following systems:
!
!
!
the DMS/MSL-100 switch
Intelligent Call Manager (ICM), formerly CompuCALL
Symposium Call Center Server
This guide explains how to configure the switch to work with Symposium Call Center Server. To find out how to configure the server, refer to the Administrator’s Guide. If you are using the Symposium Call Center Web Client, refer to the Symposium Call Center Web Client Guide and online Help for detailed instructions.
This guide assumes that you have already configured ICM to work with the switch.
Note: This guide assumes that the switch has been correctly installed and is operational with all current Product Enhancement Packages (PEPs) applied. For information on which PEPs to install on the switch, contact your Nortel Networks customer support representative.
10 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
Skills you need
Introduction
This section describes the skills and knowledge you need to use this guide effectively.
Nortel Networks product knowledge
Knowledge of, or experience with, the following Nortel Networks products can be of assistance when configuring the switch to communicate with Symposium Call Center Server:
!Symposium Call Center Server
!DMS switch
!Switch release CCM010/SCAI12 to CCM017/SCAI17
!Intelligent Call Manager switch translation release ICM00001 to ICM00075
!Maintenance Administration Position (MAP) terminal
!Service Orders (servord) utility
!Switch Translation Guide
!Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)
!other switch administration and monitoring tools
PC experience or knowledge
Knowledge of, or experience with, the following PC products is of assistance when administering the Symposium Call Center Server:
!Microsoft Windows 2000 or Windows XP
Other experience or knowledge
Other types of experience or knowledge that might be of use include
!TCP/IP networking
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
11 |

Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
What’s new in Release 5.0?
Skillset display on phoneset
Symposium Call Center Server Release 5.0 with Common Command Module (CCM)16 or Switch Computer Application Interface (SCAI)17 (or later) supports the display of skillset names on the agent and supervisor phonesets. The phoneset displays only the first 15 characters of the skillset name, and only displays the characters A through Z, and the numbers 0 through 9.
SCAI17 support
Symposium Call Center Server Release 5.0 provides SCAI17 support with backward compatibility to SCAI12.
Hold/Unhold reporting
Symposium Call Center Server Release 5.0 with CCM15/SCAI17 (or later) supports Hold/Unhold reporting which records the hold time associated with a call.
iButton
Release 5.0 provides support for iButton as an alternative to such legacy I/O devices as parallel ports. iButton provides the ability for Symposium Call Center Server to support legacy-free servers. This feature is not dependent on any SCAI level.
12 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
Components
Introduction
Symposium Call Center Server consists of three key components: telephony, server, and client.
Telephony component
The telephony component includes the switch, the Ethernet Interface Unit (EIU), Intelligent Call Manager (ICM), and the agent and supervisor phonesets.
Server component
The server in Symposium Call Center Server can be located at either the central office or customer site.
Client component
The client is installed on the supervisor workstations and accesses the server over the customer’s LAN.
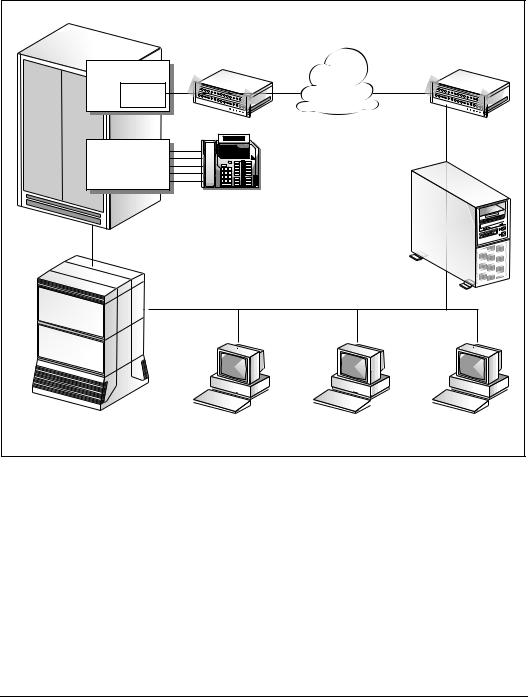
Symposium Call Center Server components
The following illustration shows the relationship of the components required for Symposium Call Center Server:
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
13 |
Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
Switch |
|
|
|
|
ICM |
Router |
|
|
Router |
|
|
|
|
|
EIU |
|
Network |
ELAN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ACD |
Agent |
|
Symposium |
|
|
Call Center |
|||
|
|
|||
|
phonesets |
Server |
|
|
Voice port lines |
|
|
|
|
|
CLAN |
|
|
|
Front-end IVR |
Client PC |
Client PC |
Third-party |
|
(optional) |
(administrator) |
(supervisor) |
application |
|
|
|
|
|
G101333 |
Switch |
|
|
|
|
The switch is the hardware and software component that provides telephony services. The switch sends and receives calls to and from Symposium Call Center Server. When a call arrives at the switch, the switch notifies the server, which performs call processing and routing.
To work with the Symposium Call Center Server, the switch must be running software load CCM010/SCAI12 or later.
14 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
Symposium Call Center Server supports the DMS, MLS-100, Succession 2000, and Communication Server 2100 switches. Throughout this guide, the term DMS Switch applies to all the supported switch types.
Note: If the link to the server goes down, ACD routing configured on the switch provides a backup method for handling calls.
3PC
The Third-Party Core (3PC) card (also known as the Call Agent Card) provides processing power for the Communication Server 2100 compact configurations.
EIU
The Ethernet Interface Unit (EIU) enables the switch to connect to an Ethernet network for communication with Symposium Call Center Server.
Note: The rules for the EIU also apply to the 3PC card.
ICM
The Intelligent Call Manager (ICM) serves as an interface between Symposium Call Center Server and the switch. The ICM receives information from the switch and transmits it to Symposium Call Center Server. It receives information from the server and transmits it to the switch.
The number available for Symposium Call Center Server depends on the number of other ICM-based applications connecting to the switch. The switch can support up to 16 ICM connections for CCM05/SCAI07 through CCM13/ SCAI15, and up to 96 for CCM14/SCAI15 and higher. (This value is determined by the data in the iphost.)
Symposium Call Center Server requires software packages ICM00001, ICM00010, or ICM00020 MSL09.
Note: You must configure certain parameters to establish a secure ICM session. For more information about configuring ICM security, see the Administrator’s Guide.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
15 |

Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
Server
The server component, which uses Microsoft Windows 2000 software, is responsible for functions such as
!the logic for call processing
!call treatment
!call handling
!call presentation
!administration of agents, skillsets, and supervisors, and agent to skillset and agent to supervisor assignments
!accumulation of historical and real-time statistics
Classic Client
The Classic Client component, located on the call center manager’s or supervisor’s desktop, has a graphical user interface based on Microsoft 2000 or Windows XP. The client provides meaningful real-time call center statistics and an easy-to-use interface for the management of the call center.
Web Client
Symposium Web Client is a browser-based thin client for administrators and supervisors. Through the Internet Explorer browser located on a client PC, you can connect to the Symposium Web Client application server to manage and configure a call center and its users, define access to data, and view real-time and historical reports.If you are using the Symposium Web Client, refer to the
Symposium Call Center Web Client Guide and online Help.
CLAN
The agent and supervisor workstations are connected to the customer LAN (either an Ethernet or a Token Ring LAN). The customer LAN also provides connections to optional third-party applications, such as an Interactive Voice Response system.
16 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
ELAN
The embedded LAN (ELAN) is a dedicated Ethernet TCP/IP LAN connecting the Symposium Call Center Server and the switch. The ELAN must be a private isolated network that is dedicated to the switch and to the call center. The ELAN must not have a physical or logical connection with the customer network. This eliminates the potential impact of caller network traffic on call processing.
Front-end IVR system (optional)
The switch can direct calls to an optional third-party Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system. This system plays voice prompts to callers and collects their responses. After the calls receive IVR treatment, the IVR system delivers the responses for the calls to Symposium Call Center Server. The server then gains control of the calls.
Third-party applications (optional)
Optional third-party applications provide the following functionality to Symposium Call Center Server:
!the ability to exchange data with the server, using Host Data Exchange (HDX)
!the ability to receive real-time updates from the server, using the real-Time API (RTI)
!the ability to receive real-time updates from the server, using the Real-Time Statistical Multicast stream (RSM)
!the ability to access configuration and statistical data in the Symposium Call Center Server database, using Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) database drivers
!the ability to trigger screen pops for inbound triggers, using Meridian Link
ICM applications using LinkPlexer 1.2 (optional)
LinkPlexer 1.2 is a Windows 2000 application that acts as a proxy to enable multiple ICM applications to share the same session and DMS/MSL-100 resources. LinkPlexer 1.2 allows applications to share a DN (Directory Number) association between different eBusiness applications. LinkPlexer 1.2 is necessary for systems where
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
17 |

Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
!Interactive Voice Response (IVR) voice ports are controlled by IVR and monitored by Symposium Call Center Server
!Symposium Call Center Server performs the call routing, IVR controls the voice response system, and Symposium TAPI Server/Symposium Agent controls softphones and screen pops
!agent positions are controlled by TAPI Server/Symposium Agent (or desktop CTI) and monitored by Symposium Call Center Server
!call queues and agent positions are monitored by third-party applications, such as voice recorders
Note: For more information, see the LinkPlexer 1.2 Installation and Configuration Guide.
18 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
How Symposium Call Center Server communicates with the switch
Introduction
Symposium Call Center Server and the switch must be able to exchange information if calls are to be successfully routed in Symposium Call Center Server. You must ensure that this communication is enabled by configuring the resources shared by both the switch and Symposium Call Center Server.
A Controlled Directory Number (CDN) is the initial point of entry for any call processed in Symposium Call Center Server. A CDN serves as a holding place while information is gathered from the call (for example, Calling Line Identification number [CLID]) and treatments are applied to the call (for example, recorded announcements).
For any call processing to begin in Symposium Call Center Server, the call must arrive at a CDN on the switch that is controlled by Symposium Call Center Server. Information that is gathered from the CDN and sent from the switch to Symposium Call Center Server is used to enable Symposium Call Center Server to define the path the call follows through the call center.
How Controlled Directory Numbers operate
A Controlled Directory Number (CDN) is a logical entity identified by a Directory Number (DN) that holds onto calls waiting to be routed using Symposium Call Center Server routing instructions. Symposium Call Center Server can route calls to any local or third party with a valid address, including agent positions and even other CDNs. In addition, call treatments (music, RAN, silence, and ringback) can be applied to calls while they are waiting for instructions from Symposium Call Center Server. Other treatments such as busy, fast busy, and disconnect can be applied to a call.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
19 |

Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
For each call arriving at a CDN, the switch informs Symposium Call Center Server of the call’s arrival and starts a timer while waiting for the routing instructions. The switch handles the call according to the response returned from Symposium Call Center Server. If the timer expires before a response is received, the switch routes the call to a default ACD group, which is defined for the CDN on the switch. For more information about default ACD routing, see “Configuring CDNs in controlled and default mode” on page 62.
ATTENTION
The timer value configured on Symposium Call Center Server must be set to a value lower than the timer value configured on the switch.
CDN operation is based on the existing ACD model on the switch. A CDN can be viewed as an “ACD group” with the following characteristics:
!In the normal operation, the switch does not control the overflow or routing for a CDN ACDGRP. Calls in the CDN are handled by Symposium Call Center Server.
!There are no agents or supervisors associated with a CDN.
!In the servord utility, ACD agents cannot be defined for a CDN’s ACDGROUP.
Note: Never add options to the tables.
!There are no subgroups assigned to a CDN.
A subgroup cannot be defined for a CDN in table ACDSGRP.
!The CDN priority is set to zero.
In table DNROUTE, the priority of the primary DN and the priority of the secondary DN of a CDN ACDGROUP is set to zero.
!A CDN group can be defined in an NACDGRP table as a networked acdgroup; however, the timers must be set correctly to keep the switch from taking the call back and sending it to another switch and agent.
!The existing table ACDGRP fields, such as ACD Ring Threshold, Priority Promotion, and Forced Night Service, are not applicable to an ACDGRP that has the CDN option.
!A CDN does not have the following call queues: Overflow In Queue, Overflow Out Queue, or Call Transfer Queue.
20 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
!A CDN has a default ACD group, which is datafilled on the switch. The default ACD group is datafilled in table ACDGRP.
!A CDN can have the following states:
! Controlled
Incoming calls are handled by Symposium Call Center Server. For an example of controlled call routing, see “Call routing in controlled and default mode” below.
! Default
Incoming calls are routed to the default ACD group. For an example of default call routing, see “Call routing in controlled and default mode” below.
! Revert to Default
All incoming calls and existing calls in the CDN queues are routed to the default ACD group.
In addition, the state can be set by Symposium Call Center Server or the switch.
!To apply MUSIC to a CDN by Symposium Call Center Server, the AUDIO option must be datafilled in table ACDGROUP.
!The current limit of the number of calls on a single CDN queue (DMS switch) is 512.
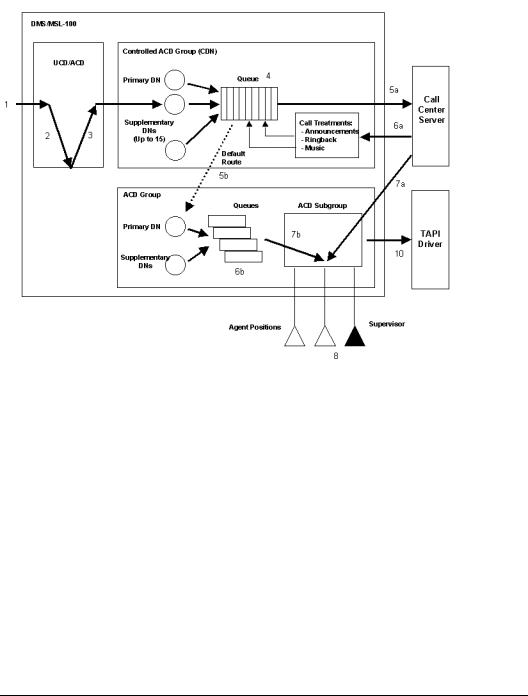
Call routing in controlled and default mode
The diagram on the next page illustrates how calls can be routed in both controlled and default mode. The text following the illustration explains how the call is processed depending on whether it is routed through controlled or default mode.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
21 |
Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
1.An incoming call arrives at the switch.
2.The call is routed to an IVR port (optional).
3.The IVR transfers the call to a CDN after the caller enters digits (optional).
4.The call is routed to an IVR port.
5.The caller receives an IVR treatment, prompting him or her to respond through the use of phoneset keys.
6.The IVR transfers the call to a CDN after the caller enters digits.
7.The call remains queued in the CDN awaiting further call processing.
8.The switch sends a call notification to Symposium Call Center Server. The call is routed in either of the following ways:
22 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
!If Symposium Call Center Server receives the notification, a return notification is sent to the switch. The call remains on the CDN under the control of Symposium Call Center Server. A call is defaulted from Symposium Call Center Server if the specified ICCM timer (defined in table ACDGRP in the option CDN) expired without any response from Symposium Call Center Server.
!If Symposium Call Center Server does not respond to the notification due to a link or server problem, the call is routed in default mode. The call is routed to the default ACD after the timeout expires.
9.The call follows a path as defined in either the controlled or default call routing mode.
!In the controlled call routing mode, Symposium Call Center Server provides treatments as specified in the script.
!In the default call routing mode, the call is removed from the queue on the CDN, and then it is sent to the default ACD group awaiting an available agent to answer the call.
10.The call follows a path as defined in either the controlled or default call routing mode.
!In the controlled call routing mode, Symposium Call Center Server routes the call to an agent qualified and available to answer the call.
!In the default call routing mode, the call is routed to an available agent in the default ACD group.
11.The call is answered by an available agent.
12.If you have purchased the Symposium Agent feature, call data sent by TAPI enables a screen pop to appear on the agent’s screen.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
23 |

Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
Support for switch features
Introduction
This section describes features configurable on the switch, and explains how they interact with Symposium Call Center Server.
ACD
You must configure Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) on the switch to provide default ACD routing when Symposium Call Center Server is not available. All calls are routed by Symposium Call Center Server. If an ACD call is sent to a group configured by Symposium Call Center Server, the priority is given to the call that gets there first.
Announcements
Announcements held in Digitally Recorded Announcement Machine (DRAM) or Enhanced Digitally Recorded Announcement Machine (EDRAM) on the switch are supported to provide Hold in Queue announcements controlled by Symposium Call Center Server.
Controlled and default call routing
Incoming calls can be routed to a default ACD group in the event that Symposium Call Center Server does not gain control of the calls after they have been forwarded from the switch. For more information about controlled and default call routing, see “Configuring CDNs in controlled and default mode” on page 62.
Phoneset keys
This section describes special considerations for the use of phoneset keys.
24 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
Unsupported keys on agent phonesets
Do not configure the following keys on agent phonesets. Use of these keys results in the incorrect agent status on the real-time displays (RTDs):
!
!
!
!
Hotline
Private line
Voice call
Dial Intercom
Transfers and conferences
A call is pegged as a transfer when the agent uses the Fast Transfer key. It is pegged as a conference when the agent uses the 3-way calling (3WC) key.
Note: The transfer or conference is pegged when the agent completes the transfer or conference by pressing the key the second time. Prior to this, RTD displays the agent in ConsultInit status.
Secondary DN keys
An agent phoneset can contain multiple secondary DN keys. However, in this release, Symposium Call Center Server can only monitor one DN key on each phoneset. Therefore, Nortel Networks recommends that you configure only one DN key on each agent phoneset.
You must add the ECM option against the secondary DN before the DN can be acquired by Symposium Call Center Server.
Note: Symposium Call Center Server does not support multiple appearance DNs.
Emergency key
The Emergency key enables an agent to forward a call to his or her supervisor in the event of an emergency. When an agent presses the Emergency key, the supervisor configured as the agent’s reporting supervisor on Symposium Call Center Server is notified. The Emergency key on the supervisor phoneset rings, and, if the supervisor is logged on to the server, the Emergency Indicator appears.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
25 |

Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
Once the agent has forwarded the call to his or her supervisor, the light next to the agent’s Emergency key flashes. If the supervisor answers the call within 30 seconds, the light next to the agent’s Emergency key no longer flashes, but remains on until the supervisor disconnects from the call.
If the reporting supervisor does not answer the call within 30 seconds, the call is forwarded to a backup associated supervisor, if one has been configured on Symposium Call Center Server. To enable emergency calls to be forwarded to the associated supervisor’s phoneset, you must define the associated supervisor as a member of a hunt group for the ACD subgroup to which the agent belongs.
The agent is disconnected from the call if either the reporting supervisor or the associated supervisor answers within 30 seconds of the call being forwarded to them. If neither the reporting supervisor nor the associated supervisor answers the call within 30 seconds, the agent can press the Emergency key again to repeat the process or the agent can answer the call.
Note: The switch does not allow agents to press the Emergency key while they are in conference with another agent.
Display Waiting Calls key
Call queuing occurs on Symposium Call Center Server rather than on the switch, so the switch and ICM cannot provide meaningful call waiting statistics.
Phoneset displays
Agent and supervisor phonesets can display information such as the Calling Line Identification (CLID) number of the caller. The information displayed on the phoneset is not controlled by Symposium Call Center Server but must be configured on the switch.
Skillset display on phoneset
Common Command Model (CCM)16/SCAI17 or later supports skillset name display on the agent and supervisor phonesets. However, the phoneset will display only the first 15 characters of the skillset name, and will only display the characters A through Z, and the numbers 0 through 9.
26 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
LOB codes
Line of Business (LOB) codes, or activity codes, identify the type of call. For example, an activity code can indicate a Sales or a Support call. To use activity codes, you must enable the LOB feature on the switch. If you want to assign names to the activity codes (for example Sales or Support) for reporting purposes, you must also define the activity codes on Symposium Call Center Server. Agents can enter up to three LOB codes during a call.
Agent actions/events |
DMS actions |
Enters the first LOB code for the call.
Enters another LOB code during the same call.
The call is released.
Buffers the code.
Sends the first LOB code to the host. Buffers the new code.
Sends the previously buffered code in dv-LOB-Event-U message. If no code is buffered, no code is sent (even if a default code was datafilled for the ADC Group).
Cancels the last LOB code entered.
Does not enter any code during the entire call.
Erases the code lying in the buffer.
Note: Only the last code may be erased, and none before the last is erased.
Does not send dv-LOB-Event-U message.
Note: This action is different from the ACD MIS that, if datafilled, reports the default codes.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
27 |

Getting started Standard 1.0
Agent actions/events DMS actions
Enters more than three LOB codes.
Enters an LOB code after the caller hangs up.
Enters an invalid LOB code.
Sends all of the entered codes to the host.
Note: This action is different from the ACD MIS that reports only the first three codes.
Waits for a fixed amount of time (2.5 seconds) before tearing the call. If an agent presses the LOB key during this interval, it waits for the agent to finish entering the code, and then sends the code in a dv-LOB-Event-U message.
Validates all the codes. Accepts only the codes from ‘000’ through ‘999’ and the special code of ‘***.’ Sends the dv-LOB-Event-U message only for the valid codes.
Presses the LOB key twice in quick succession.
Restarts the LOB feature on the second pressing of the key.
Note: This action is different from that of Nortel Networks’ PBX offering for which this action is a shortcut for the agent to enter the default code.
Notes:
1.The switch does not allow agents to press the LOB key while they are in conference with another agent.
2.The server does not monitor activity codes for DN calls.
28 |
Symposium Call Center Server |

April 2004 |
Gettingstarted |
Variable Wrap feature
When an agent releases a call, the Variable Wrap feature prevents another call from being presented to the agent for a specific period of time. Agents can use this time to perform any required post-call processing. For Symposium Call Center Server to support Variable Wrap, the feature must be configured on the switch.
There are two options available when configuring Variable Wrap:
!If Variable Wrap is set to a value greater than zero (0), once an active call is released, the agent is not available to receive any new calls for the length of time specified. For example, if Variable Wrap is set to a value of 20, the agent has 20 seconds to record call-related information before becoming available to receive new calls.
!If Variable Wrap is set to the value zero (0), once the active call is released, the agent immediately becomes available to receive new calls.
Note: If you do not configure Variable Wrap on the switch, the Release Guard feature is enabled. Release Guard prevents calls from being presented to the agent for 1 second after an active call is released.
Symposium and DMS/MSL-100 Switch Guide |
29 |

Getting started |
Standard 1.0 |
Night service feature
Skillsets go out of service under the following conditions:
!automatically, when all agents have logged off
!manually, when you change the skillset mode on the Skillset Properties window on the Symposium Call Center Server client
Two out-of-service modes are available: transition mode and night service mode.
You must put skillsets into transition mode manually. In transition mode, Symposium Call Center Server refuses any new calls, but continues to present queued calls to agents. When no more calls are waiting, the server puts the skillset into night service mode.
Skillsets go into night service mode automatically when all agents log off; you can also put them into night service mode manually. In night service mode, the server refuses calls for the skillset, and gives night treatment to any queued calls.
ATTENTION
Do not configure the night service key on supervisor phonesets. Symposium Call Center Server does not support this feature.
30 |
Symposium Call Center Server |
 Loading...
Loading...