Honeywell Mark III User Manual

Technical Overview For
Mark III Communications
Management Unit (CMU)
23 July 2002
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 1 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 2 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Mark III CMU Overview
Honeywell provides a family of Datalink products, ranging from the AFIS product for the business Jet market, to our Mark II and Mark III CMUs for the Air transport and Military market. The Mark III Communications Management Unit (CMU), discussed in this document, is Honeywell’s High-End “Next Generation” CMU. The Mark III is a fully functional ARINC 758 CMU built using the latest hardware and software technology, making it the most powerful and capable CMU in the industry today. Designed to exceed today's stringent datalink requirements, the Mark III offers the capability to grow for tomorrow's rapidly expanding datalink requirements.
The Mark III CMU is the next generation in CMU products. It offers over 100 Mbytes of memory (64 MB of volatile memory and 48 MB of non-volatile memory). Utilizing a Pentium 266 MHz processor and 2 Power PC dedicated I/O processors, the Mark III also offers a significant increase in processing power over other CMUs in the industry. The dedicated I/O processors ensure the elimination of throughput bottlenecks allowing the Mark III to concurrently process data from all data sources (today and in the future).
The Mark III CMU is a full ARINC 758 complaint unit, and is supported by an Aircraft Personality Module (APM). In addition, the Mark III CMU contains additional I/O capability above and beyond that called out for in the ARINC 758 characteristic. This includes a UHF Modem added to the unit for potential future use of UHF as a datalink subnetwork. It includes customized RS 422 ports to support non-ARINC 739 CDUs that are used on such aircraft as Embraer 135/145, and includes a PCMCIA interface for rapid dataloading. In addition, the Mark III CMU has specifically been designed to support future modifications outside of the ARINC 758 specification, to enable implementation of new technology that will provide additional benefits to our airline customers. This expansion would be introduced using the current spare card slots designed into the unit. The primary upgrade being planned is the introduction of an integrated Gatelink capability into the unit, which would allow airlines to grow the CMU to support very high speed / short range communication while on the ground using a 2.4 Ghz spread spectrum1 technology.
The baseline Mark III CMU provides the capability to communicate over HFDL, SATCOM, and VHF (Mode 0/A). By designing the Mark III CMU with the necessary hardware to support future datalink requirements, functionality like VDL Mode 2 and the Aeronautical Telecommunications Network (ATN) are added with just a software upgrade. Due to the size of the memory and processor capability contained within the unit, the Mark III CMU provides the lowest risk to an airline for introduction of such new technology, as it becomes required for future CNS/ATM operation.
The Mark III CMU utilizes a database-driven software architecture, which provides unparalleled flexibility. All I/O parameters for an entire aircraft fleet are captured in a Flexible Input Data Base (FIDB). The Mark III CMU then determines the aircraft type from the Aircraft Personality Module (APM) and applies the appropriate set of I/O signals for that aircraft type.
A user has the capability to customize their Airline Operational Communications (AOC) application through the use of the Airline Modifiable Information (AMI) database. All of the I/O parameters specified in the FIDB are available to the user as part of the AMI definition. By having the I/O parameters isolated to the FIDB, a single AMI can be subsequently generated using logical I/O parameters for all aircraft types within a fleet. The AMI allows the user to:
∙Design the screen layouts
1 The integrated Gatelink approach would provide on the order of a 1 to 11 Mbit/second network over approximately 1,000 feet utilizing the unlicensed 2.4 Ghz spread spectrum frequency. The Gatelink upgrade would also require a TWLU and antennas to be installed on the aircraft, in addtion to a hardware upgrade to the Mark III CMU.
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 3 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

∙Define uplink and downlink message formats
∙Define the format of printed messages
∙Specify trigger logic (i.e., OOOI)
∙Define the geographic area for specific frequency coverage
∙Define the subnetwork preference by region
∙Capture exceedances (mini-ACMS capability)
Once a user generates a new AMI, implementation is as simple as generating a disk containing the new AMI database and using the Mark III CMU dataload capability to load the AMI into each aircraft with no certification effort required.
The Mark III CMU also incorporates a new concept called the Honeywell Generated Information (HGI) database. The HGI is a controlled database that contains protected information used by applications. Typically, the HGI will contain protocol timers, ATC screen and printer formats, and ATC message definitions. As with the AMI, all aircraft I/O parameters from the FIDB are available for use by the HGI. Although changes to the HGI require a certification effort, no embedded operational software changes are required.
Both the AMI and the HGI are generated using a common tool called the Ground Based Software Tool (GBST). The GBST is a Windows-based application that allows the user to perform normal windowing functions such as cutting and pasting components between the various GBST screens. The GBST is based on the B-777 GBST, providing the same type of user interface as for the B-777, but providing increased functionality available in the Mark III CMU.
1.2 Datalink Capability for Today and Tomorrow
Today, datalink users have found that datalink is an indispensable tool for helping manage operations, maintenance and other functions. Datalink provides access to more data and timely data which results in time and cost savings for an airline. Datalink users have found that datalink:
∙Improves accuracy and efficiency of communicating with the flight crew
∙Improves information dissemination within airline operations
∙Provides timely availability of information
∙Reduces delay times
∙Reduces airline personnel effort (i.e., data courier, special services)
∙Improves operational performance
∙Reduces fuel costs
∙Improves maintenance operation
∙Improves passenger service
∙Reduces pilot workload
The rapid expansion of datalink requirements has stretched the existing ACARS network toward capacity and has accelerated the desire of datalink users to move away from the limited ACARS Management Unit (MU) to the more capable Communications Management Unit (CMU).
The industry is demanding new approaches to meet the new requirements. Timely and accurate information exchange between the aircraft and the ground is critical to an airline’s operation. Digital datalink communications provides a method of moving that information to the right place at the right time, saving both
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 4 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

time and money. However, to deliver the future datalink capability required by the airlines, both ground and airborne systems must have a transition to the next generation architecture.
The Mark III CMU offers a datalink user the next generation ARINC 758 CMU capable of providing the datalink functionality to meet the industry demands for today and tomorrow.
1.3 Honeywell Datalink Experience, Products, and Services
Honeywell has been developing Datalink Management Units since the early 1980s starting with the ARINC 597 ACARS. Since that time, Honeywell has continuously evolved and introduced new systems, comprised of the 724 ACARS (introduced in 1988), the Mark I 724B ACARS (introduced in 1989), and the Mark II User Re-programmable ACARS (introduced in 1991).
Honeywell currently offers two go-forward CMU products. The Mark II CMU is offered for 724B or 758 wiring installations. The 965-0758-001 PN is for 724B installations, while the 965-0758-002 is for ARINC 758 installations. The other CMU is our new Mark III CMU (PN 7519200-920), which is offered for ARINC 758 wiring solutions2, and is described in this document.
Honeywell is the leading supplier of datalink systems, with over 100-datalink customers. This is significant in light of the fact that at the beginning of the 1990s, Honeywell had only three customers. We contribute this large growth due to the fact that we have continued to invest in datalink systems and technology. The new Mark III is the latest in such product introductions.
Honeywell also developed the equivalent of an ACARS MU for the Boeing 777. This was the first dual and integrated ACARS system and the first essential ACARS system.
Airbus uses a communications unit named the Air Traffic Services Unit (ATSU) which is designed and manufactured by Aerospatiale. The ATSU is a Supplier Furnished Equipment (SFE) system but the AOC applications software is provided as Buyer Furnished Equipment (BFE). Honeywell is the leading supplier of ATSU AOC software, which is based on the same AOC software contained in the highly successful Mark II CMU.
With our offering for the B-777, the ATSU and our CMU, Honeywell is the only manufacturer that can support all three aircraft configurations.
Honeywell is also a leading supplier of datalink display systems. Whether it is a full-sized ARINC 739 MCDU, a compact ARINC 739 Multi-Input Display Unit (MIDU) or a compact CDU, there is a datalink display system for all aircraft from air transport and regional to business jet and general aviation.
The Mark III interfaces with many avionics devices, particularly Flight Management (FM) systems. Honeywell is the leading supplier of FMs, whether it is the advanced Pegasus platform in the air transport arena or the NZ-2000 in the regional and business jet market. Honeywell also provides FM systems in its integrated avionics solutions (AIMS, VIA, and Epic).
To complete a user's datalink capability, Honeywell also offers ARINC 740 cockpit printers, SATCOM, and radio systems (HF and VHF).
In addition to datalink products, Honeywell offers supporting services. The Honeywell Global Data Center (GDC) provides ground-based data services for users that do not wish to implement their own ground infrastructure. GDC currently provides a turnkey solution for over 2,200 datalink equipped aircraft. This
2 The 7519200-920 part number reflects the standard Mark III CMU designed for ARINC 758 for air transport aircraft.
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 5 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

includes such services as Providing world-wide Weather messages to the aircraft, as well as being an FAA approved distributor of messages such as Pre-Departure Clearances and ATIS. The Honeywell Aircraft Maintenance and Operational Support System (AMOSS) provides ground ACARS message processing and integration with flight planning systems. Finally, Honeywell provides world class product support worldwide.
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 6 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
2.1 Hardware Overview
The Mark III CMU is based upon the Multiple Application Processing System (MAPS) platform which is the new generation hardware that will be used for introduction of new Honeywell datalink products. This common hardware platform will facilitate the introduction of communication products that integrate new capabilities with the Mark III CMU.
The Mark III CMU is a single Line Replaceable Unit (LRU) housed in a standard 4 MCU ARINC 600 form factor. The Mark III CMU contains 4 Circuit Card Assemblies (CCAs): (1) Processor; (2) I/O; (3) Power Supply; and (4) Interconnect. There is expansion capacity for two spare CCAs.
The main processor is a 266 MHz Pentium while the I/O is handled by two MPC 860 microprocessors. These two I/O processors are able to concurrently process all I/O effectively eliminating throughput bottlenecks. Additionally, there are two dedicated digital signal processors (DSPs), one each for the VHF and UHF modems. There is a total of 64 MB of DRAM along with 48 MB of Flash EPROM.
The front panel of the Mark III CMU (see Figure 1) contains a "PUSH TO TEST" button for initiating Test Mode, two LEDs to indicate Test Mode Pass and Fail, an ARINC 615 connector, and a PCMCIA connector. The ARINC 615 connector can be used for a portable data loader, a Debug and Maintenance Terminal
ARINC 615
(DMT), or for a Data Logging Terminal (DLT).
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 7 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

Figure 1 Mark III CMU Front Panel
ARINC 607 defines the Aircraft Personality Module (APM) which contains all aircraft and system configuration information. The APM is external to the MARK III CMU and is a permanent fixture in the aircraft. Only one APM is required per MARK III CMU installation (one APM for each MARK III CMU mounting tray). The same APM part number is used on all aircraft in the fleet.
2.2 System Interfaces
The Mark III CMU supports an extensive set of interfaces. Many of these interfaces are specifically defined by ARINC 758. There are also a number of spare ARINC 429 ports available for additional devices as needed by the user. The Mark III CMU supports all of today’s ACARS interfaces used on today’s aircraft, with extensive capability for future growth.
|
|
PCMCIA |
|
|
|
Table 1 |
Mark III CMU Interfaces |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Device |
|
|
ARINC |
|
Interface |
# |
Baseline / |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Specificati |
|
|
|
Growth |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
on |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VHF Radio |
716 |
|
Audio |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
VDR: Mode 0 |
750 |
|
Audio |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
|
Mode A |
|
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
3 |
Baseline |
||||
|
|
Mode 2 |
|
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
3 |
Option |
||||
|
Satellite Data Unit (SDU) |
741 |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
2 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
761 |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
2 (note 1) |
Growth |
|
|
HF Data Radio (HFDR) |
753 |
|
Low speed ARINC 429 |
2 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
UHF |
--- |
|
Audio |
1 |
Growth |
|||||
|
Mode S Transponder |
718A |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
2 (note 7) |
Baseline |
|||||
|
Gatelink |
751 |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
Growth |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
undefined |
|
Ethernet 10BaseT |
note 2 |
Growth |
|
|
MCDU/MIDU |
739 |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
3 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
DCDU |
undefined |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
1/2 (note 5) |
Growth |
|||||
|
CDU |
---- |
|
RS-422 |
2 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
Printer |
740/744 |
|
Low speed ARINC 429 |
1 (note 3) |
Baseline (note 3) |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
744A |
|
Ethernet 10BaseT |
note 2 |
Growth |
|
|
FMC |
702 |
|
Low speed ARINC 429 |
2/3 (note 4) |
Baseline |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
702A |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
2/3 (note 4) |
Growth |
|
|
Performance Computer (PZ) |
----- |
|
RS-422 |
1 |
Growth |
|||||
|
ACMS/DFDAU |
619/429 |
|
Low speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
CMC/CFDS/CFDIU |
604/624 |
|
Low speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
Cabin Terminal |
--- |
|
Low speed ARINC 429 |
2 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
Electronic Library (ELS) |
--- |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
Growth |
|||||
|
Cockpit Voice Recorder |
757 |
|
Low speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
Growth |
|||||
|
(CVR) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
GPSSU |
743 |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
APM |
607 |
|
--- |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
Dual CMU |
758 |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
note 6 |
|||||
|
Mil-Std-1553B |
--- |
|
Mil-Std-1553B |
1 |
Growth |
|||||
|
DMT |
--- |
|
RS-232 |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
DLT |
--- |
|
RS-232 |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
Airborne Data Loader |
615 |
|
High speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
Baseline |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
|
|
Page 8 |
||||||
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.
Portable Data Loader |
615 |
High speed ARINC 429 |
1 |
Baseline |
Ethernet Data Loader |
615A |
Ethernet 10BaseT |
note 2 |
Growth |
PCMCIA |
--- |
PCMCIA |
1 |
Baseline |
Notes: |
|
|
|
|
1.Supports up to 2 total SDUs, whether ARINC 741 or 761.
2.The Mark III provides 4 10BaseT Ethernet ports which can be used for any purpose.
3.Supports 1 ARINC 740/744 printer in baseline. An additional printer can be added to one of the spare ARINC 429 ports. This requires a software upgrade.
4.Supports 3 FMCs in the AT & Mil products.
5.Supports 2 DCDUs in the AT & Mil products and 1 DCDU in the BRH product
6.The Baseline Mark III supports Cold Spare operation. A software upgrade would be required for additional dual capability.
7.The Mark II CMU interfaces with the transponder to obtain the ICAO address
2.2.1 Subnetwork Interfaces
The Mark III CMU supports a complete set of ARINC 758 subnetwork interfaces (see Figure 2).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ARINC 750 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ARINC 750 |
|
|
|
|
SDU |
|
|
|
HFDR |
|
|
|
|
VDR |
|
|
|
|
SDU |
|
|
|
HFDR |
|
|
|
|
ARINC 750 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
VDR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
VDR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ARINC 716 |
|
|
|
Mark III |
|
|
UHF |
Radio |
|
|
|
CMU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gatelink |
Mode S |
|
Mode S |
|
|
Figure 2 CMU Subnetworks
ARINC 716 VHF Radio
The Mark III CMU supports an interface with one ARINC 716 VHF radio. The interface supports VDL Mode 0, via an audio line to the Minimum Shift Keying (MSK) modem resident in the Mark III. There is also a low speed ARINC 429 transmit interface between the CMU and the ARINC 716 radio that is used to send frequency tuning information.
ARINC 750 VHF Data Radio (VDR)
The Mark III CMU can interface with up to three ARINC 750 VDRs. The Mark III supports the operation of a VDR operating in ARINC 716 mode by utilizing the same audio line as used for an ARINC 716 radio. The CMU also supports a high speed ARINC 429 interface to the VDRs for VDL Mode A.
VDL Mode 2 will utilize the same high speed ARINC 429 interface as VDL Mode A, allowing growth to VDL Mode 2 with just a software upgrade. VDL Mode 2 offers an increase of throughput from 2.4 kbps to 31.5 kbps. VDL Mode 2 is necessary both for ATN communications and for ACARS Over AVLC (AOA). VDL mode 2 is offered as an optional software package for the Mark III CMU.
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 9 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

Satellite Communications (SATCOM)
The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface with one or two ARINC 741 compliant Satellite Data Units (SDUs) via low speed ARINC 429, or can be configured for high speed 429.
The industry is still working on the definition of the ARINC 761 specification for second generation satellite communications systems, which will include access to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellite constellations. When datalink communications over ARINC 761 subnetworks is fully defined, it is planned that the Mark III will be updated (software only) to accommodate both ARINC 741 and ARINC 761 satellite communications.
HF Data Radio (HFDR)
The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface with one or two ARINC 753 compliant HFDRs (or HF Data Units -- HFDU) via low speed ARINC 429. The HFDR offers a datalink user another datalink option when line- of-site VHF and satellite communications are not available (i.e., over the ocean or poles).
UHF
The Mark III CMU contains a UHF modem to support UHF datalink. Software support of this interface requires a software upgrade. Currently there are no interfaces used with datalink for UHF, but the hardware has been added into the baseline unit to support potential future capability.
Mode S Transponder
The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface with one or two Mode S Transponders via high speed ARINC 429. Currently, datalink operation over Mode S is not defined. However, the Mark III CMU has the necessary ARINC 429 receivers in place to support such future need, if ever required. It should be noted that the Mark III CMU baseline does include the interface to the Mode S in order to obtain the ICAO 24 character address (which is then used for verification of data in the APM).
Gatelink
The current ARINC 758 specification identifies an ARINC 429 interface for gatelink interfaces. This is supported by the Mark III CMU hardware. However, Ethernet 10BaseT is a more likely Gatelink interface. The Mark III CMU supports up to four 10BaseT Ethernet ports. Honeywell will be offering a future upgrade package to the Mark III CMU that supports Gatelink capability within the unit, interfacing directly with a TWLU (Gatelink - Transceiver Wireless LAN Unit).
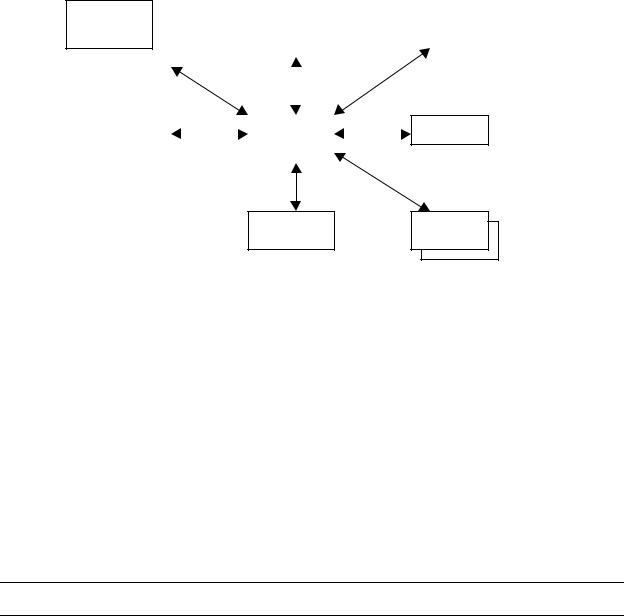
2.2.2 Flight Deck Devices Interfaces
The Mark III CMU supports interfaces to the following flight deck devices: (See Figure 2.2.2-1 for the available Datalink display devices supported by the Mark III CMU).
Multi-purpose Control and Display Unit (MCDU) / Multi-Input Display Unit (MIDU)
The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface with up to three ARINC 739 compliant display devices. These devices could be a standard MCDU or the compact MIDU. This is the standard interface on all Boeing / Airbus and many other types of aircraft. The Mark III CMU supports the ability to present different menus simultaneously on different displays, providing a high degree of flexibility to the flight crew.
Dedicated Display and Control Unit (DCDU)
The industry envisions that certain ATS Datalink Services will require a dedicated datalink display device mounted in the primary field of view. The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface with one or two DCDUs via high speed ARINC 429. Software support for these devices is likely to be available through a softwareonly upgrade once the definition of this interface is fully defined by the industry.
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 10 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

Control and Display Unit (CDU)
In the business jet and regional aircraft market place, there is limited cockpit pedestal real estate. Often, these aircraft are equipped with a 4-line-select key CDU instead of a 6-line-select key MCDU. The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface with one or two of these CDU devices via an RS-422 interface.
MCDU |
MIDU |
CDU |
Figure 2.2.2-1 Datalink Display Units
Printer
The Mark III CMU can interface with a single ARINC 740 or 744 compliant printer via low speed ARINC 429. This includes Honeywell’s ARINC 740 printer, as well as all other manufacturer’s who support the ARINC 740/744 specification.
ARINC 744A defines an Ethernet printer interface. The Mark III CMU has available Ethernet ports but requires a software upgrade to support an ARINC 744A printer. Currently, there are no aircraft configurations defined using the Ethernet interface for the CMU to printer interface.
Figure 4 Cockpit Printer
Crew Alerts
The Mark III CMU provides the interfaces necessary to support aural and visual alerts as well as an indication of NO COMM.
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 11 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.
2.2.3 LRU Interfaces
In general, the Mark III CMU can support any LRU that uses the ARINC 429 File Data Transfer Protocol or Williamsburg Protocol to communicate as an end system, as defined in ARINC 619 (ACARS file transfer protocols for other devices). ARINC 758 identifies a number of specific LRUs and the Mark III CMU supports interfaces to these LRUs:
Flight Management Computer (FMC)
The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface via low speed ARINC 429 with up to three ARINC 702 compliant FMCs operating as end systems. The Mark III CMU can alternatively be configured to interface with up to three ARINC 702A FMCs over high speed ARINC 429. The Mark III CMU can also accept ARINC 429 broadcast data from the FMCs. This broadcast data provides the CMU with data that is captured in the FIDB and available for use by the HGI and AMI.
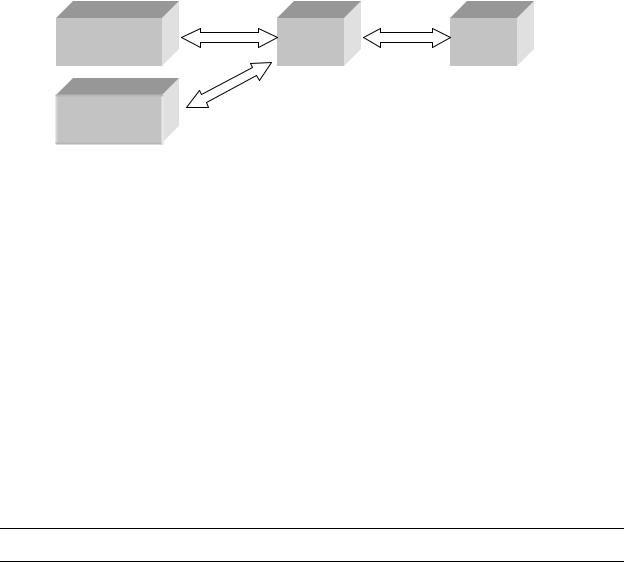
Performance Computer (PZ)
In some aircraft installations, there is a separate performance computer (PZ) in addition to an FMC. The performance computer communicates with a CDU through the CMU (See Figure 5) via RS-422. The Mark III CMU can support a single interface to a performance computer with a software upgrade.
|
|
RS-422 |
|
|
|
RS-422 |
|
|
Performance |
|
|
|
Mark III |
|
|
|
CDU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Computer |
|
|
|
CMU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NZ-2000
Figure 5 CMU/PZ Pass Through Interface
Maintenance Computer
The maintenance computer name varies depending upon the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) but is usually referred to as the Central Maintenance Computer (CMC), Centralized Fault Display System (CFDS), or Central Fault Display Interface Unit (CFDIU). The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface with one maintenance computer over low speed ARINC 429. This interface supports both end system communications as well as the maintenance computer protocol.
The maintenance computer protocol varies based upon airframe. The Boeing 747 uses broadcast fault bits while most other air transport aircraft (e.g., MD-10, MD-11, B-717, A-320, A-330, A-340) use an interactive data block transfer utilizing MCDU screens. Other aircraft types do not currently support maintenance computers (e.g., MD-80, MD-90, B-737, B-757, B767, regional and business jets). The baseline Mark III CMU supports the broadcast fault bits. Interactive data block transfer protocol will be available as a planned upgrade.
Aircraft Condition Monitoring System (ACMS)
The Mark III CMU can be configured to interface with a single Aircraft Condition Monitoring System (ACMS) or Digital Fault Data Acquisition Unit (DFDAU) via low speed ARINC 429. This interface supports end system communications using the standard ARINC 619 protocol in addition to providing the CMU access to
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 12 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

an extensive amount of ARINC 429 broadcast data providing aircraft performance related data. All of the ARINC 429 broadcast data is available via the FIDB to be used by both the HGI and the AMI.
Cabin Terminal
The Mark III CMU can be configured to support up to two Cabin Terminals operating as end systems.
Electronic Library System (ELS)
Although there are no ELS systems in use today which interface to CMUs, the Mark III CMU can be configured in the future to interface with a single ELS operating as an end system via high speed ARINC 429.
Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR)
The industry is developing ARINC Specification 757 which defines a Cockpit Voice Recorder or Digital Data and Voice Recorder (DDVR) capability. The Mark III CMU provides a single low speed ARINC 429 interface that can be used to interface with an ARINC 757 compliant device. This capability will require a software upgrade.
Global Positioning Satellite System Unit (GPSSU)
The Mark III CMU can accept high speed ARINC 429 broadcast data from ARINC 743 compliant GPSSU(s).
2.2.4 Other Interfaces
The Mark III CMU also supports the following interfaces:
Aircraft Personality Module (APM)
ARINC 607 defines the characteristics of an Aircraft Personality Module which contains aircraft and system configuration information and makes this information available to the CMU. The Mark III CMU supports a single interface to an ARINC 607 compliant APM.
Dual CMU
The Mark III CMU is capable of operating in either a standalone or dual configuration. The Mark III CMU hardware includes interfaces to support dual CMU operation. The interface between the onside and offside CMUs is via a high speed ARINC 429 cross-talk bus along with discretes that indicate active and standby states.
In a dual CMU configuration, the left CMU is normally considered the Active unit and the right CMU is normally considered the Standby unit. The Active CMU is the one that communicates with the subnetworks.
There are three possible dual CMU configurations; cold spare, warm spare, and hot spare.
The Cold Spare Configuration is the configuration in which the two CMUs on the aircraft do not communicate datalink information with each other. In the event of a failure of the Active CMU, the Standby CMU must be manually configured (via a cockpit switch) to be the Active CMU.
The Warm Spare Configuration is the configuration in which the two CMUs exchange datalink information. In the event that a fault occurs in the Active CMU, the Standby CMU will automatically be configured as the Active CMU.
The Hot Spare Configuration is the configuration in which the Standby CMU is monitoring all configuration and traffic so that it can seamlessly assume the role of Active CMU in case of a failure of the Active CMU.
The baseline Mark III CMU supports cold spare operation. Other dual operations are waiting on industry definition. The ARINC Datalink Subcomittee is planning on updating the ARINC 758 characteristic in the
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 13 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

future to define Warm and Hot spare requirements. This effort has not yet started. As the Mark III CMU hardware was designed to support Dual capability, Updated dual capability could be provided with a software upgrade.
Ethernet
ARINC 646 defines an Ethernet Local Area Network (ELAN) aboard an aircraft. The Mark III CMU provides four 10BaseT Ethernet ports that can be used for various applications which could include Gatelink connectivity, ARINC 615A data loading, ARINC 744A printer and ELAN connectivity. Software support for the Ethernet ports will require a software upgrade.
MIL-STD-1553B
Mil-Std-1553B is a military standard interface used to communicate with onboard end systems such as an FMC, MCDUs and remote annunciators. This hardware interface is only available in the military version of the Mark III CMU. Software support of this interface requires a software upgrade. This is applicable for only specific Military aircraft.
Debug Maintenance Terminal (DMT) / Data Logging Terminal (DLT)
A Debug Maintenance Terminal and Debug Logging Terminal can be used to access BITE information, program the APM, and for general debug capability. The Mark III CMU provides two RS-232 ports that can be used for a DMT and a DLT. The RS-232 ports are accessible both from the front and rear connectors and can interface with a laptop computer executing terminal emulation software. The DMT is a device that is used for Honeywell debugging and testing, and is not a device required by our airline customers.
Data Loader
The Mark III CMU supports an interface to both an ARINC 615 compliant Airborne Data Loader (ADL) and an ARINC 615 compliant Portable Data Loader (PDL) via high speed ARINC 429. The ADL interface is accessible through the rear connector while the PDL is accessible from the front connector.
High speed data loading via PCMCIA and Ethernet are software growth options.
PCMCIA
The Mark III CMU hardware is equipped with a PCMCIA interface that can be used, to provide a faster means of data loading than an ARINC 615 data loader. The PCMCIA interface is accessible only from the front panel. PCMCIA is Honeywell’s recommended method of performing complete full software loads.
OOOI
The Mark III CMU provides up to 6 high speed ARINC 429 inputs and a number of analog discrete inputs that can be used to determine Out/Off/On/In events. Data available on these interfaces typically include oil pressure, weight on wheels (WOW), flaps, parking brake, and doors.
2.3 Software Overview
In order to meet the system/safety requirements of future CNS/ATM upgrades, all of the Mark III CMU software has been developed to support a future DO-178B Level C. Today, the Mark III CMU is certified to Level D, which is the standard used for certification of ACARS and CMU units. Partitioning in the Mark III CMU is supported by the DEOS operating system which has been previously certified to DO-178B Level A.
The underlying fundamental goal for the Mark III CMU software development was to develop a single software system that could be used with minor modification on other platforms. Honeywell was able to achieve this goal through the use of advanced software development techniques, including model-based development. The model-based approach allowed the developers to design the system independent of the target hardware, capturing the requirements in a model database. The requirements/design are then turned into source code
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 14 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.
through an automated code generation system specific to the target environment. Automated test scripts are also derived from the model database. (See Figure 6).
The software architecture was developed to isolate target-specific components from the core software components. The combination of the model-based approach and isolating target-specific components allowed Honeywell to develop a Communications Management Function (CMF) that can be readily hosted on other hardware targets including the Honeywell integrated platforms VIA and Epic (and in the future B-777 AIMs). This common communications function allows Honeywell to maintain a single communications baseline across platforms, ensuring consistent implementations. This is beneficial to an airline that may have a mixed fleet containing both federated and integrated architecture aircraft. A prime example is the Embraer regional jet family. The Honeywell standalone Mark III CMU has been selected by many airlines for their ERJ-135 and ERJ-145 aircraft. The next generation ERJ-170 and ERJ-190 contain the Primus Epic integrated avionics cockpit which includes the CMF. Although the Mark III CMU and the Primus Epic are different hardware platforms, the same core CMF capability exists on both platforms.
Mark III
CMF
VIA
Target-specific
Epic
Figure 6 Communication Management Function (CMF) for Both Federated and Integrated Platforms
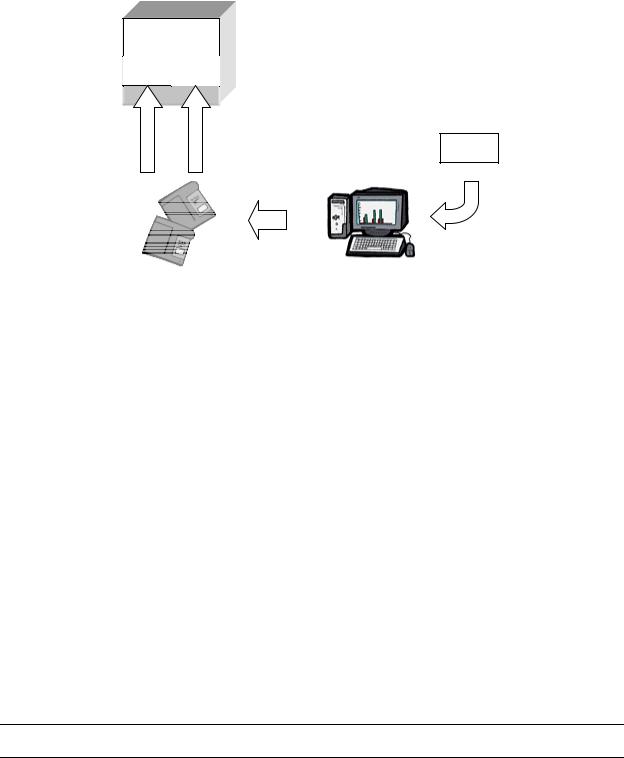
Another driving goal of the software architecture was to provide as flexible a system as possible by utilizing a database-driven design. This design approach allows quick and easy changes to the Mark III CMU without modifying the embedded operational software. (See Figure 7).
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 15 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.
CMU
AOC
HGI AMI
FIDB
GBST
Figure 7 Database Design
The Flexible Input Data Base (FIDB) contains a list of all I/O parameters available for all aircraft within a fleet. The FIDB contains information regarding LRU source, data busses, labels, scaling, and resolution for each I/O parameter.
The Airline Modifiable Information (AMI) database is generated by the user to customize their AOC application. AOC screen and print formats, message definitions and trigger logic can all be specified in the AMI. Changes to the AMI only require a dataload operation but no certification activity. This is a significant change from pervious systems, such as our Mark II CMU and competitors CMUs, which still maintain much of this processing within an AOC software segment. With the Mark III CMU, all such functionality is contained within the AMI, providing airlines significantly more control and flexibility for performing changes, as requirements change.
The Honeywell Generated Information (HGI) database provides capability similar to the AMI, but for protected data typically used by ATC applications. Unlike the AMI, HGI changes require certification although no change to the embedded operational software.
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 16 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

2.4 Certification
Honeywell received the 1st FAA certification in December 2001. This initial certification was for Embraer aircraft. The Mark III CMU has since also been type certified by Boeing. Contact Honeywell for up-to-date information on other certifications completed or in work.
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 17 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.

3 FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
The Mark III CMU is designed to provide complete datalink capability, providing interfaces and support to today’s installed equipment. In addition, Honeywell as well as the industry recognizes that Datalink features will be expanded over time, and is in fact the principle behind the current ARINC 758 characteristic. A Characteristic that was developed to define current operation (referred to as Level O.1A), and allow expansion over time to support new requirements and needs. The Mark III CMU was specifically designed to support such future growth. Growth Functionality describes potential new capabilities for post-baseline software releases. Many of the capabilities described in both the Baseline Functionality and Growth Functionality sections are configurable via the AMI or the HGI.
The Mark III CMU supports an ARINC 739 MCDU, an ARINC 739 MIDU, and a CDU for displaying ACARS information. For the purpose of simplifying the text of this section, 'datalink display' will be used generically to mean MCDU, MIDU, or CDU.
3.1 Baseline Functionality
The baseline Mark III CMU provides functionality defined as level 0.1A in ARINC 758.
For Reference, the level of functionality as defined in the ARINC 758 Characteristic is shown below. This level of functionality is defined, as the CMU is recognized within the industry as evolving over time in order to meet future CNS/ATM requirements.
A758 level |
Service Function |
|
|
0 |
ARINC 724B ACARS equivalent |
|
|
|
ARINC 618: ACARS |
|
|
|
ARINC 716: VHF |
|
|
|
ARINC 750: VHF Mode 0 |
|
|
|
ARINC 741: SATCOM |
|
|
0.1 |
+ VDR Mode A using ARINC 429 I/F |
|
|
|
ARINC 750: Mode A |
|
|
|
ARINC 761: SATCOM |
|
|
|
ARINC 753: HF |
|
|
0.2 |
AOA VDLM2 |
|
|
1 |
+ ATN Services |
|
|
|
ARINC 750: VDL Mode 2 |
|
|
2 |
+ High Speed Services |
|
|
|
Not specified at this time |
|
|
HONEYWELL Aerospace Electronic Systems |
Page 18 |
Use or disclosure of information on this page is subject to the restrictions on the title page of this document.
 Loading...
Loading...