Honeywell EGPWS User Manual

Honeywell Electronics
Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning
System (EGPWS):
Flight History Data
Jim Mulkins
EGPWS Sr. Systems Engineer
Honeywell Aerospace
August 27, 2012

EGPWS Flight History Data
•EGPWS Flight History Data was designed to:
-Provide detailed data on EGPWS alerts
to improve terrain database
to evaluate the performance of EGPWS algorithms in real-world operation
•maximize CFIT protection
•minimize nuisance alarms
•EGPWS Flight History Data can:
-Help provide data to investigate Incidents / Accidents
Where FDRs do not exist on the aircraft or fail to function
•EGPWS does not add much beyond what FDR provides
But, it wasn’t designed for accident investigation purposes
2 |
File Number |

EGPWS Flight History Data - Limitations
•EGPWS Flight History Data:
-Does NOT record Date & Time
EGPWS system time (hours:minutes:seconds) powered
Flight Leg (Leg 1 is most recent flight)
-Is NOT environmentally protected or crashworthy
The EGPWS can be damaged beyond the ability to provide any data
-Does NOT provide a rapid data rate
1 sample per second
-Does NOT record data from all sources
Typically only records source being used
This may not be the source being used by the pilot in command
3 |
File Number |

EGPWS Units – Class A TAWS
•MK V & MK VII
-2 MCU (2.5”W x 8”H x 13”D)
-Found in
All Boeing
Most Airbus
Large and Medium business jets
•MK VI & MK VIII & MK XXII
-(3”W x 6”H x 10”D)
-Found in
Medium and Small business jets
Turboprops
IFR Helicopters
4 |
File Number |
|
|

EGPWS Units – Class B TAWS
•KGP560 & KGP860 & MK XXI
-(2”W x 4”H x 6”D)
-Found in
Small business jets
Turboprops
VFR Helicopters
•KMH820 & KMH920
-4 MCU (4”W x 7”H x 13”D)
-Earlier units are black
-Found in
Small business jets
Turboprops
5 |
File Number |
|
|
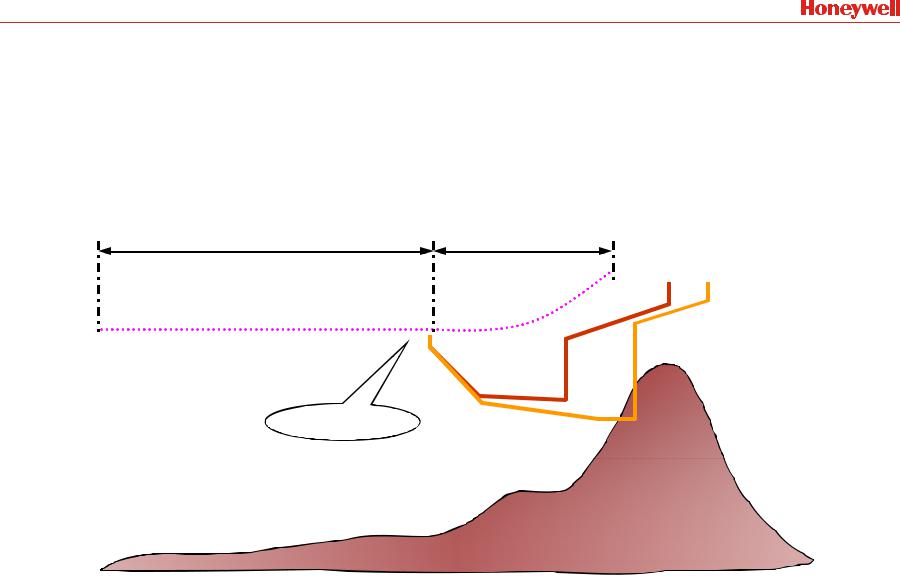
EGPWS Flight History Data (Warning/Caution)
•EGPWS records data 20 seconds before and 10 seconds after every EGPWS alert/warning
Used to determine a cause of the alert/warning and pilot reaction
20 Seconds |
10 Seconds |
Caution Terrain
6 |
File Number |
|
|

EGPWS Flight History Parameters
•List of parameters recorded in EGPWS Warning Flight History Data
Alert Type |
Terrain Database Elevation |
|
|
|
|
System Operating Time |
GPS Satellites Visible |
|
Corrected Altitude |
GPS Satellites Tracked |
|
Latitude |
Pitch Angle |
|
Longitude |
Roll Angle |
|
Position Source |
Glideslope Deviation |
|
Position Uncertainty(HFOM) |
Localizer Deviation |
|
Airspeed |
Display Range #1 |
|
True Airspeed |
Display Range #2 |
|
Ground Speed |
Terrain Display Enabled #1 |
|
Minimum Operating Speed |
Terrain Display Enabled #2 |
|
Barometric Altitude (Uncorrected) |
Landing Gear Down |
|
Geometric Altitude |
Landing Flaps Selected |
|
Geometric Altitude VFOM |
Terrain Awareness & TCF Inhibit |
|
GPS Altitude |
Audio Inhibit |
|
GPS VFOM |
Body AOA |
|
Radio Altitude |
Longitudinal Acceleration |
|
Altitude Rate |
Normal Acceleration |
|
Magnetic Track |
Inertial Vertical Acceleration |
|
True Track |
Filtered Shear/Total Shear |
|
True Heading |
Static Air Temperature |
Data #1
Data #2
Data #3
Select
Helicopter EGPWS Only
7 |
File Number |

EGPWS Flight History Data
•Does not record what is not input
-For example, no radio altitude on KGP or KMH Class B units
•Data that is invalid is noted as such
-For example, glideslope deviation when not ILS tuned
•Data is recorded even when manually inhibited by pilot
•Data can be exported to Excel spreadsheet (.xls file)
-Excel format facilitates graphing of data
•Data can be superimposed over maps/chart (KML)
8 |
File Number |

Flight History Retrieval Process
•Flight History information is stored in the EGPWS in a specific area of the non-volatile memory
•Data can be downloaded via PCMCIA or CF card
-Card must be programmed with special instruction file
-Process similar to terrain database upload, requires < 5 minutes
-Cards available upon request from Honeywell Engineering
-Data is encrypted
•Decoding of encrypted information is done by Honeywell using proprietary tools, tools are not distributed
•If unit is damaged:
-Circuit boards can be placed in donor units or fixtures
-Memory chips can be removed and data retrieved via chip reader
Honeywell can accept data directly from chip reader
Occasionally memory chips are damaged and unreadable
9 |
File Number |

Hawker 800 crash at Owatonna MN
•NTSB AAR-11/01, 31 July 2008, – 8 Fatal
-CVR, no FDR and none required
-Crashed while attempting late go-around on runway 30
•EGPWS issued Bank Angle alert
-Aircraft rolled 90 degrees after becoming airborne off rwy end
•Flight History download performed at Honeywell
-Unit functional post-accident
-Memory contained 22 seconds of data
20 before Bank Angle alert
2 after Bank Angle alert (then loss of power)
•Data used to confirm:
-Flaps down before landing
-Flaps retracted after landing
-Speed increase on runway
-8 knot tailwind
10 |
File Number |

Cessna 560 crash at Pueblo, CO
•NTSB AAR-07/02, 16 February 2005 – 8 fatal
-CVR, no FDR and none required
-Pueblo was a planned fuel stop on cross-country flight
-Crashed 4 mi short of airport in freezing rain
•EGPWS issued Bank Angle alert
-EGPWS destroyed in impact, fire
-Circuit cards returned to Honeywell for possible analysis
•1 of 2 Flight History data chips broken, data irretrievable
-Manual process used on surviving chip
-30 seconds of partial data set recovered
Altitude, descent rate
Pitch, roll
Ground speed, ground track angle
-Data correlated to radar data
11 |
File Number |
|
|

Honeywell Electronics
Non-Volatile Memory (NVM):
An Increasing Aide in Investigations
Jay Eller
Air Safety Investigator
Honeywell Aerospace
August 27, 2012
12 |
File Number |
|
|

Agenda
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What Data |
What is the manufacturer’s intended use of NVM data? |
|
|
|
|
||
|
is |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
What can we learn from data obtained from NVM? |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Available |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What types of equipment |
Airframes |
What types of airframes |
||
and |
||||
have NVM data? |
Equipment |
have NVM data? |
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Handling |
|
|
of |
|
What complications and precautions exist |
Equipment |
|
when handling equipment with NVM? |
Containing |
|
NVM |
|
|
|
|
13 |
|
File Number |
|
|
|

Intended Uses of NVM in Electronics
•Maintenance/Tracking
-Logging of failures which require maintenance at next interval.
-Logging of exceedances or failures which may require immediate attention.
-Tracking of fleet such as EMS and Fire Fighting.
•Trend analysis
-Engine performance over a period of time.
-Aircraft performance over a period of time.
-Could be specific to an altitude, temperature, or other operational condition.
•Trouble Shooting
-Capturing detailed data when a particular event has occurred.
-Event could be pilot initiated (press of a button) or a predetermined scenario.
All Could be Beneficial in Accident Investigation
14 |
File Number |

Various Levels of Data Available
•Low Fidelity Data:
•Slow sample rates (greater than 1 sample per minute)
•Minimal data precision (ie: Latitude, Longitude, altitude, etc)
•Would show long term trending with little inability to show immediate behaviors/signatures.
•Medium Fidelity Data:
•Medium sample rates from 1/sec to 1/minute
•Moderate data precision.
•Would show medium range trending with minimal ability to show immediate behaviors/signatures
•High Fidelity Data:
•High frequency rate of data capture (1Hz or faster)
•High data precision.
•
Good indication of immediate behaviors and performance just prior to the accident.
15 |
File Number |
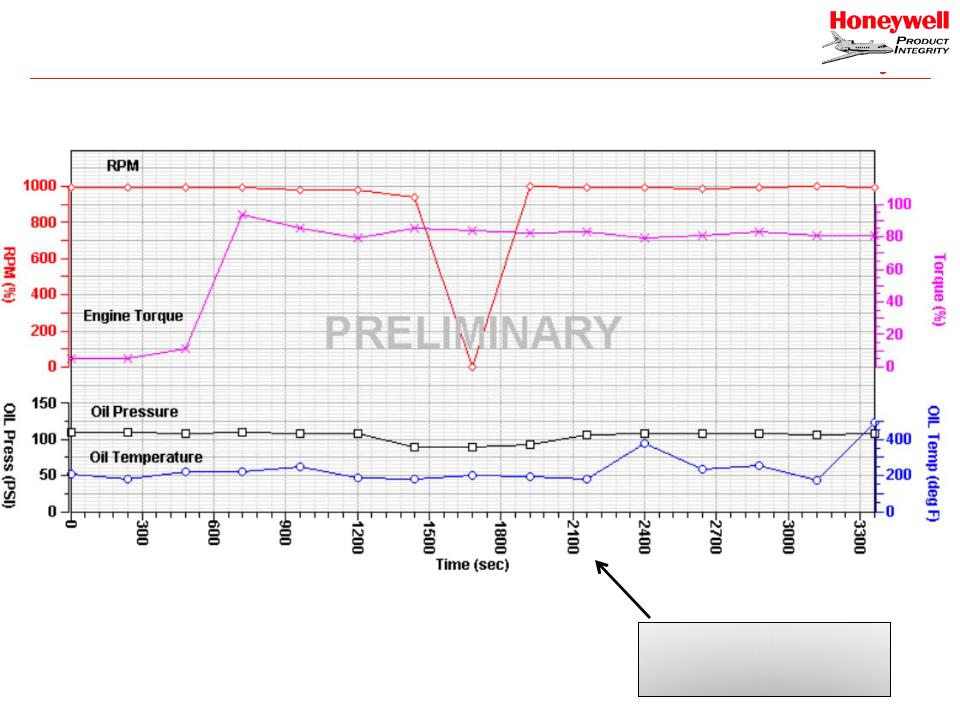
Example of Low Fidelity Data
Data points are on 4 minute increments.
16 |
File Number |
 Loading...
Loading...