GarrettCom MNS-6K User Manual

MAGNUM 6K FAMILY OF SWITCHES
Managed Network Software (MNS)
MNS-6K-SECURE 14.1.4 and MNS-6K 4.1.4
CLI User Guide

Preface
This guide describes how to use the Command Line Interface (CLI) for the Magnum 6K family of switches. For the Web Management Interface please refer to the Web Management Guide.
Some simple guidelines which will be useful for configuring and using the Magnum 6K family of switches -
If you need information on a specific command in the CLI, type the command name after you type the word “help” (help <command> ) or just type <command> [Enter].
If you need information on a specific feature in Web Management Interface, use the online help provided in the interface.
If you need further information or data sheets on GarrettCom Magnum 6K family of switches, refer to the GarrettCom web links at:
http://www.garrettcom.com/managed_switches.htm (except MP62 switch shown on the page)
GarrettCom Inc.
47823 Westinghouse Drive
Fremont, CA 94539-7437
Phone (510) 438-9071• Fax (510) 438-9072 Email – Tech support – support@garrettcom.com Email – Sales – sales@garrettcom.com
WWW – http://www.garrettcom.com/
i

Trademarks
GarrettCom Inc. reserves the right to change specifications, performance characteristics and/or model offerings without notice. GarrettCom, Magnum, S-Ring, Link-Loss-Learn, Converter Switch, Convenient Switch and Personal Switch are trademarks and Personal Hub is a registered trademark of GarrettCom, Inc.
NEBS is a registered trademark of Telcordia Technologies.
UL is a registered trademark of Underwriters Laboratories.
Ethernet is a trademark of Xerox Corporation.
Copyright © 2007 GarrettCom, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from GarrettCom, Inc.
Printed in the United States of America.
Part #: 84-00131
PK-062808
ii

Table of Contents
1 – Conventions Followed............................................................... |
19 |
Flow of the User Guide .......................................................... |
21 |
2 – Getting Started ............................................................................ |
23 |
Before starting .......................................................................... |
23 |
MNS-6K Software Updates ....................................................... |
24 |
Console connection ................................................................. |
24 |
Console setup............................................................................ |
25 |
Console screen.......................................................................... |
25 |
Logging in for the first time ................................................... |
26 |
Setting the IP parameters........................................................ |
26 |
Privilege levels........................................................................... |
29 |
Operator Privileges...................................................................... |
30 |
Manager Privileges....................................................................... |
30 |
User management..................................................................... |
30 |
Add User....................................................................................... |
30 |
Delete User................................................................................... |
31 |
Modify Password ......................................................................... |
31 |
Modify the Privilege Level ......................................................... |
31 |
Modifying Access Privileges....................................................... |
32 |
Help............................................................................................ |
34 |
Displaying Help for an Individual Command......................... |
34 |
Viewing options for a command............................................... |
34 |
Context help................................................................................. |
35 |
Exiting........................................................................................ |
36 |
iii |
|

Upgrading to MNS-6K-SECURE......................................... |
36 |
List of commands in this chapter .......................................... |
37 |
3 – IP Address and System Information..................................... |
39 |
IP Addressing............................................................................... |
39 |
Importance of an IP address .................................................. |
39 |
DHCP and bootp ........................................................................ |
40 |
Bootp Database ........................................................................... |
40 |
Configuring Auto/DHCP/Bootp/Manual ............................. |
41 |
Using Telnet ................................................................................. |
42 |
Using SSH..................................................................................... |
44 |
Domain Name System (DNS) ............................................... |
48 |
Setting serial port parameters ................................................. |
50 |
System parameters.................................................................... |
50 |
Date and time............................................................................ |
52 |
Network time (SNTP Client) ................................................. |
53 |
Network time (SNTP Server)................................................. |
54 |
Saving and loading configuration .......................................... |
54 |
Config files.................................................................................... |
58 |
Script files ..................................................................................... |
60 |
Displaying configuration......................................................... |
62 |
Displaying or hiding passwords ............................................. |
64 |
Erasing configuration .............................................................. |
65 |
Displaying Serial Number....................................................... |
66 |
List of commands in this chapter .......................................... |
67 |
Other commands ..................................................................... |
70 |
4 – IPv6 ................................................................................. |
72 |
Assumptions................................................................................. |
72 |
Introduction to IPv6................................................................ |
72 |
What’s changed in IPV6?........................................................ |
73 |
IPv6 Addressing ....................................................................... |
73 |
iv |
|

Configuring IPv6...................................................................... |
74 |
List of commands in this chapter .......................................... |
75 |
5 – DHCP Server .................................................................. |
77 |
Modes of Operation ................................................................ |
78 |
Technical Details ...................................................................... |
79 |
DHCP Discovery ..................................................................... |
79 |
DHCP Offers ........................................................................... |
80 |
DHCP Request......................................................................... |
80 |
DHCP Acknowledgement...................................................... |
80 |
DHCP Information ................................................................. |
81 |
DHCP Release.......................................................................... |
81 |
Client Configuration ................................................................ |
81 |
MNS-6K-SECURE Implementation .................................... |
81 |
List of commands in this chapter .......................................... |
83 |
6 – SNTP Server ................................................................... |
84 |
SNTP - prerequisites................................................................... |
84 |
Background ............................................................................... |
84 |
Stratum clocks........................................................................... |
85 |
MNS-6K-SECURE Implementation .................................... |
87 |
List of commands in this chapter .......................................... |
88 |
7 – Access Considerations .................................................... |
89 |
Securing access............................................................................. |
89 |
Passwords .................................................................................. |
89 |
Port Security.............................................................................. |
90 |
Network security.......................................................................... |
90 |
Configuring Port Security........................................................... |
90 |
Syslog and Logs ........................................................................ |
96 |
Authorized managers............................................................. |
102 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
103 |
v |
|

8 – Access Using RADIUS ................................................. |
106 |
RADIUS ..................................................................................... |
106 |
802.1x ....................................................................................... |
106 |
Configuring 802.1x................................................................. |
109 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
114 |
9 – Access Using TACACS+ .............................................. |
116 |
TACACS – flavors and history................................................ |
116 |
TACACS+ Flow..................................................................... |
117 |
TACACS+ Packet.................................................................. |
118 |
Configuring TACACS+ ........................................................ |
118 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
120 |
10 – Port Mirroring and Setup ............................................ |
122 |
Port monitoring and mirroring................................................ |
122 |
Port mirroring......................................................................... |
122 |
Port setup ................................................................................ |
123 |
Speed settings............................................................................. |
124 |
Flow Control .............................................................................. |
125 |
Back Pressure ............................................................................. |
126 |
Broadcast Storms....................................................................... |
128 |
Preventing broadcast storms ................................................ |
129 |
Port Rate limiting for broadcast traffic............................... |
130 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
130 |
11 – VLAN .......................................................................... |
132 |
Why VLANs?............................................................................. |
132 |
Creating VLANs..................................................................... |
134 |
Private VLANs ....................................................................... |
135 |
Using VLANs ......................................................................... |
136 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
145 |
12 – Spanning Tree Protocol (STP).................................... |
147 |
STP features and operation...................................................... |
147 |
vi |
|

Using STP................................................................................ |
148 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
158 |
13 – Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) ...................... |
159 |
RSTP concepts........................................................................... |
159 |
Transition from STP to RSTP ............................................. |
160 |
Configuring RSTP.................................................................. |
161 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
172 |
14 – S-Ring™ and Link-Loss-Learn™ (LLL).................... |
174 |
S-Ring and LLL concepts......................................................... |
175 |
Comparing resiliency methods............................................. |
176 |
RSTP/STP Operation without S-Ring ............................... |
177 |
RSTP/STP Operation with S-Ring ..................................... |
179 |
LLL with S-Ring..................................................................... |
181 |
Ring learn features.................................................................. |
181 |
Configuring S-Ring ................................................................ |
181 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
185 |
15 – Dual-Homing.............................................................. |
187 |
Dual-Homing concepts ............................................................ |
187 |
Dual-Homing Modes............................................................. |
190 |
Configuring Dual-Homing ................................................... |
190 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
192 |
16 – Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) ............... |
193 |
LACP concepts.......................................................................... |
193 |
LACP Configuration.............................................................. |
194 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
204 |
17 – Quality of Service ........................................................ |
205 |
QoS concepts ............................................................................. |
205 |
DiffServ and QoS................................................................... |
206 |
IP Precedence ......................................................................... |
207 |
vii |
|

Configuring QoS .................................................................... |
208 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
213 |
18 – IGMP........................................................................... |
214 |
IGMP concepts.......................................................................... |
214 |
IGMP-L2................................................................................. |
218 |
Configuring IGMP................................................................. |
221 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
228 |
19 – GVRP........................................................................... |
230 |
GVRP concepts ......................................................................... |
230 |
GVRP Operations.................................................................. |
231 |
Configuring GVRP ................................................................ |
235 |
GVRP Operations Notes...................................................... |
237 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
238 |
20 – SNMP.......................................................................... |
239 |
SNMP concepts ......................................................................... |
239 |
Traps......................................................................................... |
241 |
Standards ................................................................................. |
241 |
Configuring SNMP ................................................................ |
242 |
Configuring RMON .............................................................. |
251 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
252 |
21 – Miscellaneous Commands .......................................... |
256 |
Alarm Relays ........................................................................... |
256 |
Email ........................................................................................ |
260 |
Serial Connectivity ................................................................. |
265 |
Banner Message...................................................................... |
266 |
Miscellaneous commands ..................................................... |
267 |
Prompt ..................................................................................... |
269 |
Ping........................................................................................... |
270 |
FTP modes.............................................................................. |
271 |
viii |
|

System Events......................................................................... |
272 |
MAC Address Table .............................................................. |
277 |
List of commands in this chapter ........................................ |
278 |
APPENDIX 1 - Command listing by Chapter .................. |
281 |
Chapter 2 – Getting Started.................................................. |
281 |
Chapter 3 – IP Address and System Information............. |
282 |
Chapter 4 – IPv6 .................................................................... |
286 |
Chapter 5 – DHCP Server.................................................... |
286 |
Chapter 6 – SNTP Server ..................................................... |
287 |
Chapter 7 – Access Considerations..................................... |
287 |
Chapter 8 – Access Using Radius........................................ |
289 |
Chapter 9 – Access using TACACS+................................. |
290 |
Chapter 10 – Port mirroring and setup .............................. |
291 |
Chapter 11 - VLAN ............................................................... |
291 |
Chapter 12 – Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)..................... |
292 |
Chapter 13 – Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol..................... |
293 |
Chapter 14 – S-Ring and Link-Loss-Learn ........................ |
294 |
Chapter 15 – Dual-Homing.................................................. |
295 |
Chapter 16 – Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)295 |
|
Chapter 17 – Quality of Service........................................... |
296 |
Chapter 18 - IGMP................................................................ |
296 |
Chapter 19 - GVRP ............................................................... |
297 |
Chapter 20 – SNMP .............................................................. |
298 |
Chapter 21 – Miscellaneous Commands ............................ |
300 |
APPENDIX 2 - Commands sorted alphabetically............ |
303 |
APPENDIX 3 - Daylight Savings ...................................... |
326 |
Daylight Savings Time........................................................... |
326 |
APPENDIX 4 – Browser Certificates................................. |
328 |
Certificates............................................................................... |
328 |
ix |
|

Using Mozilla Firefox (ver. 3.x) ........................................... |
329 |
Using Internet Explorer (ver 7.x) ........................................ |
333 |
Using Other Browsers........................................................... |
334 |
APPENDIX 5 – Updating MNS-6K Software.................... |
335 |
1. Getting Started ...................................................... |
336 |
Selecting the proper version ..................................... |
337 |
Downloading the MNS-6K software ...................... |
337 |
Next steps .................................................................... |
341 |
2. Preparing to load the software.............................. |
342 |
Accessing the switch .................................................. |
342 |
Serial Connection......................................................... |
342 |
Network Access ........................................................... |
343 |
Saving the Configuration........................................... |
343 |
Serial Connection......................................................... |
344 |
Network Access ........................................................... |
346 |
Next steps .................................................................... |
347 |
3. Loading the MNS-6K software............................. |
348 |
Before loading the MNS-6K software .................... |
348 |
Accessing the switch .................................................. |
348 |
Serial Connection......................................................... |
349 |
Network Access ........................................................... |
350 |
Next steps .................................................................... |
351 |
4. (Optional Step) Restoring the configuration........ |
352 |
Accessing the switch .................................................. |
352 |
Reloading the configuration...................................... |
352 |
Updating boot code over the network.................... |
353 |
Index................................................................................... |
355 |
x

List of Figures |
|
FIGURE 1 - HyperTerminal screen showing the serial settings................................................................. |
25 |
FIGURE 2 - Prompt indicating the switch model number as well as mode of operation – note the |
|
commands to switch between the levels is not shown here.............................................................. |
26 |
FIGURE 3 – As the switch tries to determine its mode of operation and its IP address, it may |
|
assign and release the IP address a number of times. A continuous ping to the switch will |
|
show an intermittent response..................................................................................................... |
27 |
FIGURE 4 - Setting IP address on the switch ......................................................................................... |
28 |
FIGURE 5 - Rebooting the switch........................................................................................................... |
28 |
FIGURE 6 - Viewing the basic setup parameters. You can use ‘show setup’ or ‘show sysconfig’ to |
|
view setup parameters ................................................................................................................ |
29 |
FIGURE 7 - Switching users and privilege levels. Note the prompt changes with the new privilege |
|
level. ......................................................................................................................................... |
30 |
FIGURE 8 - Adding a user with Manager level privilege........................................................................ |
31 |
FIGURE 9 - Deleting a user.................................................................................................................. |
31 |
FIGURE 10 - Changing the password for a specific user ......................................................................... |
31 |
FIGURE 11 - Changing the privilege levels for a user.............................................................................. |
32 |
FIGURE 12 – Creating user access privileges .......................................................................................... |
33 |
FIGURE 13 – Creating user access privileges .......................................................................................... |
33 |
FIGURE 14 - Help command .............................................................................................................. |
34 |
FIGURE 15 - Help for a specific command ........................................................................................... |
34 |
FIGURE 16 - Options for the ‘show’ command ...................................................................................... |
35 |
FIGURE 17 - Listing commands available (at the operator level)............................................................ |
35 |
FIGURE 18 - Listing commands starting with a specific character .......................................................... |
35 |
FIGURE 19 - Listing commands options – note the command was not completed and the TAB |
|
key completed the command. ...................................................................................................... |
36 |
FIGURE 20 – logout command.............................................................................................................. |
36 |
FIGURE 21 – Upgrading to MNS-6K-SECURE............................................................................... |
37 |
FIGURE 22 - Checking the IP settings.................................................................................................. |
40 |
FIGURE 23 - Changing the boot mode of the switch............................................................................... |
42 |
xi |
|

FIGURE 24 - Changing telnet access – note in this case, the enable command was repeated without |
|
any effect to the switch................................................................................................................ |
42 |
FIGURE 25 - Reviewing the console parameters – note telnet is enabled.................................................. |
43 |
FIGURE 26 - Example of a telnet session ............................................................................................. |
43 |
FIGURE 27 – managing and viewing multiple telnet sessions .................................................................. |
44 |
FIGURE 28 – setting up ssh – since telnet sends the information in clear text, make sure that |
|
telnet is disabled to secure the switch. Do not telnet to the switch to disable telnet. Preferred |
|
method is to do that via the console or using SWM. The client access is not shown here. |
|
Commonly an application like PUTTY is used to access the switch via ssh. Use the show |
|
console command to verify telnet is turned off............................................................................... |
48 |
FIGURE 29 – Use of DNS .................................................................................................................. |
49 |
FIGURE 30 - Querying the serial port settings....................................................................................... |
50 |
FIGURE 31 - System parameters using the show setup command. Most parameters here cannot be |
|
changed ..................................................................................................................................... |
51 |
FIGURE 32 - System parameters using the show sysconfig command. Most parameters here can be |
|
changed. .................................................................................................................................... |
51 |
FIGURE 33 - Setting the system name, system location and system contact information ........................... |
52 |
FIGURE 34 - Setting the system date, time and time zone...................................................................... |
52 |
FIGURE 35 - Setting the system daylight saving time............................................................................. |
53 |
FIGURE 36 - Setting up SNTP services ............................................................................................... |
54 |
FIGURE 37 - Saving the configuration on a tftp server........................................................................... |
55 |
FIGURE 38 – Based on the sftp, ftp, tftp or xmodem commands – the MNS-6K based switch can |
|
upload or download different types of files and images .Other files such as log files, hosts file |
|
can also be saved or loaded onto a switch .................................................................................... |
57 |
FIGURE 39 – commands to save the configuration using ftp. Similar options will be specified using |
|
tftp etc. When using the ftp command, use the host command discussed later in this section |
|
to define the ftp server ................................................................................................................ |
58 |
FIGURE 40 – Contents of the config file................................................................................................. |
59 |
FIGURE 41 – Example of Script file. Note all the commands are CLI commands. This script |
|
provides insights into the configuration of Magnum MNS-6K settings. GarrettCom |
|
recommends that modifications of this file and the commands should be verified by the User |
|
in a test environment prior to use in a "live" production network................................................. |
61 |
FIGURE 42 – Creating host entries on MNS-6K.................................................................................. |
62 |
FIGURE 43 – Enabling or disabling the pagination............................................................................... |
62 |
FIGURE 44 – ‘show config’ command output................................................................................... |
63 |
FIGURE 45 – displaying specific modules using the ‘show config’ command....................................... |
64 |
xii |
|

FIGURE 46 – displaying configuration for different modules. Note – multiple modules can be |
|
specified on the command line..................................................................................................... |
64 |
FIGURE 47 – Hide or display system passwords .................................................................................... |
65 |
FIGURE 48 – Erasing configuration without erasing the IP address ....................................................... |
66 |
FIGURE 49 – Display the serial number, factory code and other relevant setup information ..................... |
66 |
FIGURE 50 – Configuring IPv6............................................................................................................ |
75 |
FIGURE 51 – Setting up DHCP Server on MNS-6K-SECURE........................................................ |
83 |
FIGURE 52 – Different Stratum NTP servers....................................................................................... |
86 |
FIGURE 53 – Using the SNTP commands........................................................................................... |
87 |
FIGURE 54 – Changing password for a given account ............................................................................ |
89 |
FIGURE 55 – Port security configuration mode ...................................................................................... |
90 |
FIGURE 56 – Port security configuration mode ...................................................................................... |
91 |
FIGURE 57 – Port security – allowing specific MAC addresses on a specified port. (No spaces |
|
between specified MAC addresses) ............................................................................................. |
92 |
FIGURE 58 – Port security - the port learns the MAC addresses. Note – a maximum of 200 |
|
MAC addresses can be learnt per port and a maximum of 500 per switch. Also, the |
|
‘action’ on the port must be set to none before the port ‘learns’ the MAC address |
|
information. .............................................................................................................................. |
92 |
FIGURE 59 – Enabling and disabling port security ............................................................................... |
92 |
FIGURE 60 – Viewing port security settings on a switch. On port 9, learning is enabled. This port |
|
has 6 stations connected to it with the MAC addresses as shown. Other ports have |
|
learning disabled and the MAC addresses are not configured on those ports ................................ |
93 |
FIGURE 61 – Enabling learning on a port. Note – after the learning is enabled, the port security |
|
can be queried to find the status of MAC addresses learnt. If there were machines |
|
connected to this port, the MAC address would be shown on port 11 as they are shown on |
|
port 9 ....................................................................................................................................... |
93 |
FIGURE 62 – Allowing specific MAC address on specific ports. After the MAC address is |
|
specified, the port or specific ports or a range of ports can be queried as shown .............................. |
94 |
FIGURE 63 – Removing a MAC address from port security .................................................................. |
94 |
FIGURE 64 – Setting the logging on a port ............................................................................................ |
94 |
FIGURE 65 – Steps for setting up port security on a specific port ............................................................ |
95 |
FIGURE 66 – Show log and clear log command. Note the logs are in the syslog format. The syslog |
|
commands are also displayed.................................................................................................... |
101 |
FIGURE 67 – Steps to allow deny or remove specific services ................................................................. |
103 |
FIGURE 68 – 802.1x network components......................................................................................... |
107 |
FIGURE 69 – 802.1x authentication details ....................................................................................... |
108 |
xiii |
|

FIGURE 70 – securing the network using port access ............................................................................ |
113 |
FIGURE 71 – Flow chart describing the interaction between local users and TACACS |
|
authorization .......................................................................................................................... |
117 |
FIGURE 72 – TACACS packet format............................................................................................. |
118 |
FIGURE 73 – Configuring TACACS+............................................................................................. |
120 |
FIGURE 74 – Enabling port mirroring ............................................................................................... |
123 |
FIGURE 75 – Port setup..................................................................................................................... |
124 |
FIGURE 76 – Setting up back pressure and flow control on ports.......................................................... |
128 |
FIGURE 77 – Setting up broadcast storm protection. Also shows how the threshold can be lowered |
|
for a specific port ..................................................................................................................... |
130 |
FIGURE 78 – VLAN as two separate collision domains. The top part of the figure shows two |
|
“traditional” Ethernet segments............................................................................................... |
132 |
FIGURE 79 – Ports can belong to multiple VLANs. In this figure a simplistic view is presented |
|
where some ports belong to VLANs 1, 2 and other ports belong to VLANs 2,3. Ports |
|
can belong to VLANs 1, 2 and 3. This is not shown in the figure. ......................................... |
133 |
FIGURE 80 – routing between different VLANs is performed using a router such as a Magnum |
|
DX device or a Layer 3 switch (L3-switch) ............................................................................. |
134 |
FIGURE 81 – configuring VLANs on Magnum 6K switch................................................................. |
135 |
Figure 82 – STP default values – refer to next section “Using STP” for more detailed |
|
explanation on the variables .................................................................................................... |
148 |
FIGURE 83 – Viewing STP configuration .......................................................................................... |
149 |
FIGURE 84 – STP Port status information......................................................................................... |
150 |
FIGURE 85 – Enabling STP ............................................................................................................. |
152 |
FIGURE 86 – Configuring STP parameters ........................................................................................ |
158 |
FIGURE 87 – Enabling RSTP and reviewing the RSTP variables...................................................... |
163 |
FIGURE 88 – Reviewing the RSTP port parameters............................................................................ |
164 |
Figure 89 – Path cost as defined in IEEE 802.1d (STP) and 802.1w (RSTP) ............................... |
165 |
FIGURE 90 – RSTP information from a network with multiple switches. Note the “show stp |
|
ports” command can be executed from the manager level prompt or from rstp configuration |
|
state as shown in the screen captures earlier. ............................................................................. |
166 |
FIGURE 91 – Configuring RSTP on MNS-6K.................................................................................. |
171 |
FIGURE 92 – Normal RSTP/STP operations in a series of switches. Note – this normal status |
|
is designated RING_CLOSED ............................................................................................ |
178 |
FIGURE 93 – A fault in the ring interrupts traffic. The blocking port now becomes forwarding so |
|
that traffic can reach all switches in the network Note – the mP62 as well as the ESD42 |
|
switches support LLL and can participate in S-Ring as an access switch .................................. |
179 |
xiv |
|

FIGURE 94 – More than one S-Ring pair can be selected and more than one S-Ring can be |
|
defined per switch. Note – the mP62 as well as the ES42 switches support LLL and can |
|
participate in S-Ring as an access switch .................................................................................. |
180 |
FIGURE 95 – Activating S-Ring on the switch .................................................................................... |
182 |
FIGURE 96 – S-Ring configuration commands for root switch .............................................................. |
184 |
FIGURE 97 – Link Loss Learn (LLL) setup. Setup LLL on ports connected to other switches |
|
participating in S-Ring............................................................................................................ |
185 |
FIGURE 98 – Dual-homing using ESD42 switch and Magnum 6K family of switches. In case of |
|
a connectivity break – the connection switches to the standby path or standby link ..................... |
188 |
FIGURE 99 – Dual-homing using Magnum 6K family of switches. Note the end device (video |
|
surveillance camera) can be powered using PoE options on Magnum 6K family of switches. |
|
In case of a connectivity break – the connection switches to the standby path or standby |
|
link ........................................................................................................................................ |
188 |
FIGURE 100 – Using S-Ring and dual-homing, it is possible to build networks resilient not only |
|
to a single link failure but also for one device failing on the network .......................................... |
189 |
FIGURE 101 – configuring dual-homing ............................................................................................... |
191 |
FIGURE 102 – Some valid LACP configurations................................................................................ |
195 |
FIGURE 103 – an incorrect LACP connection scheme for Magnum 6K family of switches. All |
|
LACP trunk ports must be on the same module and cannot span different modules.................. |
195 |
FIGURE 104 – In this figure, even though the connections are from one module to another, this is |
|
still not a valid configuration (for LACP using 4 ports) as the trunk group belongs to two |
|
different VLANs................................................................................................................... |
195 |
FIGURE 105 - In the figure above, there is no common VLAN between the two sets of ports, so |
|
packets from one VLAN to another cannot be forwarded. There should be at least one |
|
VLAN common between the two switches and the LACP port groups. ................................... |
196 |
FIGURE 106 – This configuration is similar to the previous configuration, except there is a |
|
common VLAN (VLAN 1) between the two sets of LACP ports. This is a valid |
|
configuration............................................................................................................................ |
197 |
FIGURE 107 – In the architecture above, using RSTP and LACP allows multiple switches to be |
|
configured together in a meshed redundant link architecture. First define the RSTP |
|
configuration on the switches. Then define the LACP ports. Then finally connect the ports |
|
together to form the meshed redundant link topology as shown above.......................................... |
197 |
FIGURE 108 – LACP, along with RSTP/STP brings redundancy to the network core or |
|
backbone. Using this reliable core with a dual-homed edge switch brings reliability and |
|
redundancy to the edge of the network....................................................................................... |
198 |
FIGURE 109 – This architecture is not recommended............................................................................ |
199 |
FIGURE 110 – Creating a reliable infrastructure using wireless bridges (between two facilities) and |
|
LACP. “A” indicates a Wi-Fi wireless Bridge or other wireless Bridges.................................. |
200 |
FIGURE 111 – Configuring LACP .................................................................................................... |
202 |
xv |
|

FIGURE 112 – The network for the ‘show lacp’ command listed below.................................................. |
203 |
FIGURE 113 – LACP information over a network ............................................................................. |
204 |
FIGURE 114 – ToS and DSCP ......................................................................................................... |
206 |
FIGURE 115 - IP Precedence ToS Field in an IP Packet Header......................................................... |
207 |
FIGURE 116 - Port weight settings and the meaning of the setting ......................................................... |
209 |
FIGURE 117 – QoS configuration and setup........................................................................................ |
213 |
FIGURE 118 – IGMP concepts – advantages of using IGMP.............................................................. |
216 |
FIGURE 119 – IGMP concepts – Isolating multicast traffic in a network............................................. |
217 |
FIGURE 120 - In a Layer 2 network, an IGMP multicast traffic goes to all the nodes. In the |
|
figure, T1, a surveillance camera, using multicast, will send the traffic to all the nodes - R1 |
|
through R6 - irrespective of whether they want to view the surveillance traffic or not. The |
|
traffic is compounded when additional cameras are added to the network. End result is that |
|
users R1 through R6 see the network as heavily loaded and simple day to day operations |
|
may appear sluggish................................................................................................................. |
219 |
FIGURE 121 - Using IGMP-L2 on Magnum 6K family of switches, a Layer 2 network can |
|
minimize multicast traffic as shown above. Each switch has the IGMPL2 turned on. |
|
Each switch can exchange the IGMP query message and respond properly. R4 wants to |
|
view surveillance traffic from T1. As shown by (1), a join request is sent by R4. Once the |
|
join report information is exchanged, only R4 receives the video surveillance traffic, as |
|
shown by (2). No other device on the network gets the video surveillance traffic unless they |
|
issue a join request as well. ...................................................................................................... |
220 |
FIGURE 122 – Enabling IGMP and query the status of IGMP......................................................... |
222 |
FIGURE 123 – Displaying IGMP groups ........................................................................................... |
223 |
FIGURE 124 – Configuring IGMP..................................................................................................... |
226 |
FIGURE 125 – Adding broadcast groups using the group command...................................................... |
227 |
FIGURE 126 - Setting IGMP-L2 ....................................................................................................... |
228 |
FIGURE 127 – GVRP operation – see description below..................................................................... |
231 |
FIGURE 128 – VLAN Assignment in GVRP enabled switches. Non GVRP enabled switches |
|
can impact VLAN settings on other GVRP enabled switches................................................. |
232 |
FIGURE 129 – Port settings for GVRP operations ............................................................................. |
233 |
FIGURE 130 – Command to check for dynamically assigned VLANs ................................................ |
234 |
FIGURE 131 – Converting a dynamic VLAN to a static VLAN ..................................................... |
234 |
FIGURE 132 – GVRP options........................................................................................................... |
235 |
FIGURE 133 – GVRP configuration example .................................................................................... |
237 |
FIGURE 134 – Configuring SNMP – most of the command here are SNMP v3 commands ................ |
251 |
FIGURE 135 – Configuring RMON groups........................................................................................ |
252 |
xvi |
|

FIGURE 136 – Predefined conditions for the relay ................................................................................ |
257 |
FIGURE 137 – Setting up the external electrical relay and alerts .......................................................... |
260 |
FIGURE 138 – setting SMTP to receive SNMP trap information via email......................................... |
265 |
FIGURE 139 – Optimizing serial connection (shown for Hyper Terminal on Windows XP). The |
|
highlighted fields are the ones to change as described .................................................................. |
265 |
FIGURE 140 – setting up a banner message ......................................................................................... |
267 |
FIGURE 141 – History commands....................................................................................................... |
269 |
FIGURE 142 – Setting custom prompts................................................................................................ |
270 |
FIGURE 143 – Using the ping command ............................................................................................. |
271 |
FIGURE 144 - Setting the FTP mode .................................................................................................. |
271 |
FIGURE 145 – Event log shown on the screen...................................................................................... |
273 |
FIGURE 146 – Using exportlog to export the event log information ...................................................... |
274 |
FIGURE 147 – Listing of severity - sorted by subsystem and severity ..................................................... |
277 |
FIGURE 148 – Display of the internal switching decision table............................................................. |
278 |
FIGURE 149 – On finding a mismatch between the certificate and the accesses site, Mozilla |
|
Firefox pops the window. Note – the site was accessed using the IP address. Typically, sites |
|
accessed by their IP address will trigger this mismatch ............................................................... |
329 |
FIGURE 150 – Mozilla Firefox tries to warn the user again about the dangers of sites with |
|
improper certificates ................................................................................................................. |
330 |
FIGURE 151 – Firefox forces you to get the certificate before it lets you access the site............................. |
331 |
FIGURE 152 – Here, you can view the certificate, permanently make an exception and confirm the |
|
exception. The locations to do those are identified in this figure.................................................. |
332 |
FIGURE 153 – Self signed certificate from GarrettCom Inc for MNS-6K............................................. |
333 |
FIGURE 154 – Using IE 7 ................................................................................................................ |
334 |
FIGURE 155 – Accessing the GarrettCom site for download. ............................................................... |
339 |
FIGURE 156 – Select the proper version to use after successful login ...................................................... |
340 |
FIGURE 157 – Navigate to MNS-6K folder to download the latest MNS-6K software and the |
|
release notes............................................................................................................................. |
340 |
FIGURE 158 – Use the copy command to copy the files to the proper location ........................................ |
341 |
FIGURE 159 - HyperTerminal screen showing the serial settings ......................................................... |
343 |
FIGURE 160 – Using telnet command to connect to a Magnum 6K switch with IP address |
|
192.168.10.11 ...................................................................................................................... |
343 |
FIGURE 161 – Example of saveconf command using serial interface..................................................... |
344 |
FIGURE 162 – Invoke the “Receive File” to start the Xmodem transfer program. In the figure |
|
above the Windows XP based HyperTerminal screen is shown ................................................. |
345 |
xvii

FIGURE 163 – Make sure to select the Xmodem protocol and the proper directory where the |
|
configuration is saved. Click on Receive. This starts the file transfer. ......................................... |
345 |
FIGURE 164 – Status window for Xmodem (using HyperTerminal under Windows XP) .................... |
346 |
FIGURE 165 – Message which shows the completion of the file transfer (from ‘saveconf’ command) ........ |
346 |
FIGURE 166 – Example of saveconf command for tftp......................................................................... |
346 |
FIGURE 167 – Upgrade using serial connection ................................................................................... |
349 |
FIGURE 168 – File upload status window under Xmodem (using HyperTerminal under Windows |
|
XP)........................................................................................................................................ |
349 |
FIGURE 169 – upgrading the switch using the serial interface ............................................................... |
350 |
FIGURE 170 – Dialog for upgrading the image using tftp..................................................................... |
351 |
FIGURE 171 – Updating the boot code over the network using the upgrade command. Make sure |
|
to reboot the switch after the boot loader upgrade is completed.................................................... |
353 |
xviii
1Chapter
1 – Conventions Followed
Conventions followed in the manual…
To best use this document, please review some of the conventions followed in the manual, including screen captures, interactions and commands with the switch, etc.
Box shows interaction with the switch command line or screen captures from the switch or computer for clarity
Commands typed by a user will be shown in a different color and this font
Switch prompt – shown in Bold font, with a “# or >” at the end. For the document we will use Magnum6K25# as the default prompt.
Syntax rules
Optional entries are shown in [square brackets]
Parameter values within are shown in < pointed brackets >
Optional parameter values are shown again in [square brackets]
Thus
Syntax command [parameter1=<value1>[, parameter2=<value2>]] parameter3=<value3|value4>
In the example above:
Parameter 1 and Parameter 2 are optional values
Parameter 2 can be used optionally only if Parameter 1 is specified Parameter 3 is mandatory.
Parameter 1 has value1 = IP address
Parameter 2 has value2 = string
Parameter 3 has value3 or value4
19

M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
j |
Related Topics |
Related topics show that GarrettCom strongly recommends reading |
|
about those topics. You may choose to skip those if you already have |
|
|
prior detailed knowledge on those subjects. |
|
Tool box – Necessary software and hardware components needed (or recommended to have) as a prerequisite. These include serial ports on a computer, serial cables, TFTP or FTP software, serial terminal emulation software etc.
Caution or take notice – Things to watch out for in case of problems or potential problems. This is also used to draw attention to a special issue, capability or fact.
MNS-6K-SECURE – The functionality described in the related section is available in MNS-6K-SECURE version only. To upgrade from MNS-6K to MNS-6K-SECURE, please contact the GarrettCom Sales or support staff. MNS-6K-SECURE has all the commands MNS-6K has and more. The additional commands in the manual will be shown by the “lock” icon shown here. MNS-6K-SECURE is a
licensed feature of GarrettCom Inc. Each switch with MNS-6K is upgraded to MNS-6K- SECURE with the license key provided for that switch from GarrettCom Inc.
Terminology – Whenever the word PC is used it implies a UNIX, Linux, Windows or any other operating system based work station, computer, personal computer, laptop, notebook or any other computing device. Most of the manual uses Windows-XP based examples. While effort has been made to indicate other Operating System interactions, it is best to use a Windows-XP based machine when in doubt.
Supported MNS-6K Version – The documentation reflects features of MNS-6K version 3.4 or later. If your switch is not at the current version, GarrettCom Inc. recommends upgrade to the latest version. Please refer to the GarrettCom Web site for information on upgrading the MNS-6K software on Magnum 6K family of switches.
Product Family – this manual is for all the Magnum 6K family of switches.
Finally, at the end of each chapter, is a list of the commands covered in the chapter as well as a brief synopsis of what they do.
20

M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
Flow of the User Guide
The manual is designed to guide the user through a sequence of events.
Chapter 1 – this chapter
Chapter 2 is the basic setup as required by the Magnum 6K family of switches. After completing Chapter 2, the configuration can be done using the web interface. Chapter 2 is perhaps the most critical chapter in what needs to be done by the network administrator once the switch is received.
Chapter 3 focuses on operational issues of the switch. This includes time synchronization using the command line or using a time server on the network.
Chapter 4 through Chapter 8 focuses on security and access consideration. Bad passwords trump any security setup, so setup the manager passwords carefully as described in Chapter 2. Chapter 4 describes how to setup port access using MAC address security.
Chapter 5 describes the functionality of a DHCP server and how the switch can be used as a DHCP server
Chapter 6 discusses time synchronization issues and SNTP services
Chapter 7 discusses access consideration and how the access can be secured.
Chapter 8 describes how a RADIUS server can be used for authentication and access.
Chapter 9 essentially is similar to Chapter 7, and talks about using a TACACS+ server for authenticating access to devices on the network.
Chapter 10 talks about port mirroring and preventing broadcast storms. Port mirroring is necessary in a network to reflect traffic from one port onto another port so that the traffic can be captured for protocol analysis or intrusion analysis.
Chapter 11 deals with VLANs. VLANs provide security as well as traffic separation. This chapter shows how VLANs can be setup and managed.
At this stage the network and the switch are secured. It is now critical to make the network more reliable. The User Guide switches gears and talks about STP, RSTP and S- Ring technologies which can be used for making the network reliable. These technologies allow resiliency in a network. Chapters 12 through Chapter 14 discuss some resiliency techniques.
21

M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
Chapter 12 shows how STP can be setup and used. Today, RSTP is preferred over STP.
Chapter 13 shows how RSTP is setup and used as well as how RSTP can be used with legacy devices which support STP only.
Chapter 14 focuses on S-Ring™ and setup of S-Ring.
Chapter 15 talks about dual homing and how dual homing can be used to bring resiliency to edge devices.
Chapter 16 describes LACP and how LACP can be used to increase the throughput using 10/100 Mbps ports or in situations where resiliency is needed between switches (trunks).
Once the network is made resilient, the network manager may want to setup prioritization of traffic.
Chapter 17 focuses on Quality of Service (QoS) and other prioritization issues.
Chapters 18 and 19 focus on advanced topics such as IGMP and GVRP.
Chapter 18 focuses on IGMP.
Chapter 19 focuses on GVRP.
Chapter 20 shows how the SNMP parameters can be setup for managing the switch with network management software such as Castle Rock SNMPc™
Chapter 21 includes miscellaneous commands to improve the overall ease of use and other diagnostic information.
22

M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E |
2 |
|
|
|
Chapter |
|
|
2 – Getting Started
First few simple steps …
This section explains how the GarrettCom Magnum 6K family of switches can be setup using the console port on the switch. Some of the functionality includes setting up the IP address of the switch, securing the switch with a user name and password, setting up VLAN’s and more.
Before starting
Before you start, it is recommended to acquire the hardware listed below and be ready with the items listed.
 For initial configuration through the serial/console port
For initial configuration through the serial/console port
1)A female-female null modem cable. This cable is available from GarrettCom Inc. as well as from LAN store (http://www.lanstore.com)
2)Serial port – if your PC does not have a serial port, you may want to invest in a USB to serial converter. This is again available from LAN store or from GarrettCom Inc. Alternately a USB to serial cable can also be used. This cable is also available from LAN store or GarrettCom Inc.
3)A PC (or a workstation/computer) with a terminal emulation program such as HyperTerminal (included with Windows) or Teraterm-pro, minicom or other equivalent software. (Make sure the software supports Xmodem protocol, as you may need this in the future to update the MNS-6K software)
4)Enough disk space to store and retrieve the configuration files as well as copy software files from GarrettCom. We recommend at least 15MB of disk space for this purpose
5)Decide on a manager level account name and password for access security
6)IP address, netmask, default gateway for the switch being configured
As a default, the switch has no IP (Internet Protocol) address and subnet mask. For first time use, the IP address has to be assigned. This can only be done by using the console interface provided.
The same procedure can also be used for other configuration changes or updates – e.g. changing the IP address, VLAN assignments and more. Once the IP address is assigned
23

M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
and a PC is networked to the switch, the switch’s command line interface (CLI) can be accessed via telnet. To manage the switch through in-band (networked) access (e.g. telnet, or Web Browser Interface), you should configure the switch with an IP address and subnet mask compatible with your network. You should also change the manager password to control access privileges from the console.
Many other features such as optimizing the switch’s performance, traffic engineering and traffic prioritizing, VLAN configuration, and improving network security can be configured through the switch’s console interface as well as in-band (networked) access, once the IP address is setup. Besides the IP address, setting up the SNMP parameters allows configuration and monitoring through an SNMP network management station running a network management program (e.g. SNMPc from Castle Rock – available from GarrettCom Inc.)
j |
MNS-6K Software Updates |
Magnum switches already have the necessary software loaded on them. If a |
software upgrade is needed or the MNS-6K software needs to be updated to the current version, please refer to the GarrettCom web site for information on updating the MNS-6K software. The documentation on how to update the MNS-6K is
included as an Appendix in this manual.
The Login prompt is shown when the connection to the GarrettCom Magnum 6K Switch is successful and the switch is ready for the configuration commands. Should you get a boot prompt, please contact GarrettCom technical support.
The IP address of the switch is assigned automatically from a DHCP server or a BootP server. If these servers do not exist, the switch will be assigned an IP address which was previously configured or a static IP address of 192.168.1.2 with a netmask of 255.255.255.0 (if that address is not in use). It is recommended that the user uses Secure Web Management (SWM) capabilities built into MNS-6K to setup and manage the switch. Please refer to the SWM user guide for more information.
Console connection
The connection to the console is accessed through the DB-9 RS232 connector on the switch marked on the Magnum 6K family of switches as a console port. This interface provides access to the commands the switch can interpret and is called the Command Line Interface (or CLI). This interface can be accessed by attaching a VT100 compatible terminal or a PC running a terminal emulation program to the console port on the Magnum 6K family of switches.
USB to serial adapters are also available for laptops or computers that do not native serial ports but have access to USB ports.
The interface through the console or the Console Management Interface (or CMI) enables you to reconfigure the switch and to monitor switch status and performance.
24
M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
 Once the switch is configured with an IP address, the Command Line Interface (or CLI) is also accessible using telnet as well as the serial port. Access to the switch can be either through the console interface or remotely over the network.
Once the switch is configured with an IP address, the Command Line Interface (or CLI) is also accessible using telnet as well as the serial port. Access to the switch can be either through the console interface or remotely over the network.
The Command Line Interface (CLI) enables local or remote unit installation and maintenance. The Magnum 6K family of switches provides a set of system commands which allow effective monitoring, configuration and debugging of the devices on the network.
Console setup
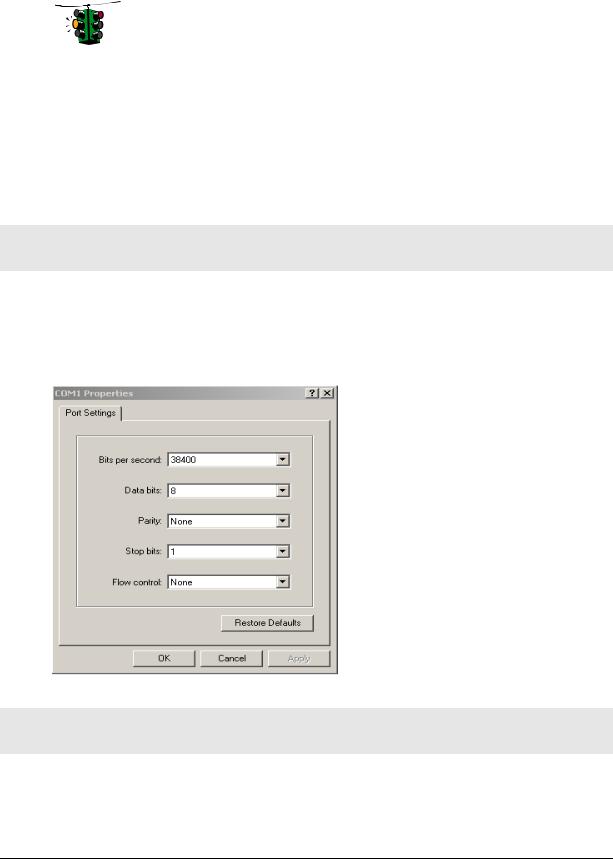
Connect the console port on the switch to the serial port on the computer using the serial cable listed above. The settings for the HyperTerminal software emulating a VT100 are shown in Figure 1 below. Make sure the serial parameters are set as shown (or bps = 38400, data bits=8, parity=none, stop bits=1, flow control=none).
FIGURE 1 - HyperTerminal screen showing the serial settings
Console screen
Once the console cable is connected to the PC and the software configured, MNS-6K legal disclaimers and other text scrolls by on the screen.
25

M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
The switch has three modes of operation – Operator (least privilege), Manager and Configuration. The prompts for the switches change as the switch changes modes from Operator to Manager to Configuration. The prompts are shown in Figure 2 below, with a brief explanation of what the different prompts indicate.
Magnum6K> |
Operator Level – for running operations queries |
Magnum6K# |
Manager Level – for setting and reviewing commands |
Magnum6K## |
Configuration Level – for changing the switch parameter values |
FIGURE 2 - Prompt indicating the switch model number as well as mode of operation – note the commands to switch between the levels is not shown here.
The prompt can be changed by the user. See the Chapter on Miscellaneous Commands, sub section Prompt for more details. This manual was documented on a Magnum 6K25 switch, and for clarity, the prompt shown in the manual will be Magnum6K25
jFor additional information on default users, user levels and more, see User Management in this guide.
Logging in for the first time
For the first time, use the default user name and passwords assigned by GarrettCom for the Magnum 6K family of switches. They are:
Username – manager |
Password – manager |
Username – operator |
Password – operator |
We recommend you login as manager for the first time to set up the IP address as well as change user passwords or create new users.
Setting the IP parameters
To setup the switch, the IP address and other relevant TCP/IP parameters have to be specified. A new GarrettCom Magnum switch looks for a DHCP or a BootP server. If a DHCP or a BootP server is present, the switch will be assigned an IP address from those servers. Failing to find these servers, the IP address is automatically assigned to 192.168.1.2 with a netmask of 255.255.255.0.
26
M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
Should a situation arise when there are multiple new switches powered up at the same time, there could be a situation of duplicate IP addresses. In this situation, only one Magnum switch will be assigned the IP address of 192.168.1.2 and netmask of 255.255.255.0. The other switches will not be assigned an IP address till the static IP address of 192.168.1.2 is freed up or reassigned.
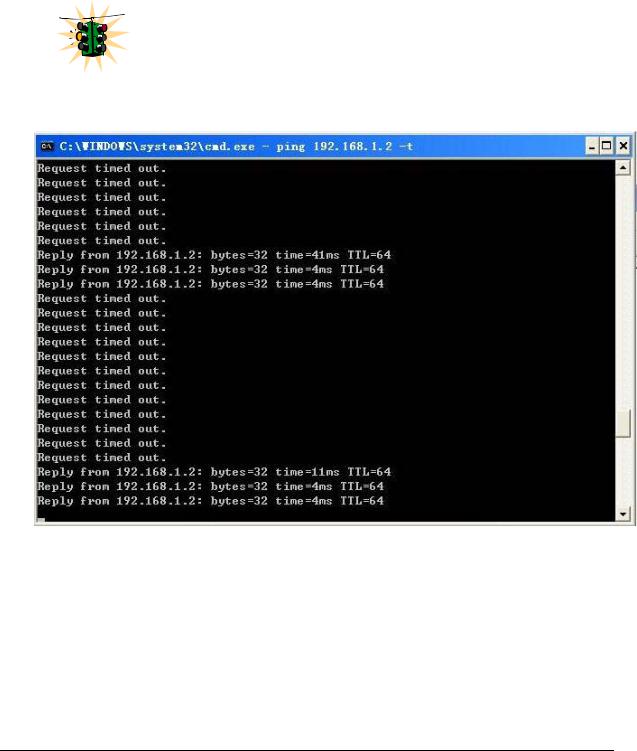
This situation may not be prevalent in all cases. As the switch tries to
determine the mode of operation and its IP address it may assign and
release the IP address a number of times. A continuous ping to the switch will show an intermittent response as this happens. This is normal behavior and is shown below. Once the switch assigns itself an IP address
the intermittent ping issue is no longer prevalent.
FIGURE 3 – As the switch tries to determine its mode of operation and its IP address, it may assign and release the IP address a number of times. A continuous ping to the switch will show an intermittent response
To change the IP address, please ensure that the IP address to be assigned to the switch is known or contact your system/network administrator to get the IP address information. Follow the steps listed below to configure the IP address manually.
•Ensure the power is off
•Follow the steps described above for connecting the console cable and setting the console software
27
M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
•Power on the switch
•Once the login prompt appears, login as manager using default password (manager)
•Configure the IP address, network mask and default gateway as per the IP addressing scheme for your network
•Set the Manager Password (recommended–refer to next section)
•Save the settings (without saving, the changes made will be lost)
•Power off the switch (or a software reboot as discussed below)
•Power on the switch – login with the new login name and password
•From the PC (or from the switch) ping the IP address specified for the switch to ensure connectivity
•From the switch ping the default gateway specified (ensure you are connected to the network to check for connectivity) to ensure network connectivity
Syntax ipconfig [ip=<ip-address>] [mask=<subnet-mask>] [dgw=<gateway>]
[add|del]
Magnum6K25# ipconfig ip=192.168.1.150 mask=255.255.255.0 dgw=192.168.1.10
Magnum6K25# save
FIGURE 4 - Setting IP address on the switch
This document assumes the reader is familiar with IP addressing schemes as well as how net mask is used and how default gateways and routers are used in a network.
Reboot gives an opportunity to save the configuration prior to shutdown. For a reboot – simply type in the command “reboot”. (Note – even though the passwords are not changed, they can be changed later.)
Magnum6K25# reboot
Proceed on rebooting the switch? [ 'Y' or 'N' ] Y
Do you wish to save current configuration? [ 'Y' or 'N' ] Y
Magnum6K25#
FIGURE 5 - Rebooting the switch
MNS-6K forces an answer the prompts with a “Y” or a “N” to prevent accidental keystroke errors and loss of work.
The parameters can be viewed at any time by using the ‘show’ command. The show command will be covered in more detail later in various sections throughout the document.
Magnum6K25# show setup
28

M A G N U M 6 K S W I T C H E S , M N S - 6 K U S E R G U I D E
Version |
: Magnum 6K25 build 14.1 Jul 28 2008 07:51:45 |
||
MAC Address |
: 00:20:06:25:b7:e0 |
||
IP Address |
: 192.168.1.150 |
||
Subnet Mask |
: 255.255.255.0 |
||
Gateway Address |
: 192.168.1.10 |
||
CLI Mode |
: Manager |
|
|
System Name |
: Magnum6K25 |
||
System Description |
: 25 Port Modular Ethernet Switch |
||
System Contact |
: support@garrettcom.com |
||
System Location |
: Fremont, CA |
||
System ObjectId |
: 1.3.6.1.4.1.553.12.6 |
||
Magnum6K25# show sysconfig |
|
||
System Name |
|
: Magnum6K25 |
|
System Contact |
|
: support@garrettcom.com |
|
System Location |
|
: HO, Fremont, CA |
|
Boot Mode |
|
: manual |
|
Inactivity Timeout(min) |
: |
10 |
|
Address Age Interval(min) |
: |
300 |
|
Inbound Telnet Enabled |
: Yes |
||
Web Agent Enabled |
: Yes |
||
Time Zone |
|
: GMT-08hours:00minutes |
|
Day Light Time Rule |
: USA |
||
System UpTime |
|
: 36 Days 7 Hours 49 Mins 48 Secs |
|
Magnum6K25#
FIGURE 6 - Viewing the basic setup parameters. You can use ‘show setup’ or ‘show sysconfig’ to view setup parameters
Some of the parameters in the Magnum 6K family of switches are shown above. The list of parameters below indicates some of the key parameters on the switch and the recommendations for changing them (or optionally keeping them the same).
Privilege levels
Two privilege levels are available - Manager and Operator. Operator is at privilege level 1 and the Manager is at privilege level 2 (the privilege increases with the levels). For example, to set up a user for basic monitoring capabilities use lower number or operator level privilege (Level 1)
The Manager level provides all Operator level privileges plus the ability to perform system-level actions and configuration commands. To select this level, enter the ‘enable <user-name>’ command at the Operator level prompt and enter the Manager password, when prompted.
Syntax enable <user-name>
For example, switching from an Operator level to manager level, using the ‘enable’
29
 Loading...
Loading...