Ericsson T39 User Manual

EN/LZT 108 4786 R1A
Mobile Phone
T39
White Paper
Ericsson is the leading provider in the new telecoms world, with communications solutions that combine telecom and datacom technologies with freedom of mobility for the user. With more than 100,000 employees in 140 countries, Ericsson simplifies communications for its customers - network operators, service providers, enterprises and consumers - the world over.
First edition (June 2001)
Publication number: EN/LZT 108 4786 R1A
This document is published by Ericsson Mobile Communications AB, without any warranty.
Improvements and changes to this text necessitated by typographical errors, inaccuracies of current information or improvements to programs and/or equipment, may be made by Ericsson Mobile Communications AB at any time and without notice. Such changes will, however, be incorporated into new editions of this document. Any hard copies or locally stored copies of this document are to be regarded as temporary reference copies only.
All rights reserved.
© Ericsson Mobile Communications AB, 2001
Contents
PREFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Purpose Of This Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
PRODUCT OVERVIEW . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
T39 Powerfully Attractive And Always Online . . . . . . . . . . . 6 Functions And Features For Productivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
BLUETOOTHTM WIRELESS TECHNOLOGY . . . 8
Using Bluetooth Wireless Technology In The T39 . . . . . . . . . 9
GENERAL PACKET RADIO SERVICES . . . . . . . 10
Using GPRS In The T39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
WAP SERVICES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Using WAP In The T39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Bearer Type Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Gateway Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Security Using WAP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Over-The-Air Provisioning Of WAP Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuration Of WAP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Push Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
POWERFUL MESSAGING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Enhanced Messaging Service (EMS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
MOBILE INTERNET AND E-MAIL . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Data Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Built-in E-mail Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Mobile Positioning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
MODEM AND AT COMMANDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
GSM Data Communication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
AT Commands Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
SYNCHRONIZE CALENDAR AND PHONE BOOK 25
Synchronize With Local Calendar And Phone Book . . . . . . 25 Synchronize Over WAP Using SyncML . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Hierarchical Phone Book With Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26 Synchronization Software And The T39 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
INFRARED TRANSCEIVER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Connection Via Infrared . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Connection Via Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
FUNCTIONS AND FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
In-phone Functions And Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Network-Dependent Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
SIM APPLICATION TOOLKIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
TERMINOLOGY AND ABBREVIATIONS . . . . . . 40
3
RELATED INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
APPENDIX: TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS . . . 45
4

PREFACE
Purpose Of This Document
The Ericsson T39 White Paper is designed to give the reader a deeper technical understanding of how the T39 is designed, and of how it interacts with other media. This document will make it easier to integrate the T39 with the IT and communications solutions of a company or organization.
People who can benefit from this document include:
•Corporate buyers
•IT Professionals
•Software developers
•Support engineers
•Business decision-makers
The best place to find all the extras you need to support your phone and daily life is at the Ericsson Mobile Internet, http://mobileinternet.ericsson.com. Here you will find downloadable ring tones, games, news, information, and a host of exciting links to other sites.
More information, useful for product, service and application developers, is published on the Ericsson Mobility World. The site at http://www.ericsson.com/mobilityworld contains up-
to-date information about technologies, products and tools.
5
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The T39 is a Triple Band phone with built-in BluetoothTM wireless technology, high speed data, GPRS and Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) support. It integrates wirelessly with personal office tools and corporate calendars, phone books and services, to form a unique communications tool for the organization.
T39 Powerfully Attractive And Always Online
Bluetooth™
Synchronization
WAP, security
High Speed Data
Bluetooth wireless technology
|
Using a high speed radio link, Bluetooth wireless technology elimi- |
|
nates the need for cables for connecting the phone to handheld devices, |
|
accessories and laptops. It provides secure short-range communication |
|
without cables – even without line of sight between the devices. |
|
Bluetooth wireless technology can be used for synchronization with |
|
laptops and PDAs, for wireless headset, for turning the phone into a |
|
wireless modem, for exchanging calendar events and business cards |
|
with other phones, and more. |
Synchronization |
Synchronization with PCs, a Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) or cal- |
|
endar is effortless. Appointments and tasks in the phone’s calendar and |
|
entries in the phone book can be synchronized via Bluetooth connec- |
|
tion, infrared or a cable, and also via WAP using SyncML. The T39 |
|
features a hierarchical phone book in which you can store contact |
|
details. |
Secure WAP |
Internet browsing and secure mobile services are supported over Wire- |
|
less Application Protocol, WAP. The built-in browser supports WAP |
|
June2000 (WAP 1.2.1) with push services and secure transaction meth- |
|
ods, such as digital signatures. Depending on network services, the |
|
T39 provides WAP over GPRS with constant connection, GSM Data or |
|
SMS. |
High speed and GPRS The T39 enables high speed data communication and WAP browsing with a constant connection, as required by the application. In GSM Data connections, High Speed Data supports a high transmission rate, and a fast download speed. Furthermore, by supporting General Packet Radio Services (GPRS) networks, the T39 is designed to remain “always-online” with a cost efficient IP connection which enables rapid data transmission.
6

Functions And Features For Productivity
Triple Band support
Triple Band support means that you can use the phone on GSM 900/1800/1900 networks almost all over the world.
Messaging
E-mail client (POP3/SMTP) and support for linked SMS messages (long messages). Data connections feature makes it easy to manage all connection settings in one place, for internet etc.
Connectivity
Infrared link to be used as a complement to a Bluetooth connection, for synchronization, for turning the phone into a wireless modem, and more. An optional cable can also be used if no infrared is available on the PC or handheld.
Voice and user interface
Built-in voice memo recorder and enhanced voice control functions. A full graphic display with grey scales and an easy to navigate, user interface software. Predictive text input,
T9® Text Input, makes typing quicker and easier.
Profiles feature
Groups of settings preset to suit certain environment Profiles, such as “In Car”, “Meeting”, “Home”. Numbered shortcuts make it possible to prepare settings into a favourite menu which the user accesses quickly and easily.
Accessories
A wide range of Ericsson accessories are available, such as Bluetooth wireless headset, to enhance productivity further.
Services on the network
The T39 supports the SIM Application Toolkit (online services), which makes it possible for operators to provide new services to existing users over the air, including new menus and functions in the phone. Support for mobile positioning enables the design and implementation of new productivity and commercial solutions.
7
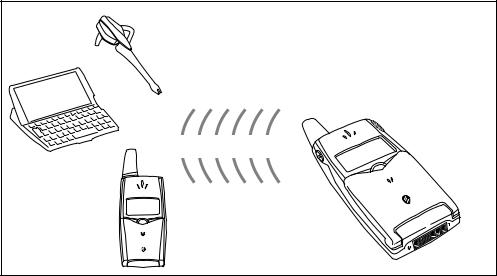
BLUETOOTHTM WIRELESS TECHNOLOGY
The T39 has built-in Bluetooth wireless technology. Short-range radio links operate in a globally available 2.4 GHz radio frequency band, and ensures fast and secure communications up to a range of 10 metres (typically) between devices. Please note that in countries where the use of Bluetooth wireless technology is not allowed, you must ensure that the Bluetooth function is set to off. Contact the Ericsson representative to check if the use of Bluetooth wireless technology is restricted in your country.
Bluetooth wireless technology is designed to be fully functional even in very noisy radio frequency environments and it provides a high transmission rate. All data transfer is protected by advanced error-correction methods that ensure a high level of data security.
Bluetooth wireless technology facilitates instant connections which are maintained even when the devices are not within line of sight. Bluetooth wireless technology facilitates high-quality voice transmissions, even under severe conditions. For example, you can connect your headset to your mobile phone to keep your hands free for more important tasks.
Ericsson is a founding partner of the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG). Bluetooth wireless technology devices that are expected to be available in the near future, include:
•Headset for wireless voice transmission and remote call control
•PCs, laptops, PDAs, palmpads for data transfer, synchronization etc.
•PC cards for Bluetooth wireless technology in laptops and PDAs
•MP3 music player
•Other phones for exchanging business cards, ring signals, playing games etc.
•Digital still and motion video cameras
•Printers, hard disks and other storage devices
•Handheld scanners for text, barcodes and images
•Household appliances with built-in logic, as well as games and entertainment devices
•Access points in hotel lobbies and airports for connecting to computer networks and the internet
Bluetooth
8

Using Bluetooth Wireless Technology In The T39
The built-in Bluetooth wireless technology allows a very fast data transfer speed, when one or more Bluetooth devices is within a range of 10 metres. For example, the services available via infrared communication are replaced by Bluetooth wireless technology communication, and with a better performance. Key benefits of using Bluetooth wireless technology in the T39 are:
Replace cable and infrared
Bluetooth wireless technology gives a true wireless connection to headset, computers, networks, printers and other devices.
Several devices |
The T39 identifies and maintains several devices in a pairing list. |
Radio link |
No line of sight required; the phone can remain in a briefcase or in a |
|
pocket, as long as no solid objects are in between (whereas infrared |
|
requires line of sight). |
Secure data connection |
A Bluetooth wireless technology PC/laptop can connect to the phone, |
|
turning it into a modem for accessing the internet and for data transfer, |
|
via GSM Data or via General Packet Radio Services (GPRS). |
Synchronization |
Fast synchronization, even without line of sight, of calendar and phone |
|
book with PC/laptop, PDA and quick exchange of business cards, cal- |
|
endar events and melodies with other phones and devices. |
Phone management |
Manage the phone book and the phone settings from a Bluetooth PC. |
Print from the phone |
When connected to a printer via Bluetooth wireless technology, the |
|
user can print items directly from the phone. Items that can be printed |
|
include overviews in the calendar, appointments and tasks, contacts, |
|
business cards and text messages. |
9
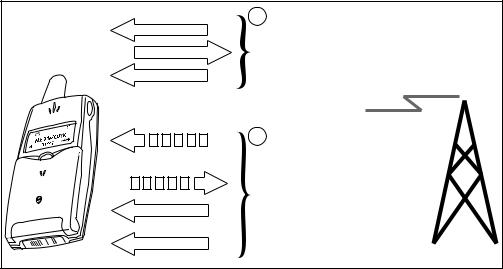
GENERAL PACKET RADIO SERVICES
The introduction of GPRS (General Packet Radio Services) is one of the key steps in the evolution of today’s GSM networks to enhance the capabilities for data communication. Data traffic is increasing enormously over both wired and wireless networks. This growth in demand for internet access and services has paralleled the explosion in demand for mobile communications. Users want access to the internet while they are away from their offices and homes. The main applications driving the wireless internet development are e-mail access, web browsing and pull content, also known as web clipping. User surveys have found that a vast majority of executives and business professionals want wireless internet access to both send and receive e-mail on a portable device, as well as web browsing with both text and graphic capabilities! The demand for high-speed internet access will be the key driver for coming generations of wireless services equal to, or faster than wired, and GPRS can deliver this mobile internet functionality. GPRS will allow innovative services to be created, enabling new and previously inaccessible market segments to be addressed, increasing customer loyalty and reducing churn. Machine-to-machine and person-to-machine communications will become possible.
GPRS applications can be developed both as horizontal and vertical applications. Vertical applications can for example be operations like police and emergency, taxi, delivery or automated services such as vending machines, supervision, vehicle tracking. Horizontal applications are generic, such as internet access, e-mail, messaging, e-commerce and entertainment. One of the advantages with GPRS is that it will profit from the global coverage of existing GSM networks. Therefore applications developed for GPRS can be deployed on a large scale and will gain economies of scale. GPRS also provides an ideal secure medium for connections to private networks, banking and financial services.
The T39 supports GPRS, which means that the data is sent in packages at a very high speed. The phone remains connected to the network all the time without using any transmission capacity, until data needs to be sent or received. This illustration gives a comparison.
1
9,600/14,400
9,600/14,400
9,600/14,400
9,600/13,200
9,600/13,200
9,600/13,200
9,600/13,200
GSM 9,600 bps
14,400, 19,200 or 28,800 bps (HSCSD)
2
GPRS
9,600, 13,200, 19,200, 26,400, 28,800 or 39,600 bps
•1. A normal GSM call only uses one of eight repeating time slots in the GSM channel, giving a data speed of 9,600 bps. The T39 supports a more efficient coding scheme, giving data speeds of up to 14,400 bps (providing the network supports this). Furthermore, High Speed Circuit Switched Data (HSCSD) gives the possibility to use two time slots for receiving data. This can increase the data speed up to 28,800 bps (network-dependent)
•2. In GPRS, data is sent in packets, and up to three time slots can be combined to provide the necessary bandwidth, up to 39,600 bps for receiving data, depending on coding scheme
10

Using GPRS In The T39
Instead of occupying a whole voice channel for the duration of the call, data is sent in small packets as needed, just like IP on the internet. Capacity is used only when data is being sent or received, which means that it is possible to be “constantly” connected, as required by the application in use. If the user wants to send e-mail, it may be sufficient to share a channel with several other users. On the other hand, the phone has access to several time slots if a higher capacity is needed.
The GPRS specification includes four coding schemes with different data speeds. The T39 works with the first two coding schemes, but the data speed will naturally vary according to network configuration.
The GSM system's design limits the ability to use all eight time slots. Instead, the T39 uses up to three time slots for receiving data, and one slot for transmitting. This means the speed for receiving data is up to 39,600 bps and for sending data up to 13,200 bps.
Information about the identity of phone and the characteristics of the connection are described in the PDP context (Packet Data Protocol context). This information is stored both in the phone and in the mobile network, so that each phone is identified and “visible” to the system. In T39, multiple PDP context settings can be set via the menu system, or by OTA provisioning.
Using GPRS with the T39 gives several advantages, for example:
Constant connection |
Keep an open connection to the e-mail system or the company net- |
|
work, staying online to receive and send messages at all times. All con- |
|
nection settings can be managed by using the Data connections feature. |
High speed |
Gain access automatically to increased bandwidth when downloading |
|
large files, images etc. |
Cost efficient |
GPRS being an IP-based connection means that a high transmission |
|
capacity is only used when needed. This makes it possible to stay con- |
|
nected via GPRS, whereas keeping a constant circuit switched connec- |
|
tion would be more expensive. |
WAP over GPRS |
Access the internet via WAP at high speed and with a constant connec- |
|
tion. The user can run the WAP functions such as browsing. |
E-mail over GPRS |
This means that the user can be connected to the e-mail system while |
|
reading and preparing messages, and that the messages are sent at a |
|
high speed. |
Data communication |
Using GPRS, this provides data and internet/Intranet access, for a PC, |
|
PDA or handheld device connected via Bluetooth wireless technology, |
|
infrared or cable. |
Data and voice |
The T39 can maintain a data connection when conducting a voice call. |
|
For example, the user can conduct voice calls while maintaining an |
|
uninterrupted connection to an e-mail system. |
Provide settings |
The GPRS configuration settings can be sent from the provider over |
|
the air, OTA. This way, the user can use GPRS without making any set- |
|
tings in the phone. |
User controlled settings Full user control is enabled in the T39. In the Data connections menu, the user can set up multiple descriptions and access advanced settings for GPRS, for example Data compression and Quality of Service.
11

WAP SERVICES
The typical WAP client is a small, portable device which is connected to a wireless network. This includes mobile phones, pagers, smart phones, PDAs and other small devices. In these devices, you have a limited user interface, low memory and computing power compared to desktop and laptop computers.
The WAP browser in the T39 is compliant with WAP June2000 (WAP 1.2.1) includes WTLS class 3 and mechanisms for digital signatures. It is designed for WML and cannot read ordinary HTML pages, but it is suitable for interaction with customer services, e.g. ticket reservation. It is also handy when you want to access text-based information, such as timetables, share prices and exchange rates and internet banking and other interactive services.
Using WAP In The T39
The built-in WAP browser gives the user portable, fast and secure access to a wide variety of services, with the possibility of personalized services. WAP in the T39 offers new opportunities to companies and service providers:
Push service |
A useful feature for companies and service providers to push contents |
|
or service indications to work groups or customers. This is used for |
|
notifications, mail alerts, messaging, news, stock quotes, contacts, |
|
meeting requests, games etc. |
Provide settings |
Using SMS message, configuration settings can be sent over the air, |
|
OTA, so that the user does not need to configure the WAP access set- |
|
tings manually. WAP settings may also be customized by the operator. |
Adapt to phone type |
When creating a WAP service, you want to make sure that the user |
|
experience is what you intended, regardless of client device type. The |
|
function User Agent Profile is supported by the T39 to allow the con- |
|
tents to be automatically optimized for the phone. |
Security |
Service providers can offer commercial and business critical services |
|
with high security to mobile users, compliant with Wireless Transport |
|
Layer Security (WTLS) class 1, 2 and 3. Digital signatures and Wire- |
|
less Identification Module (WIM) are supported in the T39. The WIM |
|
is used to store security related information. |
Several bearer types |
The T39 accesses WAP over a standard GSM Data connection as well |
|
as over a GPRS connection. SMS is available as bearer type also. (Net- |
|
work-dependent services.) |
Bandwidth efficiency |
One of the key advantages WAP has over text-based HTML pages on |
|
mobile devices, is the bandwidth efficiency for communication. This is |
|
due partly to the fact that the WAP application is communicated to the |
|
wireless devices in the form of binary encoded data. Over a GPRS con- |
|
nection, bandwidth is used even more efficiently. See “Using GPRS In |
|
The T39” on page 11. |
12
Easy create for WAP |
Creating a WAP service is no harder than creating an Intranet/internet |
|
service today since WML and WMLScript are based on well-known |
|
internet technology. New market segments can be addressed by |
|
launching innovative mobile Value Added Services. |
Using standard tools |
It is possible for the service creator to use standard tools like ASP or |
|
CGI to generate content dynamically. You can utilize existing invest- |
|
ments in databases etc. that are the basis of existing internet services. |
|
Create a service once and make it accessible on a broad range of wire- |
|
less networks. |
Maintain customer base You can adapt existing internet services to WAP. The actual binary encoding can be handled by the WAP Gateway which makes it possible to create WAP applications using the text-based language WML and other tools. In fact, existing HTML-based applications on the internet can be viewed in the WAP browser, if an automatic conversion is performed in the WAP Gateway.
Improve productivity |
Improve and simplify the communication flow within an organization |
|
by making information available to mobile users. A company or orga- |
|
nization can use a WAP gateway to provide a secure connection to the |
|
company network for their users. |
The WAP profiles |
The T39 holds five WAP profiles, each with a group of network set- |
|
tings and a home page. If you provide a corporate WAP service on your |
|
Intranet, it is useful to enter an Intranet WAP profile in user phones. |
|
The WAP profile holds network settings and user identification. The |
|
users switch easily between the corporate services and WAP services |
|
on the internet, simply by switching WAP profile. |
13

Bearer Type Characteristics
The phone accesses WAP services over SMS or IP, where IP can be provided either over GSM Data or GPRS depending on network services.
Typical differences which distinguish the bearer types are listed below.
GPRS Access
•The connection is maintained “constantly”, as required by the application, and data is transmitted in packets. This means that the phone is connected almost all the time without using network capacity.
•Higher transmission speed than with GSM Data and SMS access.
•Pricing of GPRS can be dependent on the actual use of bandwidth, which means very low cost when no data is sent or received, while the phone remains connected to the WAP service.
•When transmitting large amounts of data, bandwidth can be increased automatically to allow faster transmission speed.
•GPRS is ideal for Complex Pull services, Browsing, Data transfer, Provisioning, Pager service, Messaging services, Info services, Push initiations.
GSM Data Access
•Circuit connection of data call which means that the phone is connected during the entire WAP session.
•Comparably higher transmission speed than with SMS access.
•Pricing of GSM Data access can be compared to pricing of data calls in the network.
•GSM Data is suitable for Complex Pull services, Browsing and Data transfer.
•GSM Data is not suitable for Provisioning, Pager service.
SMS Access
•SMS point-to-point is used and not SMS Cell Broadcast.
•The connection is maintained by the automatic exchange of ”messages” between the phone and the SMS Service Center.
•Comparably lower transmission speed than with GSM Data access.
•Pricing of SMS access can be compared to pricing of the normal SMS service in the network.
•SMS is suitable for Messaging services, Info services, Push initiations, Provisioning.
•SMS is not suitable for Browsing, Data transfer.
Gateway Characteristics
The WAP Gateway provides services in the company’s Intranet, a banking or stock trading service on the internet, or access to other WAP applications on web addresses anywhere on the internet. A Gateway is identified by an IP number or by a phone number, depending on access type.
14

Security Using WAP
When using certain WAP services the user may want a secure connection between the phone and the WAP gateway, for example when using banking services. An icon in the display indicates when a secure connection is used. The T39 is based on the WAP June2000 (WAP 1.2.1) specifications where security functionality is specified with a technology called Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS).
The WAP protocols that handle the connection, its transport and its security are structured in protocol layers. The security is handled by the WTLS layer operating above the transport protocol layer. There are WTLS classes that define the levels of security for a WTLS connection:
•WTLS class 1 involves encryption with no authentication.
•WTLS class 2 involves encryption with server authentication.
•WTLS class 3 involves encryption with both server and client authentication
Server authentication |
Requires a server certificate stored at the server side and a root certifi- |
|
cate stored at the client side. |
Client authentication |
Requires a client certificate stored at the client side and a trusted certif- |
|
icate stored at the server side. |
A Wireless Identity Module (WIM) can contain both trusted and client certificates, private keys and algorithms needed for WTLS handshaking, encryption/decryption and signature generation. The WIM module can be placed on a SIM card and will then be referred to as a SWIM card.
Certificates
To use secure connections, the user needs to have certificates saved in the phone. There are two types of certificates:
Trusted certificate |
A certificate that guarantees that a WAP site is genuine. If the phone |
|
has a stored certificate of a certain type, it means the user can trust all |
|
WAP gateways that use the certificate. Trusted certificates can be pre- |
|
installed in the phone, pre-installed in the SWIM, or downloaded from |
|
the trusted supplier’s WAP page. |
Client certificate |
A personal certificate that verifies the user’s identity. A bank that the |
|
user has a contract with may issue this kind of certificate. Client certif- |
|
icates can be pre-installed in the SWIM card. |
WIM Locks (PIN Codes)
There are two types of WAP security locks (PIN codes) for the WIM on SIM. The locks protect the subscription from unauthorized use when browsing. The locks should typically be supplied from the supplier of the SWIM.
Access lock |
An access lock protects the data in the WIM. The user is asked to enter |
|
the PIN code the first time the SWIM card is accessed when establish- |
|
ing a connection. |
Signature lock |
A signature lock is used for confirming transactions - like a digital sig- |
|
nature. |
In the T39, the user can check which transactions have been made with the phone when browsing. Each time the user confirms a transaction with a signature lock code, a contract is saved in the phone. The contract contains details about the transaction.
15

Over-The-Air Provisioning Of WAP Settings
To simplify configuring WAP settings in a number of phones, all settings can be sent as an SMS message to each phone. This makes it easy for an operator, a service provider or a company to distribute settings for internet/Intranet, and WAP, without having to configure each phone manually. This also makes it easy to upgrade the services provided to the users, without the need for users to perform any manual configuration.
•The OTA configuration message is distributed via SMS point-to-point
•The setup information is a binary encoded XML message, according to WBXML. To receive information about OTA specifications, please contact your local Ericsson representative for consumer products. A configurator that utilizes OTA provisioning can be tested on the Ericsson Mobile Internet
•The user is not alerted about new settings until the ongoing browsing session ends. Furthermore, settings are not changed during an ongoing browsing session
•The necessary user interaction is limited to receiving and accepting/rejecting the configuration message, and selecting which WAP profile to allocate the settings to
•Security can be handled using a keyword identifier displayed on the screen as a shared secret between the SMS sender and the receiver. It is important that the user has a way to verify that the configuration message is authentic
Configuration Of WAP Settings
An easy way to perform the WAP configuration of a single phone is by using the step-by-step WAP configurator provided on the Ericsson Mobile Internet. The configurator utilizes OTA provisioning, and it is available on http://mobileinternet.ericsson.com, no login required.
Another way to perform the WAP configuration of a single phone is by using the Ericsson Phone Settings program which is available on the CD supplied with the phone. There, you can find all configuration settings needed for the phone to access the WAP services.
A manual configuration is made using the menu system in the phone. This is described in the User’s Guide.
Push Services
These are useful for sending updated WAP site contents or WAP links to mobile users. Examples of services that can be implemented using push services:
•Notifications about new e-mails, voice mails, etc. Instant messaging and chat
•News, sport results, weather forecasts, financial information (stock quotes etc.)
•Personal Information Manager (PIM) - delivery of contacts, meeting requests etc.
•Fill up a smart card with e-cash
•Interactive games, e.g. play poker with a friend
In the T39, the user can select if push messages are allowed to be received or not. There are two different forms of Push services, Service Indication and Service Loading.
Service Indication (SI)
This is basically a text message to the user, that informs of a WAP page. It contains a link to a URL. If the user decides to load the suggested URL, normal WAP browsing commences.
When a service indication is received in the T39, the user can decide to load it, to postpone it or
16
to delete it. Service indications that are received are stored in the Push Inbox, and can be viewed and loaded at a later time.
The push inbox has a list that shows the first part of each received message, which is sorted by:
1)Action attribute, high/medium/low (highest first), and
2)Reception time for messages of each attribute level
Service Loading (SL)
This is a WAP page with the updated information, that is displayed if the user accepts it. If it is not accepted, it is loaded and stored in the cache for later use. The user can start the browser and load the page from the cache manually.
17

POWERFUL MESSAGING
The T39 is capable of sending and receiving SMS messages, linked messages and it supports Enhanced Messaging Services (EMS). Please note that EMS is only valid for T39m versions.
•With the Short Message Service, a user can send text messages containing up to 160 characters to and from GSM mobile stations (up to 70 characters using Chinese text)
•Status report is supported, which means that the user can see if a sent message has been delivered or not (network-dependent service).
•With the linked SMS, the user can link several SMS messages together to create a longer message (network-dependent service)
•With EMS, the T39 lets the user insert sounds, pictures and melodies, or ring tones in outgoing messages. Also, the phone will display pictures and play melodies, sounds and animations included in incoming messages (network-dependent service, and only valid for T39m versions)
The T39 also lets you save often-used text messages as templates. You can save up to ten templates consisting of up to twenty-five characters each in the phone's memory. The T39 also features an SMS counter allowing you to keep track of SMS messages that you have sent.
Enhanced Messaging Service (EMS)
Enhanced Messaging Service (EMS) is a powerful enhancement of the SMS standard specified by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). It is supported by the major network operators and mobile phone manufacturers. With it, mobile phone users can add life to SMS text messaging in the form of pictures, melodies, sounds, animations and formatted text. This gives the users new ways to express feelings, moods and personality in SMS messages.
Add life to messages to and from the T39 by inserting melodies.
Users can express feelings and personality by inserting pictures in messages.
As well as messaging, users will enjoy collecting and swapping pictures and ring signals and other melodies, downloading them from the internet or editing them directly on the phone. See related documents listed under “Documents” on page 25. EMS is a network-dependent service.
One message may contain several EMS objects, such as a picture, an animation and a sound. The message is limited by size. If concatenation is used, up to six segments of 128 bytes each can be combined in one message.
Most phones without support for the EMS standard will simply ignore the EMS information when the message is received, and will just display the text in the message. This prevents the phone from displaying unreadable contents to the user.
18
 Loading...
Loading...