Cisco Systems ASR 1000 User Manual

Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
Cisco IOS XE Release 2.1
May 5, 2008
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc. 170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706 USA http://www.cisco.com Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387) Fax: 408 527-0883
Customer Order Number: OL-15421-01
THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco StadiumVision, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn is a service mark; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet, Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0804R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
© 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C O N T E N T S |
||||||
|
|
|
Preface ix |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Document Revision History |
ix |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Objectives |
ix |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intended Audience |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Organization |
x |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Documentation |
xi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router Documentation |
i-xi |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
Cisco IOS Release 12.2SR Software Publications |
xi |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Document Conventions |
xi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request xiii |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview 1-1 |
|||||||||||||
C H A P T E R |
1 |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Contents |
1-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General Overview |
1-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Distributed and Unified Models 1-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
Supported Integrated Session Border Controller Features |
1-4 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Deployment of the Integrated Session Border Controller |
1-8 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment Scenario |
1-8 |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
C H A P T E R |
2 |
2-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
Contents |
2-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prerequisites for Integrated Session Border Controller |
2-1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Restrictions for Integrated Session Border Controller |
2-1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment |
2-2 |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
Prerequisites |
2-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
What To Do Next |
2-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Examples |
2-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Troubleshooting Tips |
2-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Configuring H.248 Logging Level |
2-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Enabling H.248 Logging Requests and Responses |
2-8 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Example H.248 Log Output |
2-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Configuration Examples |
2-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
SBC DBE Configuration Steps: Example 2-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
iii |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||

Contents
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Primary IP and Primary Media IP Addresses: Example 2-10 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Secondary IP and Secondary Media IP Addresses: Example 2-11 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Making Global Changes to Controllers: Example |
2-11 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Making Changes to Individual Controller Settings: Example |
2-13 |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco H.248 Profile |
2-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Overview of Profile |
2-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Profile Packages |
2-15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
DTMF Interworking |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
C H A P T E R |
3 |
|
3-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Contents |
3-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Information About DTMF Interworking |
3-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RTP to SIP Interworking |
3-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
SIP to RTP Interworking |
3-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Default Duration of a DTMF Event |
3-2 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Prerequisites |
3-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Media Address Pools |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
C H A P T E R |
4 |
|
4-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Contents |
4-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prerequisites for Implementing Media Address Pools |
4-1 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Restrictions for Configuring Media Address Pools |
4-1 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Information About Media Address Pools |
4-2 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Media Address Pools 4-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Media Address Pools Example |
4-4 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Quality of Service and Bandwidth Management |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
C H A P T E R |
5 |
|
5-1 |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Contents |
5-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H.248 Traffic Management Package Support |
5-1 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
DSCP Marking and IP Precedence Marking |
5-3 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
DSCP Re-Markings |
5-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
QoS Bandwidth Allocation 5-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RTCP Policing 5-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RTCP Policing Using Tman Package |
5-4 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
RTCP Policing Not Using Tman Package |
5-4 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Two-Rate Three-Color Policing and Marking |
5-5 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Enabling Two-Rate Three-Color Policing and Marking 5-5 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Implementing Two-Rate Three-Color Policing and Marking |
5-5 |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
5-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
iv |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

Contents
|
|
|
Related Commands |
5-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
H.248 Packages—Signaling and Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
C H A P T E R |
6 |
|
6-1 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
Contents |
6-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enabling Optional H.248 Packages |
6-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Related Commands |
6-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
H.248 Address Reporting Package |
6-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
H.248 Gate Information (Ginfo) Package Becomes Optional 6-2 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
6-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H.248 Segmentation Package Support |
6-2 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
6-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Commands |
6-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
H.248 Session Failure Reaction Package |
|
6-3 |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
6-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H.248 Termination State Control Package |
6-4 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
The tsc-quiesce Feature |
6-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
The tsc-suspend Feature |
6-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
6-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Commands |
6-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
H.248 Traffic Management Package Support 6-6 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
H.248.1v3 Support 6-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
6-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Commands |
6-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
H.248 VLAN Package Syntax-Level Support |
6-6 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
6-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Commands |
6-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
MGC-Controlled Gateway-Wide Properties |
6-7 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
6-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H.248 Services—Signaling and Control |
|
|
|
|
||||||
C H A P T E R |
7 |
7-1 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Contents |
7-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Signaling Pinhole Support 7-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extension to H.248 Audit Support |
7-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Extension to H.248 Termination Wildcarding Support 7-3 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flexible Address Prefix Provisioning |
7-4 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
v |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||

Contents
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Local Source Properties (Address and Port) 7-5 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Locally Hairpinned Sessions |
7-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Twice NAPT Pinhole Hairpinning 7-5 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
No NAPT Pinhole Hairpinning |
7-5 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MGC-Specified Local Addresses or Ports |
7-6 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Multi-Stream Terminations |
7-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nine-Tier Termination Name Hierarchy |
7-7 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Restrictions for Nine-Tier Termination Name Hierarchy |
7-7 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Information About Nine-Tier Termination Name Hierarchy 7-8 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Displaying the Nine-Tier Termination Name Hierarchy |
7-8 |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Displaying the Nine-Tier Termination Name Hierarchy: Example 7-9 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Optional Local and Remote Descriptors |
7-10 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remote Source Address Mask Filtering |
7-11 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
RTP Specific Behavior Support |
7-11 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ServiceChange Notification for Interface Status Change 7-11 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring the ServiceChange Notification for Interface Status Change 7-12 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Example Output |
7-13 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
T-MAX Timer 7-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Commands 7-14 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
The tsc-Delay Timer |
7-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
7-14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Video on Demand (VOD) Support |
7-14 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
Integrated Session Border Controller Security 8-1 |
|
|
|||||||
C H A P T E R 8 |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Contents 8-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firewall (Media Pinhole Control) |
8-2 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
H.248 Address Reporting Package |
8-2 |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
8-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H.248 Session Failure Reaction Package |
8-2 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
H.248 Termination State Control Package |
8-2 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Interim Authentication Header Support |
8-3 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||

Contents
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
8-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Related Commands |
|
8-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
IP NAPT Traversal Package and Latch and Relatch Support |
8-3 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Latch and Relatch Support |
8-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
8-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Related Commands |
|
8-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Local Source Properties (Address and Port) |
8-4 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
8-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
NAPT and NAT Traversal |
8-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Remote Source Address Mask Filtering 8-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
8-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Related Commands |
|
8-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Topology Hiding |
|
8-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Traffic Management Policing |
8-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Two-Rate Three-Color Policing and Marking |
8-6 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
Topology Hiding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
C H A P T E R |
9 |
9-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
Contents |
9-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NAPT and NAT Traversal |
9-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
IP NAPT Traversal Package and Latch and Relatch Support |
9-2 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
IPv4 Twice NAPT |
9-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
IPv6 Inter-Subscriber Blocking |
9-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
QoS Policy-Map-Based Inter-Subscriber Blocking Method 9-3 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
ACL-Based Inter-Subscriber Blocking Method 9-5 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
9-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
IPv6 Support |
9-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IPv6 Pinholes |
9-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
IPv6 No NAPT Support for Media Flows |
9-6 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
IPv6 Single NAPT for Signaling 9-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
9-8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Related Commands |
|
9-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
No NAPT Pinholes |
9-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
DBE Restrictions |
9-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
High Availability Support |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
C H A P T E R |
10 |
10-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
Contents |
10-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Integrated Session Border Controller High Availability 10-1 |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
vii |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Contents
|
Hardware Redundancy |
10-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Software Redundancy |
10-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Route Processor Redundancy (RPR) |
10-2 |
|
|
|||
|
SSO Support |
10-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ISSU Support |
10-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quality Monitoring and Statistics Gathering 11-1 |
|
|||||
C H A P T E R 11 |
|
||||||
|
Contents 11-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Billing and Call Detail Records |
11-2 |
|
|
|||
|
congestion-threshold Command |
11-2 |
|
|
|||
|
DBE Status Notification |
11-2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enhanced Event Notification and Auditing |
11-2 |
|
||||
|
Retention and Returning of H.248 Event Information |
11-3 |
|||||
|
Permanent H.248 Event Storage |
11-3 |
|
||||
|
H.248 Events Storage Until Event Acknowledgment 11-3 |
||||||
|
Association Reset |
11-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Silent Gate Deletion 11-4 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Resetting the Media Timeout Timers |
11-4 |
|
||||
|
DBE Restrictions |
11-4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Commands |
11-4 |
|
|
|
||
|
H.248 Network Package Quality Alert Event and Middlebox Pinhole Timer Expired Event 11-5 |
||||||
|
Network Package Quality Alert Event |
11-5 |
|
||||
|
Middlebox Pinhole Timer Expired Event |
11-5 |
|
||||
|
DBE Restrictions |
11-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Command |
11-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provisioned Inactivity Timer |
11-6 |
|
|
|
||
|
Related Command |
11-6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ServiceChange Notification for Interface Status Change |
11-6 |
|||||
I N D E X
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
viii |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|

Preface
This preface describes the objectives and organization of this document and explains how to find additional information on related products and services. This preface contains the following sections:
•Document Revision History, page ix
•Objectives, page ix
•Intended Audience, page x
•Organization, page x
•Related Documentation, page xi
•Document Conventions, page xi
•Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, page xiii
Document Revision History
The Document Revision History records technical changes to this document. The table shows the software release number and document revision number for the change, the date of the change, and a brief summary of the change.
Release No. |
Revision |
Date |
Change Summary |
|
|
|
|
2.1 |
OL-15421-01 |
May 5, 2008 |
This document was first published. |
|
|
|
|
Objectives
This document describes the Integrated Session Border Controller functions, features, restrictions, and configuration tasks for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. It is not intended as a comprehensive guide to all of the software features that can be run using the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers, but only the Integrated Session Border Controller software specific to these routers.
For information on general Cisco IOS software features that are also available on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers, see the feature module or the technology guide for that software feature.
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
ix |
|

Preface
Intended Audience
This document is intended for the following people:
•Experienced service provider administrators
•Cisco telecommunications management engineers
•Customers who use and manage Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers
Organization
This document contains the following chapters:
Chapter |
Title |
Description |
|
|
|
1 |
Integrated Session Border Controller |
Describes general architecture, list of supported |
|
for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers |
features, and deployment scenario. |
|
Overview |
|
|
|
|
2 |
Configuring Integrated Session Border |
Describes configuration tasks for data border |
|
Controller |
element (DBE) functionality, prerequisites, |
|
|
restrictions, configuration examples, and the Cisco |
|
|
H.248 profile. |
|
|
|
3 |
DTMF Interworking |
Describes support of dual-tone multifrequency |
|
|
(DTMF) to interwork between two end points that |
|
|
do not use the same way of relaying DTMF tones. |
|
|
|
4 |
Media Address Pools |
Describes how to configure the DBE address by |
|
|
address pool, with or without port range, and define |
|
|
class of service for each port range. |
|
|
|
5 |
Quality of Service and Bandwidth |
Describes features the DBE has to enhance Quality |
|
Management |
of Service (QoS). |
|
|
|
6 |
H.248 Packages—Signaling and |
Describes support of standard H.248 packages. |
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
7 |
H.248 Services—Signaling and |
Describes different H.248 services and controlling |
|
Control |
functions of the DBE. |
|
|
|
8 |
Integrated Session Border Controller |
Describes various high security features and |
|
Security |
policing of incoming data. |
|
|
|
9 |
Topology Hiding |
Describes the various features by which Integrated |
|
|
Session Border Controller protects the network by |
|
|
hiding the network address and names for both the |
|
|
customer and core network sides, and properly |
|
|
translating the IP address and port when a user |
|
|
connects to the outside network. |
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
x |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|

Preface
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chapter |
Title |
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
High Availability Support |
Describes hardware and software redundancy |
|
|
|
|
support for Integrated Session Border Controller |
|
|
|
|
on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
Quality Monitoring and Statistics |
Describes DBE support for monitoring events, and |
|
|
|
Gathering |
generation of event notification, correct billing and |
|
|
|
|
call usage records. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Documentation
This section refers you to other documentation that also might be useful as you configure your
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers. The documentation listed below is available online.
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router Documentation
For information on Integrated Session Border Controller commands, see the Cisco IOS Integrated Session Border Controller Command Reference that was provided as part of this release. For information on new Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router commands and commands in existing Cisco IOS features, see the Cisco IOS command reference books on Cisco.com for this release.
For hardware documentation for this router, see the hardware documentation that was provided as a part of this release.
For information on new software features, see the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers Software Configuration Guide, new feature module documents, and the Cisco IOS XE release notes that were provided as part of this release.
Cisco IOS Release 12.2SR Software Publications
Documentation for the related Cisco IOS Release 12.2SR, including command reference and system error messages, can be found at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6922/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Document Conventions
This documentation uses the following conventions:
|
|
Convention |
Description |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
^ or Ctrl |
The ^ and Ctrl symbols represent the Control key. For example, the key com- |
|||
|
|
|
bination ^D or Ctrl-D means hold down the Control key while you press the |
|||
|
|
|
D key. Keys are indicated in capital letters but are not case sensitive. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
string |
A string is a nonquoted set of characters shown in italics. For example, when |
|||
|
|
|
setting an SNMP community string to public, do not use quotation marks |
|||
|
|
|
around the string or the string will include the quotation marks. |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
|
|
|
||
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
xi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||

Preface
Command syntax descriptions use the following conventions:
Convention |
Description |
|
|
bold |
Bold text indicates commands and keywords that you enter exactly as shown. |
|
|
italics |
Italic text indicates arguments for which you supply values. |
|
|
[x] |
Square brackets enclose an optional element (keyword or argument). |
|
|
| |
A vertical line indicates a choice within an optional or required set of keywords |
|
or arguments. |
|
|
[x | y] |
Square brackets enclosing keywords or arguments separated by a vertical line |
|
indicate an optional choice. |
|
|
{x | y} |
Braces enclosing keywords or arguments separated by a vertical line indicate a |
|
required choice. |
|
|
Nested sets of square brackets or braces indicate optional or required choices within optional or required elements. For example:
Convention |
Description |
|
|
|
|
[x {y | z}] |
Braces and a vertical line within square brackets indicate a required choice |
|
|
|
within an optional element. |
|
|
|
Examples use the following conventions: |
||
|
|
|
Convention |
Description |
|
|
|
|
screen |
Examples of information displayed on the screen are set in Courier font. |
|
|
|
|
bold screen |
Examples of text that you must enter are set in Courier bold font. |
|
|
|
|
< |
> |
Angle brackets enclose text that is not printed to the screen, such as passwords. |
|
|
|
! |
|
An exclamation point at the beginning of a line indicates a comment line. (Ex- |
|
|
clamation points are also displayed by the Cisco IOS software for certain pro- |
|
|
cesses.) |
|
|
|
[ |
] |
Square brackets enclose default responses to system prompts. |
|
|
|
The following conventions are used to attract the attention of the reader:
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to materials that may not be contained in this manual.
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
xii |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|

Preface
Tip Means the following information will help you solve a problem. The tips information might not be troubleshooting or even an action, but could be useful information, similar to a Timesaver.
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
xiii |
|

Preface
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
xiv |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|

C H A P T E R 1
Integrated Session Border Controller for the
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
This chapter presents an overview of the Integrated Session Border Controller (SBC), supported features, and deployment of the Integrated Session Border Controller on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.
Contents
•General Overview, page 1-1
•Supported Integrated Session Border Controller Features, page 1-4
•Deployment of the Integrated Session Border Controller, page 1-8
•Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment Scenario, page 1-8
General Overview
The Integrated Session Border Controller is integrated with other features on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers, without requiring additional application-specific hardware, such as service blades. SBC is integrated with layer 2 and layer 3 services, such as security, QoS, IP Multicast, that eliminate the need to create an overlay network of standalone SBC appliances. With Integrated SBC, SBC functionality and routing functionality both reside on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Router. The integration also allows SBC to build on the security and admission control features and virtual private network (VPN) awareness of the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.
In general, session border controllers are used as key components in interconnecting Voice over IP (VoIP) and multimedia networks of different enterprise customers and service providers. SBCs are deployed at the edge of networks to meet the need for secure, intelligent border element functions. Using SBCs, the end user can make voice and video calls to another end user without being concerned about protocols, network reachability, or safety of the network.
The SBC enables direct IP-to-IP interconnect between multiple administrative domains for session-based services providing protocol interworking, security, and admission control and management. The SBC is a session-aware device that controls access to VoIP and other types of primarily media-related networks. A primary purpose of an SBC is to protect the interior of the network from excessive call load and malicious traffic.
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
1-1 |
|
|
|
Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
General Overview
The SBC functions break down into two logically distinct areas, as follows:
•The signaling border element (SBE) function. SBEs may support functions that include interworking between various signaling protocols such as H.323 and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), call admission control, advanced routing policy management, network attack detection, or call billing using RADIUS or DIAMETER. As part of the call admission control function, an SBE informs the data border element (DBE) of the various quality of service (QoS) and Network Address and Port Translation (NAPT) requirements for the call. An SBE typically controls one or more media gateways.
An SBE may be known as a media gateway controller (MGC).
•The data border element (DBE) controls access of media packets to the network, provides differentiated services and quality of service (QoS) for different media streams, and prevents service theft. The DBE consists of a set of data path functions and responds to the requests made by the SBE to open pinholes, taking into account the specified Network Address Translation (NAT)/firewall traversal and QoS requirements.
The Integrated Session Border Controller implements the DBE function on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers. A table of DBE supported features is listed in Table 1-1 on page 1-4.
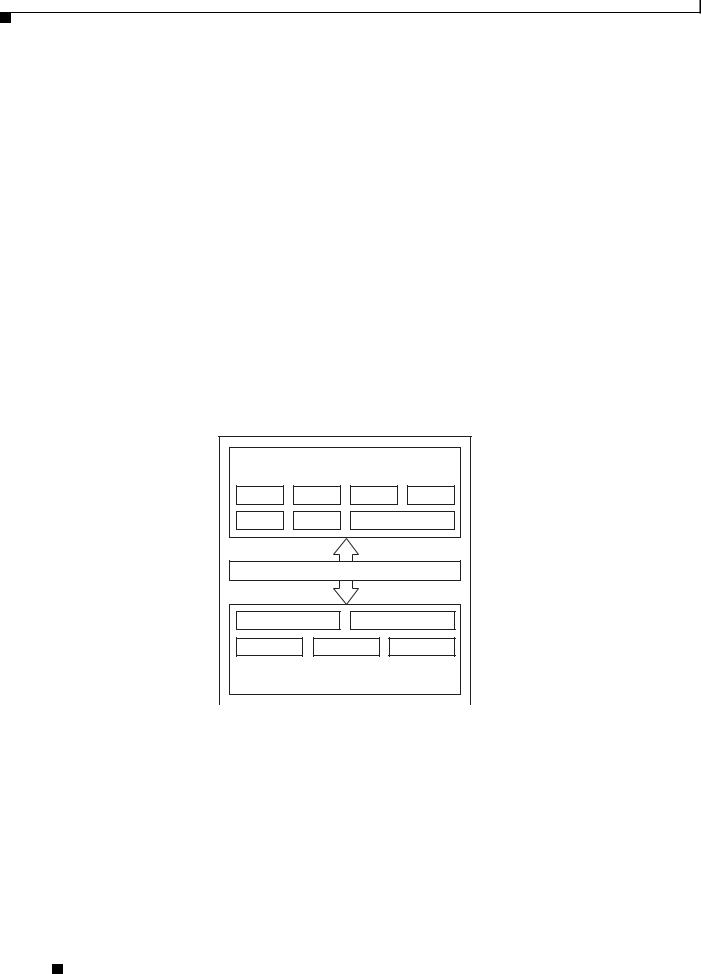
Figure 1-1 shows an example SBE/DBE architecture; your SBC architecture may differ.
Figure 1-1 Example of SBC High Level Architecture
Signaling Border Element |
|||
|
(SBE) |
|
|
H.323 |
SIP |
Policy |
HA |
AAA |
CDR |
VPN control |
|
|
H.248 interface |
|
|
NAPT |
|
QoS |
|
RTP |
Policy |
HA |
|
|
Data Border Element |
||
|
(DBE) |
280018 |
|
|
|
|
|
Distributed and Unified Models
The SBC can operate in two modes or models—unified and distributed.
•In the unified model, both the SBE and DBE logical entities co-exist on the same network element.
•In the distributed model, the SBE and the DBE entities reside on different network elements. Logically, each of the SBE entities could control multiple DBE elements. The DBE is controlled by one SBE at any one time.
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
1-2 |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
General Overview
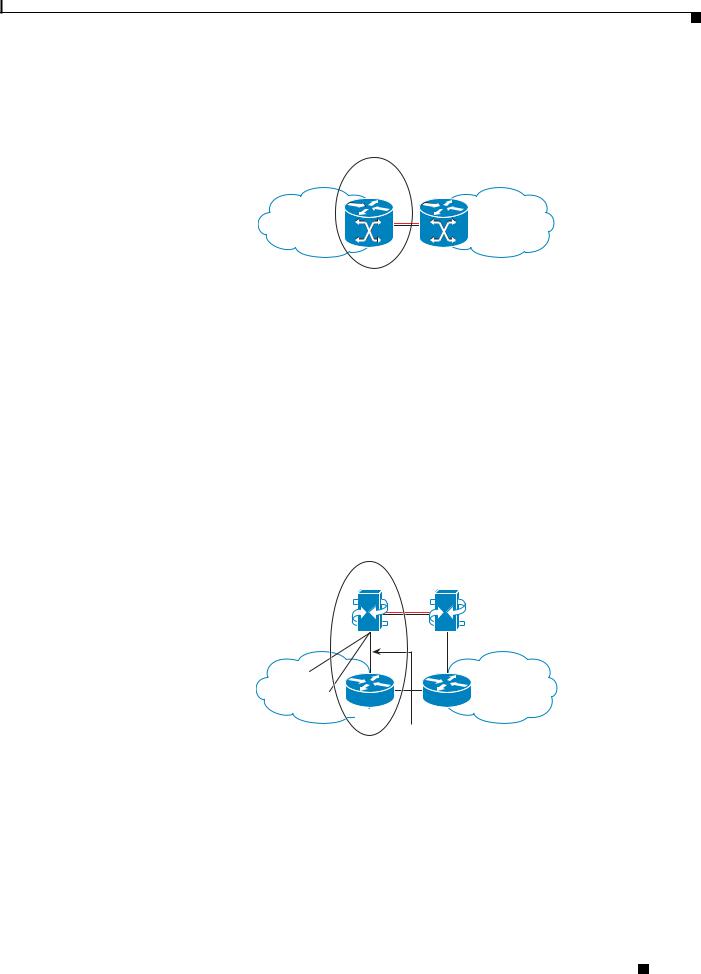
Figure 1-2 on page 1-3 illustrates the unified model.
Figure 1-2 Unified SBC Model
SBE+DBE
Domain A |
Domain B |
271026
The Integrated Session Border Controller runs under the distributed model and provides the DBE functionality.
The distributed model offers advantages over the unified model, as follows:
•Scalable to a larger number of sessions.
•Operational advantages, because the SBE can be upgraded or serviced separately from the DBE.
•The distributed model aligns well with typical voice deployments where the SBE can be co-located with part of the call agent.
•The many-to-many interface offers capability to load share and balance across networks. Operators have the flexibility to optimize on loading of the SBE or DBE.
Figure 1-3 on page 1-3 illustrates the distributed model.
Figure 1-3 Distributed SBC Model
SBC
SBE
Domain A |
Domain B |
|
DBE |
|
Standard |
|
H.248 |
|
Interface |
271027
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
1-3 |
|
|
|

Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
Supported Integrated Session Border Controller Features
Supported Integrated Session Border Controller Features
The supported features roadmap lists the features documented in this guide, Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers, and provides links to where they are documented. Any related configuration commands for a feature are listed and documented in the Cisco IOS Integrated Session Border Controller Command Reference.
Finding Support Information for Platforms and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS Software Images
Use Cisco Feature Navigator to find information about platform support and Cisco IOS and Catalyst OS software image support. To access Cisco Feature Navigator, go to: http://www.cisco.com/go/fn. An account on Cisco.com is not required.
Note Table 1-1 lists only the Cisco IOS XE software release that introduced support for a given feature in a given Cisco IOS XE software release train. Unless noted otherwise, subsequent releases of that Cisco IOS XE software release train also support that feature.
Table 1-1 lists features in alphabetical order and associated SBC commands that are supported on the Integrated Session Border Controller DBE deployment on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.
Table 1-1 |
Supported Integrated Session Border Controller Features |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chapter Where |
Release |
|
Feature Name |
Related SBC Commands |
Documented |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
|
Billing and Call Detail Records |
None. |
Chapter 11, “Quality |
XE Release |
|
|
|
Monitoring and |
2.0 |
|
|
|
Statistics Gathering” |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
|
DTMF Interworking |
dtmf-duration |
Chapter 3, “DTMF |
XE Release |
|
|
|
Interworking” |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
|
DBE Signaling Pinhole Support |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
|
|
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
|
DBE Status Notification |
None. |
Chapter 11, “Quality |
XE Release |
|
|
|
Monitoring and |
2.0 |
|
|
|
Statistics Gathering” |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
|
DSCP Marking and IP Precedence |
None |
Chapter 5, “Quality of |
XE Release |
|
Marking |
|
Service and Bandwidth |
2.0 |
|
|
|
Management” |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
|
Enabling Optional H.248 |
package |
Chapter 6, “H.248 |
XE Release |
|
Packages |
|
Packages—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
|
Enhanced Event Notification and |
h248-association-timeout |
Chapter 11, “Quality |
XE Release |
|
Auditing |
h248-event-storage |
Monitoring and |
2.0 |
|
|
Statistics Gathering” |
|
|
|
h248-preserve-gates |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
1-4 |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|

Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
Supported Integrated Session Border Controller Features
|
|
|
|
|
Chapter Where |
|
||
|
|
Release |
Feature Name |
Related SBC Commands |
Documented |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Extension to H.248 Audit Support |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
|
|
Services—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Extension to H.248 Termination |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Wildcarding Support |
|
Services—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Firewall (Media Pinhole Control) |
None. |
Chapter 8, “Integrated |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
|
|
Session Border |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
Controller Security” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Flexible Address Prefix |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Provisioning |
|
Services—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248 Address Reporting Package |
None. |
Chapter 8, “Integrated |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
|
|
Session Border |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
Controller Security” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248 Gate Information (Ginfo) |
None. |
Chapter 6, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Package Becomes Optional |
|
Packages—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248 Network Package Quality |
h248-media-alert-event |
Chapter 11, “Quality |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Alert Event and Middlebox |
|
Monitoring and |
|
||
2.0 |
Pinhole Timer Expired Event |
|
Statistics Gathering” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248 Segmentation Package |
package segment |
Chapter 6, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Support |
max-pdu-size |
Packages—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
package segment |
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
seg-timer-value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
show sbc dbe controllers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248 Session Failure Reaction |
None. |
Chapter 6, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Package |
|
Packages—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248 Termination State Control |
show sbc dbe |
Chapter 6, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Package |
media-flow-stats |
Packages—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
show sbc dbe |
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
signaling-flow-stats |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248 Traffic Management |
None. |
Chapter 5, “Quality of |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Package Support |
|
Service and Bandwidth |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
Management” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248 VLAN Package |
show sbc dbe |
Chapter 6, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
Syntax-Level Support |
media-flow-stats |
Packages—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
show sbc dbe |
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
signaling-flow-stats |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Cisco IOS |
H.248.1v3 Support |
h248-version |
Chapter 6, “H.248 |
|
||
|
|
XE Release |
|
|
Packages—Signaling |
|
||
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|
|
1-5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||

Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
Supported Integrated Session Border Controller Features
|
|
|
Chapter Where |
Release |
Feature Name |
Related SBC Commands |
Documented |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Integrated Session Border |
None |
Chapter 10, “High |
XE Release |
Controller High Availability |
|
Availability Support” |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Interim Authentication Header |
transport (see |
Chapter 8, “Integrated |
XE Release |
Support |
interim-auth-header |
Session Border |
2.0 |
|
keyword) |
Controller Security” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
IP NAPT Traversal Package and |
h248-napt-package |
Chapter 8, “Integrated |
XE Release |
Latch and Relatch Support |
|
Session Border |
2.0 |
|
|
Controller Security” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
IPv4 Twice NAPT |
None |
Chapter 9, “Topology |
XE Release |
|
|
Hiding” |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
IPv6 Inter-Subscriber Blocking |
None. |
Chapter 9, “Topology |
XE Release |
|
|
Hiding” |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
IPv6 Support |
ipv6 address (session |
Chapter 9, “Topology |
XE Release |
|
border controller) |
Hiding” |
2.0 |
|
media-address ipv6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
media-address pool ipv6 |
|
|
|
port-range (ipv6) |
|
|
|
debug sbc filter (see ipv6 |
|
|
|
keyword) |
|
|
|
show sbc dbe |
|
|
|
media-flow-stats (see |
|
|
|
ipv6 keyword) |
|
|
|
show sbc dbe |
|
|
|
signaling-flow-stats (see |
|
|
|
ipv6 keyword) |
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Local Source Properties (Address |
None. |
Chapter 8, “Integrated |
XE Release |
and Port) |
|
Session Border |
2.0 |
|
|
Controller Security” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Locally Hairpinned Sessions |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
|
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Logging Level in Configuring |
logging level |
Chapter 2, |
XE Release |
H.248 Logging Level |
logging filter control |
“Configuring |
2.1 |
|
Integrated Session |
|
|
protocol |
||
|
|
Border Controller” |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Media Address Pools |
media-address pool ipv4 |
Chapter 4, “Media |
XE Release |
|
media-address pool ipv6 |
Address Pools” |
2.0 |
|
|
|
|
port-range |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
1-6 |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|

Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
Supported Integrated Session Border Controller Features
|
|
|
Chapter Where |
Release |
Feature Name |
Related SBC Commands |
Documented |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
MGC-Controlled Gateway-Wide |
None. |
Chapter 6, “H.248 |
XE Release |
Properties |
|
Packages—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
MGC-Specified Local Addresses |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
or Ports |
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Multi-Stream Terminations |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
|
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
NAPT and NAT Traversal |
None. |
Chapter 8, “Integrated |
XE Release |
|
|
Session Border |
2.0 |
|
|
Controller Security” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Nine-Tier Termination Name |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
Hierarchy |
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Optional Local and Remote |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
Descriptors |
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Provisioned Inactivity Timer |
h248-inactivity-duration |
Chapter 11, “Quality |
XE Release |
|
|
Monitoring and |
2.0 |
|
|
Statistics Gathering” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
QoS Bandwidth Allocation |
None. |
Chapter 5, “Quality of |
XE Release |
|
|
Service and Bandwidth |
2.0 |
|
|
Management” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Remote Source Address Mask |
media-address ipv4 |
Chapter 8, “Integrated |
XE Release |
Filtering |
media-address pool ipv4 |
Session Border |
2.0 |
|
Controller Security” |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
RTCP Policing |
None |
Chapter 5, “Quality of |
XE Release |
|
|
Service and Bandwidth |
2.0 |
|
|
Management” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
RTP Specific Behavior Support |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
|
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
ServiceChange Notification for |
sbc interface-id |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
Interface Status Change |
|
Services—Signaling |
2.1 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
T-MAX Timer |
tmax-timer |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
|
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
The tsc-Delay Timer |
None. |
Chapter 7, “H.248 |
XE Release |
|
|
Services—Signaling |
2.0 |
|
|
and Control” |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
1-7 |
|
|
|

Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
Deployment of the Integrated Session Border Controller
|
|
|
Chapter Where |
Release |
Feature Name |
Related SBC Commands |
Documented |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
transaction-pending command |
transaction-pending |
Cisco IOS Integrated |
XE Release |
|
|
Session Border |
2.0.1 |
|
|
Controller Command |
|
|
|
Reference |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS |
Two-Rate Three-Color Policing |
control-dscp |
Chapter 5, “Quality of |
XE Release |
and Marking |
marker-dscp |
Service and Bandwidth |
2.0 |
|
pdr-coefficient |
Management” |
|
|
show sbc dbe |
|
|
|
forwarder-stats |
|
|
|
|
|
Deployment of the Integrated Session Border Controller
Deployment of the DBE function on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers integrates a subset of the Integrated Session Border Controller feature set with Cisco IOS XE software. A likely deployment scenario is that typical routing and broadband features are configured on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers serving as the DBE operating with an external SBE. The Integrated Session Border Controller functionality on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers will eventually comprise both DBE and SBE functions, with DBE being the first to be deployed.
DBE deployment of the SBC feature set is an optional feature supported on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers. DBE deployment on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers does not include SBE support and no SBE-related CLIs are implemented.
In the deployed distributed model, the SBE and the DBE entities reside on different network elements and the DBE is controlled by one SBE at any one time. The SBE interacts with the DBE using the H.248 Megaco (media gateway controller) protocol. The SBE controls the DBE via the H.248 interface. In this model, the bearer (or media flow) always flows through the DBE, and the SBE participates only in the signaling flow.
The DBE is responsible for the media flows and consists of a set of data path functions. The DBE responds to the requests made by the SBE to open pinholes, taking into account the specified NAT/firewall traversal and QoS requirements.
For the DBE, a new interface type is defined for the SBC virtual interface. You configure a virtual interface as part of the SBC configuration and the virtual interface has media IPs as primary or secondary IP addresses. The SBC virtual interface does not support any existing Cisco IOS features.
The Cisco IOS XE image containing SBC software leverages existing Cisco IOS install and packaging facilities for software release, delivery, and installation.
Cisco IOS commands have been introduced to configure the DBE. For information on commands, see the Cisco IOS Integrated Session Border Controller Command Reference.
Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment Scenario
One potential deployment scenario for Integrated Session Border Controller on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers is in a network architecture where the service provider (SP) provides voice, data, and video services to their residential broadband customers over a single link.
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
1-8 |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment Scenario
This scenario requires the SP to provide capabilities such as opening pinholes for the duration of a conversation, and doing this without exposing the devices behind the firewall to malicious threats. In addition, given that voice is extremely sensitive to issues such as delay, latency, and packet loss, ensuring adequate performance is a challenge. QoS mechanisms can be implemented to ensure proper priority is assigned to voice packets.
In this deployment scenario, multiple applications share a common link. Thus a mechanism that will limit bandwidth available to individual applications to ensure appropriate end-to-end quality is needed. For voice, this would involve correctly marking the packet to ensure appropriate priority, as well as controlling the number of simultaneous calls at the network entry point. Because the SP cannot dictate what IP phones their customers use, protocol conversion functionality is needed—especially H.323-to-SIP conversion.
Service providers require measurement of traffic for reporting and billing purposes in this potential scenario. Some carriers may also want to offer service level agreement (SLA) for voice, for which they want to be able to provide their customers with the proof that these SLAs are being met.
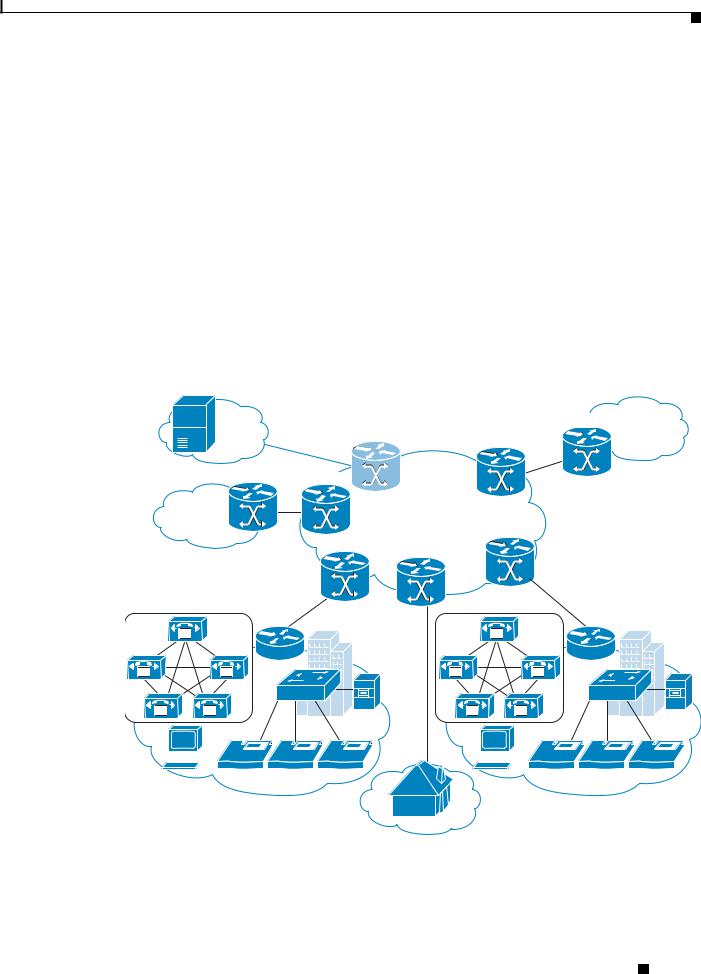
Figure 1-4 on page 1-9 illustrates a deployment where Integrated SBC is used for VoIP interworking.
Figure 1-4 Integrated SBC Used for VoIP Interworking
SP3 |
|
|
SBC |
SP2 |
|
|
IP/MPLS |
||
PSTN |
|
SBC |
|
|
|
|
Network |
||
|
|
|
||
SBC |
SBC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data |
|
SP1 |
|
|
|
IP/MPLS Network |
|
|
|
Center |
|
|
|
|
|
SBC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SBC |
SBC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SBC

 M
M


 M
M


 M
M


 M
M


 M
M



 IP
IP
 IP
IP
 IP
IP
SBC

 M
M


 M
M


 M
M


 M
M


 M
M



 IP
IP
 IP
IP
 IP
IP
Managed Enterprise |
Unmanaged Enterprise |
Residential Broadband
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
1-9 |
|
|
|

Chapter 1 Integrated Session Border Controller for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers Overview
Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment Scenario
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
|
|
|
|
||
|
1-10 |
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|
|
||

C H A P T E R 2
Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller
This chapter describes fundamental configuration tasks required for typical data border element (DBE) deployment of the Integrated Session Border Controller (SBC). The Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Router serves as the DBE. The DBE operates with a Signaling Border Element (SBE), also called a media gateway controller (MGC).
For a complete description of commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco IOS Integrated Session Border Controller Command Reference.
Contents
•Prerequisites for Integrated Session Border Controller, page 2-1
•Restrictions for Integrated Session Border Controller, page 2-1
•Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment, page 2-2
•Configuring H.248 Logging Level, page 2-6
•Configuration Examples, page 2-9
•Cisco H.248 Profile, page 2-14
Prerequisites for Integrated Session Border Controller
When running SBC with 500 or more active calls, ensure you configure the huge buffer size to 65535 bytes with the buffer huge size 65535 command. The increased buffer size is required because by default Cisco IOS software sets the “huge” buffer size to be 18084 bytes, which is not large enough for H.248 audit responses when there are more than 500 active calls.
Restrictions for Integrated Session Border Controller
The following are not supported by the SBC function on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers:
•Signaling Border Element (SBE) function and SBE CLIs
•Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) and VRF-Lite
•Digital signal processing (DSP)
•Network management system (NMS) configuration
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
2-1 |
|
|
|

Chapter 2 Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller
Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment
•Transcoding
•SBC virtual interface does not support any existing Cisco IOS features
Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller DBE
Deployment
This section contains steps to configure a typical DBE on the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers.
Prerequisites
When running SBC with 500 or more active calls, configure the huge buffer size to 65535 bytes with the buffer huge size 65535 command to ensure the buffer is large enough for H.248 audit responses.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.enable
2.configure terminal
3.interface sbc {interface-number}
4.ip address ip-address
5.exit
6.sbc {sbc-name} dbe
7.vdbe [global]
8.h248-version version
9.h248-napt-package [napt | ntr]
10.local-port {port-num}
11.control-address h248 ipv4 {A.B.C.D}
12.controller h248 {controller-index}
13.remote-address ipv4 {A.B.C.D}
14.remote-port {port-num}
15.transport {udp | tcp} [interim-auth-header]
16.exit
17.attach-controllers
18.exit
19.location-id {location-id}
20.media-address ipv4 {A.B.C.D}
21.activate
22.end
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
2-2 |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|

Chapter 2 Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller
Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment
DETAILED STEPS
|
Command or Action |
Purpose |
Step 1 |
|
|
enable |
Enables privileged EXEC mode. |
|
|
|
• Enter your password if prompted. |
|
Example: |
|
|
Router> enable |
|
Step 2 |
|
|
configure terminal |
Enters global configuration mode. |
|
|
Example: |
|
|
Router# configure terminal |
|
Step 3 |
|
|
interface sbc {interface-number} |
Creates an SBC virtual interface numbered 1 in the example |
|
|
|
and enters into interface configuration mode. |
|
Example: |
|
|
Router(config)# interface sbc 1 |
|
Step 4 |
|
|
ip address ip-address |
Configures an IP address on the SBC virtual interface. |
|
|
Example: |
|
|
Router(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 |
|
Step 5 |
|
|
exit |
Exits interface configuration mode. |
|
|
Example: |
|
|
Router(config-if)# exit |
|
Step 6 |
|
|
sbc {sbc-name} dbe |
Creates the DBE service on the SBC called “mySbc” in the |
|
|
|
example and enters into SBC-DBE configuration mode. |
|
Example: |
|
|
Router(config)# sbc mySbc dbe |
|
Step 7 |
|
|
vdbe [global] |
Enters into VDBE configuration mode with a default DBE |
|
|
|
named “global.” |
|
Example: |
Only one DBE is supported and its name must be “global.” |
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe)# vdbe global |
|
Step 8 |
|
|
h248-version version |
Specifies that the DBE uses an H.248 version when it forms |
|
|
|
associations with an H.248 controller. |
|
Example: |
Version 2 is the default. |
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe)# h248-version 3 |
|
Step 9 |
|
|
h248-napt-package [napt | ntr] |
Defines whether the DBE uses the Network Address and |
|
|
|
Port Translation (NAPT) or NAT Traversal (NTR) H.248 |
|
Example: |
package for signaling NAT features. NTR is the default. |
|
|
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe)# h248-napt-package |
The example configures the DBE to use NAPT. |
|
napt |
|
Step 10 |
|
|
local-port {port-num} |
Configures the DBE to use the specific local port number |
|
|
|
when connecting to the default media gateway controller |
|
Example: |
(MGC). |
|
|
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe)# local-port 2947 |
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
2-3 |
|
|
|

Chapter 2 Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller
Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment
|
|
Command or Action |
Purpose |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 11 |
control-address h248 ipv4 {A.B.C.D} |
Configures the DBE to use a specific IPv4 H.248 control |
||
|
|
|
|
address, which is the local IP address the DBE uses as its |
|
|
|
Example: |
own address when connecting to the SBE. |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe)# control-address |
|
|
|
|
|
h248 ipv4 210.229.108.254 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 12 |
controller h248 {controller-index} |
Configures the H.248 controller for the DBE and enters into |
||
|
|
|
|
Controller H.248 configuration mode. |
|
|
|
Example: |
In the example, the configured number 1 identifies the |
||
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe)# controller h248 1 |
H.248 controller for the DBE. |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 13 |
remote-address ipv4 {A.B.C.D} |
Configures the IPv4 remote address of the H.248 controller |
||
|
|
|
|
for the SBE. |
|
|
|
Example: |
In the example, 210.229.108.252 is configured as the |
||
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe-h248)# |
remote SBE IP address. |
||
|
|
remote-address ipv4 210.229.108.252 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 14 |
remote-port {port-num} |
Configures the port number of the H.248 controller that is |
||
|
|
|
|
used to connect to the SBE. |
|
|
|
Example: |
|
|
|
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe-h248)# remote-port |
|
|
|
|
|
2947 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 15 |
transport {udp | tcp} [interim-auth-header] |
Configures the DBE to use either UDP or TCP for H.248 |
||
|
|
|
|
control signaling. The command also configures the H.248 |
|
|
|
Example: |
controller to insert the interim authentication header into |
||
|
|
the H.248 messages and set all fields in the header to zeroes. |
|||
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe-h248)# transport udp |
|||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
interim-auth-header |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 16 |
exit |
Exits Controller H.248 configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: |
|
|
|
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe-h248)# exit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 17 |
attach-controllers |
Attaches the DBE to an H.248 controller. |
||
|
|
Example: |
|
|
|
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe)# attach-controllers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 18 |
exit |
Exits VDBE configuration mode. |
||
|
|
Example: |
|
|
|
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe-vdbe)# exit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 19 |
location-id {location-id} |
Configures a location ID for the DBE. |
||
|
|
|
|
The location ID is used by the network to route calls. |
|
|
|
Example: |
|
|
|
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe)# location-id 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Step 20 |
media-address ipv4 {A.B.C.D} |
Adds the IPv4 address to the set of addresses, which can be |
||
|
|
|
|
used by the DBE as a local media address. This address is |
|
|
|
Example: |
the SBC virtual interface address. |
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe)# media-address ipv4 |
Configure this command for each IP address that you |
||
|
|
1.1.1.1 255.0.0.0 |
specified under the SBC virtual interface in Step 4. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers |
||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2-4 |
|
|
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
|
|
|
||

Chapter 2 Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller
Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller DBE Deployment
|
Command or Action |
Purpose |
Step 21 |
|
|
activate |
Initiates the DBE service of the SBC. |
|
|
Example: |
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe)# activate |
|
Step 22 |
|
|
end |
Exits SBC-DBE configuration mode and returns to |
|
|
|
privileged EXEC mode. |
|
Example: |
|
|
Router(config-sbc-dbe)# end |
|
|
|
|
What To Do Next
See the “Configuring H.248 Logging Level” section on page 2-6 if you want to set console logging other than default logging and turn on H.248 logging messages.
See Chapter 4, “Configuring Media Address Pools” for information on what to configure next on the DBE.
Examples
The DBE does not always attach or detach from its controller immediately. You can use the show sbc dbe controllers command to display status information on whether the controller is attached or detached.
The following example uses the show sbc dbe controllers command to display status information showing that the vDBE with a location ID of 1 on an SBC called “mySbc” is attached to its controller:
Router# show sbc mySbc dbe controllers
SBC Service “mySbc”
vDBE in DBE location |
1 |
|
|
|
Media gateway |
controller in use: |
|
|
|
H.248 controller |
address |
|
|
|
210.229.108.252:2944 |
|
|
||
Status: |
|
Attached |
|
|
|
Sent |
Received |
Failed |
Retried |
Requests |
1 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
Replies |
6 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Configured controllers:
H.248 controller 1:
Remote address: 210.229.108.252:2944 (using default port)
Transport: UDP
Troubleshooting Tips
Use this troubleshooting tip when you receive a “Bad getbuffer” log message.
Problem: You receive a “Bad getbuffer” log message
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
|
OL-15421-01 |
2-5 |
|
|
|

Chapter 2 Configuring Integrated Session Border Controller
Configuring H.248 Logging Level
You run over 500 active calls on your DBE deployment and you receive the following log message:
*Feb 11 11:35:52.909: %SYS-2-GETBUF: Bad getbuffer, bytes= 34506 -Process= "SBC main process", ipl= 0, pid= 183
-Traceback= 70EDFC 747354 9942D0 AFC6E4 B01AC4 29637B0 2960FCC 24C7F04 24C7918 24C7AD0 24D97AC 24D8790 2987C70
*Feb 11 11:35:52.909: %SBC-2-MSG-0303-0046: (sckrecv2.c 991) Socket write error.
Sockets error code = 255 Socket ID = 0
*Feb 11 11:35:52.909: %SBC-2-MSG-0303-0025: (sckis.c 112) General sockets layer error detected.
Sockets error code = 255
*Feb 11 11:35:52.909: %SBC-2-MSG-2E01-0014: (gctpfsm.c 730) An association with a peer has become disconnected.
Peer's address = 200.10.255.252 Peer's port = 2944
Reason code = 0X04
Solution: Change huge buffer size.
Change your huge buffer size to 65535 bytes. This is the recommended huge buffer size for deployment of more than 500 active calls due to the need for increased buffer size for H.248 audit responses.
Configuring H.248 Logging Level
This section contains steps to configure a sample configuration where console logging for H.248 messages sent and received is turned on and the H.248 protocol message filter is enabled to display only the H.248 text without any internal message logs.
SUMMARY STEPS
1.enable
2.configure terminal
3.sbc {sbc-name} dbe
4.vdbe [global]
5.h248-version version
6.h248-napt-package [napt | ntr]
7.local-port {port-num}
8.control-address h248 ipv4 {A.B.C.D}
9.logging level [value]
10.logging filter control protocol (Optional)
11.controller h248 {controller-index}
12.remote-address ipv4 {A.B.C.D}
13.remote-port {port-num}
14.exit
15.attach-controllers
Cisco IOS XE Integrated Session Border Controller Configuration Guide for the Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers
2-6 |
OL-15421-01 |
|
|
 Loading...
Loading...