Abit IT5 User Manual

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction of IT5 Series Features
¬ IT5V ..................................................................................... |
1-2 |
• Specifications .................................................................... |
1-2 |
• Layout diagram ................................................................. |
1-4 |
• System block diagram ....................................................... |
1-5 |
- IT5H ..................................................................................... |
1-6 |
• Specifications .................................................................... |
1-6 |
• Layout diagram ................................................................. |
1-8 |
• System block diagram ....................................................... |
1-9 |
Chapter 2 Installing the Mainboard |
|
¬ Standard External Connectors ................................................ |
2-3 |
- Jumpers and Switches .......................................................... |
2-10 |
® Presentation and Installation of the CPU ............................... |
2-11 |
¯ Installing Pipeline Burst SRAM............................................. |
2-14 |
° Installing System Memory DRAM Memory ................ |
2-15 |
Chapter 3 Introduction to BIOS |
|
¬ CPU setup CPU SOFT MENU™ ................................ |
3-4 |
- Standard CMOS Setup Menu.............................................. |
3-10 |
® BIOS Features Setup Menu ................................................. |
3-12 |
¯ Chipset Features Setup Menu............................................... |
3-18 |
° Power Management Setup Menu.......................................... |
3-20 |
± PCI & Onboard I/O Setup................................................... |
3-24 |
² Load BIOS Defaults ............................................................ |
3-30 |
³ Load Setup Defaults............................................................. |
3-30 |
´ Password Setting ................................................................. |
3-31 |
µ IDE HDD Auto Detection.................................................... |
3-32 |
Part Number:MN-090-B41-91 |
Rev:1.04 |
Appendix A Quick Installation
Appendix B Intel Pentium CPUs
Appendix C AMD-K5 CPUs
Appendix D Cyrix 6x86 CPUs
Appendix E General Discussion about HDD Installation
Appendix F Technical Support
Appendix G Flash BIOS User Instructions

Introduction of IT5 Series Features |
1-1 |
Chapter 1 Introduction of IT5
Series Features
The IT5 series has been especially designed for File server, Workstation and Professional users. It can support a wide range of processors, including all Intel CPUs (P54C) and Intel CPUs with MMX (P55C), as well as all AMD-K5 and Cyrix 6x86/6x86L CPUs. It also takes into account, as much as possible, all future CPUs.
This series uses SOFT MENU™ technology, which means that all the parameters can be configured without using DIP switches or jumpers. The configuration is entirely achieved through a “Soft Switch” that allows the user to set CPU speed and operating voltage with ease.
The IT5 series uses Intel 430VX and 430HX series chipsets, and has 256K or 512K Level-2 Pipeline Burst SRAM on board. It also provides an extension slot allowing the user to upgrade Pipeline Burst SRAM to 512K.
Two 168-pin DIMM slots and four 72-pin SIMM slots meet the requirements for all memory configurations required by high level computing. The 168-pin DIMM slots support traditional Fast Page and EDO DRAM as a memory standard for next generation 64-bit systems. The two 168-pin DIMM slots have been reserved to meet requirements for both present and future upgrades.
This series also provides two Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports and meets the Concurrent PCI Rev. 2.1 standard. It also supports IDE interface for Fast HDD (Mode 0~4), as well as IDE Bus Master. These features also meet present and future interface standards and needs.
System BIOS features include Plug-and-Play (PnP), Advanced Power Management (APM), the newest Desktop Management Interface (DMI), as well as IT5’s unique CPU operating frequency and voltage setup feature in order to meet modern computing demands.

1-2 |
Chapter 1 |
¬ IT5V
• Specifications:
1. CPU frequency and voltage setup with CPU “SOFT MENU™ ”
•Setup of the mainboard’s frequency and voltage without DIP Switches or Jumpers.
•Modification of CPU operating voltage and frequency through software configuration.
•Modification of CPU operating voltage and frequency directly on screen.
2.Uses ZIF CPU Socket 7 for easy CPU installation
•Three voltage regulator/cooling plate sets for a more stable CPU operating environment
•Supports Intel Pentium® CPUs: 75MHz to 200MHz and P55C CPUs with MMX
• |
Supports all AMD sixth generation AMD-K5™ CPUs: 75MHz |
|
to 166MHz, AMD-K6™ CPUs: 200MHz and 233MHz |
• |
Supports all Cyrix sixth generation 6x86™ CPUs: P120+, P133+, |
|
P150+, P166+ |
•Reserved circuitry supports future sixth generation CPUs
3.Chipset
•Intel 430VX chipset
•Supports standard version PCI 2.1
4.L2 Cache Memory
•256K or 512K of cache memory (Pipeline Burst SRAM)
•Cache memory upgradeable to 512K
5.System DRAM
•Four 72-pin SIMM sockets: support FP and EDO DRAM
•Two 168-pin DIMM sockets: support FP, EDO and Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM)
•DIMM sockets use PC modules (3.3V Unbuffered DRAM)
•Up to 128MB memory configuration possible
Introduction of IT5 Series Features |
1-3 |
6. System BIOS
•AWARD BIOS
•Supports Plug-and-Play (PnP)
•Supports Advanced Power Management (APM)
•Supports Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
7.Multi I/O features
•Two Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports
•Four fast IDE channels (PIO mode 0~4 and Bus Master)
•One EPP/ECP parallel port and one 16550 serial port
•Two floppy disk drive connectors (FDD) (360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M and 2.88M)
8.Other features
•Standard AT architecture dimensions
•Four ISA bus slots and four PCI bus slots
•Supports 3-MODE for a special Japanese floppy disk drive
•Supports two bootable hard disks--able to run two different operating systems
Note: All brand names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1-4 |
Chapter 1 |
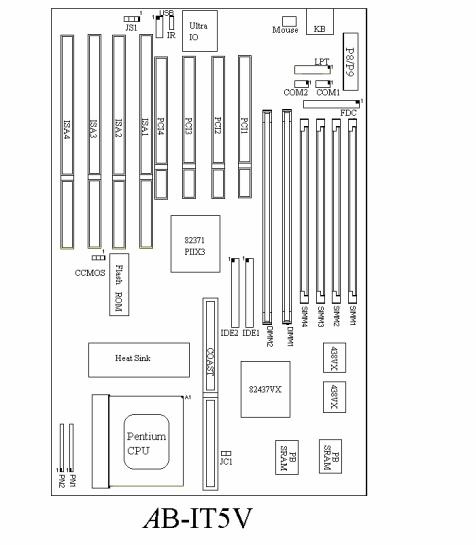
• Layout diagram
Fig 1-1 Layout diagram
Introduction of IT5 Series Features |
1-5 |
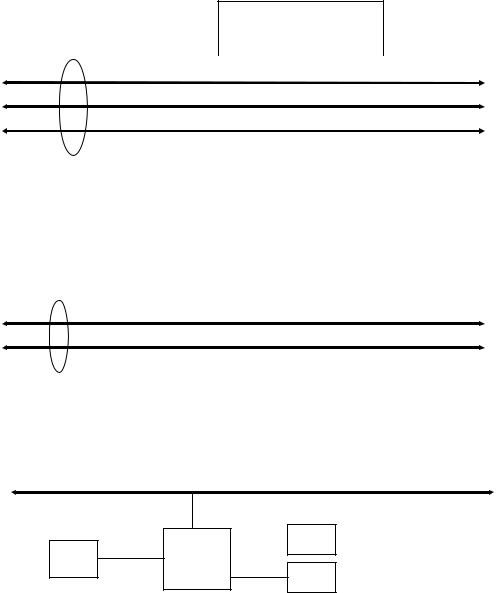
• System block diagram
Pentiumä Processor
3.3V
|
|
Host BUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Second Level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Cache |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ctrl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
CACHE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addr |
|
Main |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
(SRAM) |
Tag Ctrl |
|
|
TVX |
|
Ctrl |
Memory |
|
|
|
|
TDX |
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
TIO[0..7] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
TAG |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(DRAM) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plink |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TXD Ctrl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
PCI BUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address/Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
USB |
|
USB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Fast |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCI Device(s) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
CD ROM & |
|
IDE |
PIIX3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Hard Disk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ISA Devi ce(s) |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Universal Serial Bus |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
ISA BUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ALi |
|
LPT |
|
||
|
|
Serial
M5123
FDC
Fig. 1-2 System block diagram

1-6 |
Chapter 1 |
- IT5H
• Specifications:
1.CPU frequency and voltage configuration with CPU “SOFT
MENU™ ”
• Setup of the mainboard’s frequency and voltage without DIP Switches or Jumpers.
• Modification of CPU operating voltage and frequency through software configuration.
• Modification of CPU operating voltage and frequency directly on screen.
2.Uses ZIF CPU Socket 7 for easy CPU installation
•Three voltage regulator/cooling plate sets for a more stable CPU operating environment
•Supports Intel Pentium® CPUs: 75MHz to 200MHz and P55C CPUs with MMX
• Supports all AMD sixth generation AMD-K5™ CPUs: 75MHz to 166MHz, AMD-K6™ CPUs: 200MHz and 233MHz
• Supports all Cyrix sixth generation 6x86™ CPUs: P120+, P133+, P150+, P166+
•Reserved circuitry supports future sixth generation CPUs
3.Chipset
•Intel 430 HX chipset
•Supports standard version PCI 2.1
4.L2 Cache Memory
•256K or 512K of cache memory (Pipeline Burst SRAM)
•Cache memory upgradeable to 512K
5.System DRAM
•Four 72-pin SIMM sockets: support FP and EDO DRAM
•Two 168-pin DIMM sockets: support FP, EDO
•DIMM sockets use PC modules (3.3V Unbuffered DRAM)
•Supports error check and correction (ECC) function
•Up to 512MB memory configuration possible
Introduction of IT5 Series Features |
1-7 |
6. System BIOS
•AWARD BIOS
•Supports Plug-and-Play (PnP)
•Supports Advanced Power Management (APM)
•Supports Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
7.Multi I/O features
•Two Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports
•Four fast IDE channels (PIO mode 0~4 and Bus Master)
•One EPP/ECP parallel port and one 16550 serial port
•Two floppy disk drive connectors (FDD) (360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M and 2.88M)
8.Other features
•Standard AT architecture dimensions
•Four ISA bus slots and four PCI bus slots
•Supports 3-MODE for a special Japanese floppy disk drive
•Supports two bootable hard disks--able to run two different operating systems
Note: All brand names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1-8 |
Chapter 1 |
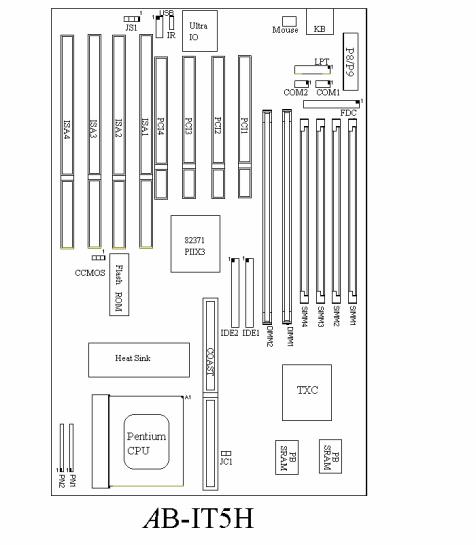
• Layout diagram
Fig. 1-3 Layout diagram

Introduction of IT5 Series Features |
1-9 |
• System block diagram
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pentiumä Processor |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
Host BUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.3V |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Second Level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Cache |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ctrl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Addr |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
CACHE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Tag Ctrl |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
(SRAM) |
|
|
TXC |
|
Ctrl |
|
Memory |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
TIO[0..7] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(DRAM) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ECC |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
TAG |
|
TIO[8..10] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCI BUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address/Data |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
USB |
|
|
USB |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
Fast |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PCI Device(s) |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
CD ROM & |
|
IDE |
|
PIIX3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Hard Disk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ISA Device(s) |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Universal Serial Bus |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
ISA BUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ALi |
|
LPT |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Serial |
|
|
|
|||
|
M5123 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
FDC |
||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1-10 |
Chapter 1 |
Fig. 1-4 System block diagram
Introduction of IT5 Series Features |
1-11 |

Installing the Mainboard |
2-1 |
Chapter 2 Installing the
Mainboard
This mainboard series not only provides all standard equipment for classic personal computers, but also provides great flexibility for meeting future upgrade demands. This chapter will introduce step by step all the standard equipment and will also present, as completely as possible future upgrade capabilities. This mainboard is able to support all Intel Pentium including P55C with MMX, Cyrix 6x86, 6x86L and AMD-K5 processors now on the market. (For details, see specifications in Chapter 1.) However, we cannot guarantee that the description given in this manual on the circuitry of your mainboard will work for processors not listed in Chapter 1. For example, the operating voltage of Cyrix’s next generation CPUs is unknown at the present time. Thus we were not able to include these specifications in your motherboard. We will supply further information about CPU support when new CPUs arrive on the market.
This chapter is organized according the following features: ΠStandard external connectors
• Jumpers and switches
ŽInstalling the CPU--steps for installing Intel, Cyrix and AMD processors.
•Installing cache memory--If you don’t want to upgrade the cache memory you can skip this chapter.
•Installing the system memory.
NNNN
Before proceeding with the installation
Before installing the mainboard please be sure to turn off or disconnect the power supply unit. Before making any modifications to the hardware configuration of the mainboard, the power supply to any areas of the mainboard you plan to modify should be turned off to avoid unnecessary damage to the hardware.
2-2 |
Chapter 2 |
&
User friendly instructions
Our objective is to enable the novice computer user to perform the installation by themselves. We have attempted to write this document in a very clear, concise and descriptive manner to help overcome any obstacles you may face during installation. Please read our instructions carefully and follow them carefully step-by-step.
Installing the Mainboard |
2-3 |
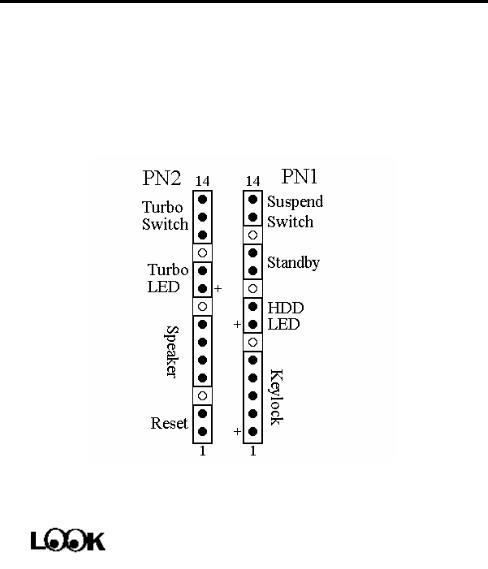
¬ Standard External Connectors
Inside the case of any computer several cables and plugs have to be connected. These cables and plugs are usually connected one-by-one to connectors located on the mainboard. You need to carefully pay attention to any connection orientation the cables may have and, if any, notice the position of the first pin of the connector. In the explanations that follow, we will describe the significance of the first pin.
PN1 - Keylock connector Please pay attention to pin position and
orientation
This connector has a specific orientation. Connect the five-thread keylock connector cable to the PN1 connector pins on the mainboard.
Pin number |
Name or significance of signal |
1 |
+5VDC |
2 |
No connection |
3 |
Ground |
4 |
Keyboard inhibit Signal |
5 |
Ground |

2-4 |
Chapter 2 |
Computer The “keylock switch” is used to lock the computer’s Knowledge keyboard. This disables the keyboard so that unauthorized persons cannot use it. When this function is in use, you will
need to use the unlock key to activate the keyboard.
PN1 - IDE LED connector
This connector has a specific orientation. connector cable attached to the case to mainboard.
Connect the two-thread IDE LED the IDE LED connector on the
Pin number |
Name or significance of signal |
7 |
LED’s Cathode |
8 |
LED’s Anode |
PN1 - Standby connector
There is no specific orientation. Most of the present AT cases do not support this feature so most of you can ignore this instruction. If your case has a cable for the Standby feature, you should connect this cable to the connector on the Mainboard.
Pin number |
Name or significance of signal |
10 |
Standby power supply +5VSB |
|
|
11 |
Control signal of computer switch of the case |
Computer knowledge
The “standby connector,” unlike the traditional mechanical switch, is an electronic way to turn the computer’s power off. To use this feature, the power supply system must permit a shutdown power supply (+5VSB), support the electronic switch feature, and must also be used with connector JS1 on the mainboard. For example, when using Windows 95, your computer will automatically shut down after having saved your work when you exit Windows. You do not need to use the mechanical switch to turn the computer off.
Installing the Mainboard |
2-5 |
PN1 - Hardware Suspend switch
There is no specific orientation. Connect the two-thread hardware suspend plug to the PN1 connector pins on the mainboard. Since most cases do not support this feature, most of you ignore this instruction. Furthermore, this feature is not necessary as it is already a part of the mainboard.
Pin number |
Name or significance of the signal |
13 |
Suspend |
14 |
Ground |
PN2 - Hardware Reset connector
There is no specific orientation. Connect the two-thread hardware reset cable to the PN2 connector pins on the mainboard.
Pin number |
Name or significance of signal |
1 |
Ground |
2 |
Hardware reset signal |
Computer knowledge
The “Hardware Reset” is used to reset the computer during operation without turning the computer off and back on. For example, if you are running an application that stops responding to the computer, you may press the Reset button to restart the computer.
PN2 - Speaker connector
There is no specific orientation. Connect the four-thread speaker cable to the PN2 connector pins on the mainboard.
Pin number |
Name or significance of signal |
4 |
+5VDC |
5 |
Ground |
6 |
Ground |
7 |
Sound Signal |

2-6 |
Chapter 2 |
PN2 - Turbo switch LED connector
This connector has a specific orientation. Connect the two-thread turbo switch LED plug to the PN2 connector pins on the mainboard.
Pin number |
|
Name or significance of signal |
|
9 |
|
Anode terminal of Turbo LED |
|
10 |
|
Cathode terminal of Turbo LED |
|
Computer |
The “hardware Turbo LED” indicates the status of hardware |
||
knowledge |
operating speed. |
||
JS1 - Power Control connector
This has a specific orientation. The present power supply units of AT computer do not support this feature, so you can ignore this connector. If your power supply unit features this connector, insert plug JS1, but be sure that the signification of the signal cable is the same, and be sure to use this feature in connection with the Standby connector on connector PN1.
Pin number |
Name of the signal or signification |
1 |
Power supply control signal PS_ON |
|
|
2 |
Standby power supply +5VSB |
|
|
3 |
Ground |

Installing the Mainboard |
2-7 |
FAN - CPU Fan power connector
This has a specific orientation. Connect the three-threads CPU fan cable to the Fan connector.
Pin number |
Name of the signal or signification |
1 |
Ground |
2 |
+12V |
3 |
Ground |
Mouse - PS/2 Mouse connector Watch the pin number and the orientation
This has a specific orientation. Connect the six-threads PS/2 Mouse cable provided to the Mouse connector on the mainboard.
Pin number |
Name of the signal or signification |
1 |
Mouse data |
2 |
No connection |
3 |
Ground |
4 |
+5VDC |
5 |
Ground |
6 |
Mouse clock |
Computer knowledge
The “PS/2 Mouse Port” is different from COM1 or COM2 serial ports to which you can also connect a Mouse. This mainboard features an extra PS/2 Mouse port, so when you buy a mouse, be sure that it is a PS/2 Mouse before connecting it to this port. But if you cannot find any PS/2 Mouse, you can still use COM1 or COM2 to connect a serial mouse to your computer.

2-8 |
Chapter 2 |
J2 - Keyboard Connector
This has an orientation pin. Connect your keyboard connector to connector J2 on the mainboard.
Pin number |
Name of the signal or signification |
1 |
Keyboard clock |
2 |
Keyboard data |
3 |
No connection |
4 |
Ground |
5 |
+5VDC |
P8/P9 - Power input Connectors Watch the pin number and the orientation
These have a specific orientation. The three warning marks indicate that if you make a mistake in pin number or connection orientation, you could destroy your equipment. During installation, you just need to connect to the correct pins and in the correct orientation, and to connect connectors P8 and P9 of the power supply unit to the connectors on the mainboard.
Pin number |
Name of the signal or |
Pin number |
Name of the signal or |
|
signification |
signification |
|||
|
|
|||
1 |
POWERGOOD |
7 |
Ground |
|
2 |
+5VDC |
8 |
Ground |
|
3 |
+12VDC |
9 |
-5VDC |
|
4 |
-12VDC |
10 |
+5VDC |
|
5 |
Ground |
11 |
+5VDC |
|
6 |
Ground |
12 |
+5VDC |

Installing the Mainboard |
2-9 |
IR - Infrared remote Connector Watch the pin number and the orientation
This has a specific orientation. Your mainboard supports this feature, but you must buy the infrared remote device as an option.
Pin number |
Name of the signal or signification |
1 |
+5VDC |
2 |
No connection |
3 |
Receive data |
4 |
Ground |
5 |
Transmit data |
I/O Port connectors Watch the pin number and the orientation
Connector name |
Pin number |
Name of the peripheral connected |
IDE 1 |
40 |
IDE Channel 1 |
|
|
|
IDE 2 |
40 |
IDE Channel 2 |
|
|
|
FDC |
34 |
Floppy Disk connector |
|
|
|
LPT |
26 |
Parallel port connector |
|
|
|
COM1 |
10 |
Serial port COM1 connector |
|
|
|
COM2 |
10 |
Serial port COM2 connector |
|
|
|
USB |
16 |
Universal Serial Bus connector |
|
|
|

2-10 |
Chapter 2 |
- Jumpers and Switches
CCMOS : Delete the contents of the CMOS
This jumper is set on pins 1 and 2 at the factory, in order for the computer to function normally, so please do not change this setting. The main feature of this jumper is to solve situations where the computer crashes due to improper usage. For instance:
•You have forgotten the password you set.
•You have changed inappropriately the settings in the BIOS menu.
•You want to change the version of flash BIOS.
All these errors are very serious, you must avoid them. But if you have made one of these errors, this jumper can save your life. First turn off the power supply and open the computer case, than place the jumper on pins 2 and 3 in order to save your computer. But if you use your computer normally, you should not need to use this feature.
After you have deleted the CMOS information, the computer is saved, but you still have to go back to the BIOS Setup menu, and reset one by one all the specifications: CPU, date, hour, FDD and HDD parameters. etc., before your computer will get back into normal operation.
JC1 Installing the cache memory in the cache memory extension slot (COAST)
On delivery, the IT5 mainboard comes with a 256K or 512K cache memory. If you already have 512K, your mainboard will not need a cache extension, and you will not be able to see the extension slot. But if you have only 256K, we have reserved an extension slot which permits you to extend the cache to 512K. This is set up at the factory with no jumper, which is what we call OFF status. You will need to put the jumper in place only when you extend the cache. For more details, refer to the section which deals with cache memory.

Installing the Mainboard |
2-11 |
® Presentation and Installation of the CPU
Jumperless Mainboard (Mainboard with no DIP Switch or Jumper)
This mainboard series can be installed with CPU without the hardware setting of the CPU.
On other boards, when you want to install the CPU, you have, more or less, to setup some jumpers or DIP switches. With this mainboard, you will not need to adjust any jumper or switch. The CPU speed and model is set up by software, in order to allow the user to complete setup and installation procedures easily. After you have inserted the CPU on the CPU socket, you can close the computer case and turn the computer on. You just need to enter the CPU SOFT MENU™ located in the BIOS Setup, and to setup the speed and the voltage of the CPU to compete the installation. Even if you don’t need to setup any switch, we recommend you to read our presentation of the CPUs, it will be useful information for you.
Since 1996, every two or three months, Intel adds new models to the Pentium CPU series. That is why the CPU market is filled with a lot of different models and brands. All CPUs have different electrical specifications. That’s why installing a CPU is becoming more and more complex. You can’t help that, because everybody wants to be able to upgrade its hardware. So, you have to take a bit of time to read this section, in order to be able to install a cheaper and better processor.
This mainboard does not only support all the CPUs listed in the specifications, but also has reserved several circuits in order to be able to support future processors. But before we go further in our presentation, we must clarify that “we have only tested the CPUs listed in Chapter 1”, we cannot guarantee that this board will be able to support future products, because we cannot forecast future developments. But we will do our best to support any possible CPU.
Related terminology :
External clock
Also referred to as the external CPU clock, or “Bus clock”, it is the input clock of the CPU. For instance, Intel Pentium P90, P120 and P150 all have a 60MHz external CPU clock, but have different internal clock
2-12 |
Chapter 2 |
multiplier factors.
Installing the Mainboard |
2-13 |
Clock multiplier factor
The real operation clock within the CPU is the multiple of the external clock. We refer to this factor as the clock multiplier factor. The four factors possible are 1.5, 2, 2.5 and 3. The factor differs from one CPU to another. For instance, the Intel Pentium 166 CPU has a 66MHz external clock, with a multiplier factor of 2.5, so that the speed of the internal clock is 66MHz x 2.5.
Internal clock
Also referred to as the real internal CPU clock, it is the actual internal operating clock of the CPU. The Internal Clock is a multiple of the external clock and of the clock multiplier factor. For instance, the Intel Pentium 90 CPU has a 60MHz external clock and its clock multiplier factor is 1.5; the Intel Pentium P133 CPU has a 66MHz external clock and its clock multiplier factor is 2.
Internal CPU clock = clock multiplier factor x external CPU clock
AT Bus clock
Also referred to as ISA SPEED, or AT CLOCK, or even ISA Bus clock. Ten years ago, the original specification of AT Bus clock installed in the first generation PC/AT computers was 8MHz, this means that there are some interface cards which can only work at 8MHz. In order to guarantee compatibility with older hardware, we still support 8MHz AT Bus clock, but if your interface card is newer or faster, you can choose a higher speed for the AT Bus clock, in order to increase the transmission rate of the interface cards. But we recommend you not to be too ambitious. An 8MHz setup ensures maximum compatibility.
CPU Voltage - Vcore and Vio
From the voltage point of view, 586 series CPU can be divided into two categories: single voltage CPU and dual voltage CPUs. Single voltage CPUs include: Intel Pentium P54C series, AMD-K5 and Cyrix 6x86, etc. Dual voltage CPUs include: Intel P55C with MMX, future AMD CPUs, Cyrix 6x86L and M2.
The voltage of dual voltage CPUs has two components: Vcore and Vio. Vcore provides all the power for internal processing, and its power consumption is quite important. Vio provides the power necessary for the external interface of the CPU.

2-14 |
Chapter 2 |
P-Rating
The P-Rating was defined by some manufacturers other than Intel to rate the performance of their CPU in comparison with Intel Pentium CPUs. For instance, Cyrix 6x86 P166+ has a higher actual speed compared with Intel Pentium P166, its internal clock needs only 133MHz versus 166MHz for Intel’s product. The main reason is that Cyrix has improved the internal architecture of the 6x86 CPU, which means that with the same internal clock speed, the actual clock speed will be different.
Having read the related terminology above, please refer to the information in appendices B, C or D for the type and specifications of your own CPU. We suggest that you note down these specifications, which will help you when you install the CPU.
CPU Settings:
CPU SOFT MENU
To configure the speed and the voltage of the CPU, you must enter to the CPU SOFT MENU in BIOS Setup.

Installing the Mainboard |
2-15 |
¯ Installing Pipeline Burst SRAM
This mainboard features a 256K or 512K cache memory. It also features a cache memory extension socket (COAST) in order to permit you to upgrade 256K cache to 512K, and this with only one JC1 to choose from. Installation is very easy. Refer to the table below:
Configuration |
With 32K32 |
With 64K32 |
Cache socket |
Cache total |
JC1 |
|
SRAM |
SRAM |
settings |
||||
|
|
|
||||
Mode 1 |
NO |
NO |
NO |
0K |
OFF |
|
Mode 2 |
YES |
NO |
NO |
256K |
OFF |
|
Mode 3 |
YES |
NO |
256K module |
512K |
ON |
|
Mode 4 |
NO |
NO |
256K module |
256K |
OFF |
|
Mode 5 |
NO |
NO |
512K module |
512K |
ON |
|
Mode 6 |
NO |
YES |
NO |
512K |
OFF |
Notes 1. If your mainboard features a 512K cache when it is delivered from the factory (Mode 6 in the table), the mainboard will not have any cache extension slot (COAST) or JC1 jumper.
2.The configurations listed in the table are all the possible configurations reserved when the board was designed. The actual configuration when the board is delivered depends mainly on the demands of the market.

2-16 |
Chapter 2 |
° Installing System Memory DRAM Memory
When this mainboard was designed, we not only have taken into account the present needs, but we have also tried to care about demands for future upgrades:
1.Two 168-pin DIMM sockets:
Within 3 to 5 years, you may not be able to buy 72-pin SIMM memory modules anymore, just as now you cannot find 30-pin SIMM memory modules anymore. If you want to extend your memory capacity, you will have no solution other than to use 168-pin 3.3V unbuffered DIMM sockets.
2.Four 72-pin SIMM sockets:
Currently, the most common memory modules on the market are 72-pin SIMM modules. The four 72-pin SIMM sockets of this mainboard will meet your needs.
3.Easy installation
You just need to insert the modules, without the help of God. Isn’t it great?
Besides the features mentioned above, you can use simultaneously 72-pin SIMM modules and 168-pin DIMM modules, but you will rarely encounter this kind of configuration. Before you proceed with installation, be patient, first read what follows:
1.Factory default setting of the mainboard is for 70ns FP or EDO modules.
If your memory modules are faster than 70ns, say 60ns or 45ns, you can modify the BIOS settings in order to speed up the operating speed of the system. But if you don’t want to modify these settings, or if you don’t know how to modify them, it’s no big deal.
But if you set the external CPU clock at 66MHz or more, we recommend you use 60ns or even faster DRAM modules.
2.Memory error check and correction feature on this mainboard.
 Loading...
Loading...