3COM 5500-SI User Manual

3Com® Switch 5500 Family
Configuration Guide
Switch 5500-SI
Switch 5500-EI
Switch 5500G-EI
www.3Com.com
Part Number: 10014922 Rev. AC Published: December 2006
3Com Corporation
350 Campus Drive
Marlborough, MA
USA 01752-3064
Copyright © 2006, 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation, transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in content from time to time without obligation on the part of 3Com Corporation to provide notification of such revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or condition of any kind, either implied or expressed, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties, terms or conditions of merchantability, satisfactory quality, and fitness for a particular purpose. 3Com may make improvements or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this documentation at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it is furnished under a license agreement included with the product as a separate document, in the hard copy documentation, or on the removable media in a directory file named LICENSE.TXT or !LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to locate a copy, please contact 3Com and a copy will be provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the software described herein are provided to you subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and developed solely at private expense. Software is delivered as “Commercial Computer Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014 (June 1995) or as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR 2.101(a) and as such is provided with only such rights as are provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the Software. Technical data is provided with limited rights only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015 (Nov 1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987), whichever is applicable. You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any licensed program or documentation contained in, or delivered to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the United States and may or may not be registered in other countries.
3Com and the 3Com logo are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation.
Cisco is a registered trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc.
Funk RADIUS is a registered trademark of Funk Software, Inc.
Aegis is a registered trademark of Aegis Group PLC.
Intel and Pentium are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Novell and NetWare are registered trademarks of Novell, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and other countries, licensed exclusively through X/Open Company, Ltd.
IEEE and 802 are registered trademarks of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.
ENVIRONMENTAL STATEMENT
It is the policy of 3Com Corporation to be environmentally-friendly in all operations. To uphold our policy, we are committed to:
Establishing environmental performance standards that comply with national legislation and regulations.
Conserving energy, materials and natural resources in all operations.
Reducing the waste generated by all operations. Ensuring that all waste conforms to recognized environmental standards. Maximizing the recyclable and reusable content of all products.
Ensuring that all products can be recycled, reused and disposed of safely.
Ensuring that all products are labelled according to recognized environmental standards.
Improving our environmental record on a continual basis.
End of Life Statement
3Com processes allow for the recovery, reclamation and safe disposal of all end-of-life electronic components.
Regulated Materials Statement
3Com products do not contain any hazardous or ozone-depleting material.
Environmental Statement about the Documentation
The documentation for this product is printed on paper that comes from sustainable, managed forests; it is fully biodegradable and recyclable, and is completely chlorine-free. The varnish is environmentally-friendly, and the inks are vegetable-based with a low heavy-metal content.

3
CONTENTS
CONTENTS
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
|
Organization of the Manual 21 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Intended Readership 22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Conventions |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Related Manuals |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
GETTING STARTED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Product Overview |
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XRN Overview |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Major Technologies |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Typical Networking Topology |
26 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Product Features |
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Logging in to the Switch |
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Setting up Configuration Environment through the Console Port |
29 |
|||||||
|
Setting up Configuration Environment through Telnet 31 |
|
|||||||
|
Setting up Configuration Environment through a Dial-up Modem |
33 |
|||||||
|
Command Line Interface |
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Command Line View |
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Features and Functions of Command Line |
40 |
|
||||||
|
User Interface Configuration |
42 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
User Interface Configuration |
43 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Displaying and Debugging User Interface |
49 |
|
||||||
2 |
|
|
|||||||
ADDRESS MANAGEMENT CONFIGURATION |
|
||||||||
|
Introduction to Address Management |
51 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring Address Management |
51 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring a Port-Based Address Management IP Address Pool |
51 |
|||||||
|
Binding the MAC Address and IP Address of a Legal User to the Specified Port 51 |
||||||||
|
Address Management Configuration Example |
52 |
|
||||||
|
Port-Based Address Management IP Address Pool Configuration Example 52 |
||||||||
|
Configuration Example of Binding the MAC Address and IP Address of a Legal |
||||||||
|
User 53 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
PORT OPERATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Ethernet Port Configuration Introduction |
55 |
|
|
|||||
|
Ethernet Port Configuration |
55 |
|
|
|
||||
|
EthernetPort Security Features |
62 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Displaying and Debugging Ethernet Port |
66 |
|
||||||
4 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
|
Displaying Port Configuration Information in Brief |
67 |
|||
|
Ethernet Port Configuration Example |
67 |
|
|
|
|
Ethernet Port Troubleshooting |
68 |
|
|
|
|
Link Aggregation Configuration 68 |
|
|
|
|
|
Link Aggregation Configuration |
71 |
|
|
|
|
Displaying and Debugging Link Aggregation 74 |
|
|||
|
Link Aggregation Configuration Example |
75 |
|
||
|
Global Broadcast Suppression Feature |
76 |
|
|
|
|
Configuring Global Broadcast Suppression |
76 |
|
||
|
Global Broadcast Suppression Configuration Example 76 |
||||
|
Configuration procedure 76 |
|
|
|
|
|
Displaying Information About a Specified Optical Port |
77 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 XRN CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Introduction to XRN 79 |
|
|
|
|
Configuring an XRN Fabric 79 |
|
|
|
Specifying the Stacking VLAN of the Switch |
80 |
||
Setting Unit IDs for Switches |
80 |
|
|
Saving the Unit ID of Each Unit in the Fabric |
81 |
||
Specifying the Fabric Port of the Switch 81 |
|
||
Setting Unit Names for Switches |
81 |
|
|
Setting a Fabric Name for Switches |
81 |
|
|
Setting an XRN Authentication Mode for Switches 82 |
|||
Displaying and Debugging a Fabric |
82 |
|
|
Fabric Configuration Example |
82 |
|
|
RMON on XRN 83 |
|
|
|
|
Configuration Commands for RMON on XRN 84 |
||||
|
Clustering on XRN |
84 |
|
|
|
|
Peer Fabric Port Detection |
84 |
|
|
|
|
Work Flow of the Peer Fabric Port Detection Function 84 |
||||
|
Prompt Information and Solution |
85 |
|||
|
Multiple Fabric Port Candidates |
86 |
|
||
5 |
|
|
|
||
DLDP CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|||
|
DLDP Overview 89 |
|
|
|
|
|
DLDP Fundamentals |
90 |
|
|
|
|
Precautions During DLDP Configuration 93 |
||||
|
DLDP Configuration |
93 |
|
|
|
|
Resetting DLDP Status |
94 |
|
|
|
|
DLDP Configuration Example |
94 |
|
||
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
VLAN OPERATION |
|
|
|
||
|
VLAN Configuration |
97 |
|
|
|
|
VLAN Overview |
97 |
|
|
|
|
Configuring a VLAN |
97 |
|
|
|
|
Displaying and Debugging VLAN |
99 |
|||
|
VLAN Configuration Example One |
99 |
|||
|
VLAN Configuration Example Two |
100 |
|||
5
Protocol-Based VLAN Configuration |
100 |
|
Configuring Protocol-Based VLANs |
100 |
|
Displaying the Information about Protocol-Based VLANs 101 |
||
Voice VLAN Configuration |
102 |
|
Voice VLAN Configuration 102 |
|
|
Displaying and Debugging of Voice VLAN 106 |
||
Voice VLAN Configuration Example |
106 |
|
Creating VLANs in Batches |
107 |
|
Voice VLAN Configuration |
107 |
|
|
Configuring the Voice VLAN Function |
108 |
|
||||
|
Voice VLAN Displaying and Debugging |
109 |
|
||||
|
Voice VLAN Configuration Example 109 |
|
|||||
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
GVRP CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Introduction to GVRP |
111 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
GVRP Working Scheme |
111 |
|
|
|
||
|
GVRP Packet Format |
113 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Protocol Specifications |
113 |
|
|
|
||
|
GVRP Configuration |
114 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Prerequisite |
114 |
|
|
|||
|
Configuration Procedure |
114 |
|
|
|
||
|
Configuration Example |
115 |
|
|
|
||
|
Displaying GVRP 116 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
8 VLAN-VPN CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
||||
|
VLAN-VPN Overview |
117 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Implementation of VLAN-VPN |
117 |
|
|
|||
|
Adjusting the TPID Values of VLAN-VPN Packet |
118 |
|||||
|
VLAN-VPN Configuration |
118 |
|
|
|
||
|
Configuration Prerequisites |
118 |
|
|
|||
|
Configuration procedure |
118 |
|
|
|
||
|
Inner VLAN Tag Priority Replication Configuration |
119 |
|||||
|
Configuration Prerequisites |
119 |
|
|
|||
|
Configuration procedure |
119 |
|
|
|
||
|
TPID Adjusting Configuration |
119 |
|
|
|
||
|
Configuration Prerequisites |
119 |
|
|
|||
|
Configuration Procedure |
119 |
|
|
|
||
|
VLAN-VPN Configuration Example |
120 |
|
|
|||
|
Network requirements |
120 |
|
|
|
||
|
Network diagram |
120 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Procedure |
121 |
|
|
|
||
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DHCP OVERVIEW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Introduction to DHCP |
123 |
|
|
|
|
|
DHCP IP Address Assignment |
124 |
IP Address Assignment Policy |
124 |
DHCP IP Address Preferences |
124 |
Sending Device Information through DHCP Option60 124

6 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
10 DHCP SERVER CONFIGURATION
|
Introduction to DHCP Server |
125 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Usage of DHCP Server |
|
125 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
DHCP Fundamentals |
|
125 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
DHCP Packet Processing Modes |
127 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
DHCP Address Pool |
127 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Global Address Pool-Based DHCP Server Configuration |
128 |
||||||||
|
Configuration Overview |
128 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Enabling DHCP |
128 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Global Address Pool Mode on Interface(s) |
129 |
||||||||
|
Configuring How to Assign IP Addresses in a Global Address Pool 129 |
|||||||||
|
Configuring DNS Services for DHCP Clients |
130 |
|
|
||||||
|
Configuring NetBIOS Services for DHCP Clients |
131 |
|
|||||||
|
Customizing DHCP Service |
132 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring Gateway Addresses for DHCP Clients |
132 |
||||||||
|
Interface Address Pool-based DHCP Server Configuration |
132 |
||||||||
|
Configuration Overview |
132 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Enabling DHCP |
133 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring to Assign the IP addresses of Local Interface-based address pools to DHCP |
|||||||||
|
Clients |
133 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring to Assign IP Addresses of Interface-based Address Pools to DHCP |
|||||||||
|
Clients |
133 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring DNS Services for DHCP Clients |
135 |
|
|
||||||
|
Configuring NetBIOS Services for DHCP Clients |
136 |
|
|||||||
|
Customizing DHCP Service |
137 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
DHCP Security Configuration |
137 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Prerequisites |
137 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Private DHCP Server Detecting |
137 |
|
|
||||||
|
Configuring IP Address Detecting |
137 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Option 184 Supporting Configuration |
138 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Prerequisites |
139 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring the Option 184 Supporting Function |
139 |
||||||||
|
Configuration Example |
142 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
DHCP Server Displaying and Debugging 144 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
DHCP Server Configuration Example |
144 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Troubleshooting DHCP Server |
146 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
11 DHCP RELAY CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Introduction to DHCP Relay |
147 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Usage of DHCP Relay |
|
147 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
DHCP Relay Fundamentals |
147 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
DHCP Relay Configuration |
148 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
DHCP Relay Configuration Tasks |
148 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Enabling DHCP |
148 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring an Interface to Operate in DHCP Relay Mode 148 |
|||||||||
|
DHCP Relay Displaying |
149 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
DHCP Relay Configuration Example |
149 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Troubleshooting DHCP Relay |
150 |
|
|
|
|
||||

7
12 VRRP CONFIGURATION |
|
|
VRRP Overview 151 |
|
|
Virtual Router Overview |
152 |
|
Introduction to Backup Group 153 |
|
|
VRRP Configuration 155 |
|
|
Configuring a Virtual Router IP address |
155 |
|
Configuring Backup Group-Related Parameters 156 |
||
Displaying and Clearing VRRP Information |
157 |
|
VRRP Configuration Example |
157 |
|
|
Single-VRRP Backup Group Configuration Example |
157 |
|||||||
|
VRRP Tracking Interface Example |
158 |
|
|
|||||
|
Multiple-VRRP Backup Group Configuration Example |
160 |
|||||||
|
Troubleshooting VRRP |
162 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
13 MSTP CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
MSTP Overview |
163 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MSTP Protocol Data Unit |
163 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Basic MSTP Terminologies |
164 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Fundamentals of MSTP |
166 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
MSTP Implementation on Switches |
168 |
|
|
|||||
|
Root Bridge Configuration |
168 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring an MST Region |
169 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Setting the Switch as the Root/Secondary Root Bridge |
|
170 |
||||||
|
Setting the Bridge Priority of a Switch |
171 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring MSTP Operation Mode |
172 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring the Maximum Hop Count of an MST Region |
172 |
|||||||
|
Configuring the Diameter of a Switched Network 173 |
|
|||||||
|
Configuring MSTP Time Parameters |
173 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring the Timeout Time Factor |
175 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring the Maximum Transmission Speed of a Port |
175 |
|||||||
|
Setting a Port as an Edge Port |
|
176 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Specifying whether a Port Connect to Point-to-Point Link |
177 |
|||||||
|
Enabling MSTP |
179 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Leaf Node Configuration |
180 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Prerequisites |
180 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring an MST Region |
180 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring MSTP Operation Mode |
181 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring the Timeout Time Factor |
181 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring the Maximum Transmission Speed of a Port |
181 |
|||||||
|
Setting a Port as an Edge Port |
|
181 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuring the Path Cost of a Port |
181 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring the Priority of a Port |
183 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring a Port to Connect to Point-to-Point Link |
184 |
|||||||
|
Enabling MSTP |
184 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mCheck Configuration |
184 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Prerequisites |
184 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Procedure |
185 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuration Example |
185 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Protection Functions Configuration |
185 |
|
|
|||||
8 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
|
Introduction to the Protection Functions |
185 |
|
|
||||||||
|
Prerequisites |
186 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring BPDU Protection |
187 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring Root Protection |
|
187 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring Loop Prevention |
188 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring TC-BPDU Attack Prevention |
188 |
|
|
||||||||
|
BPDU Tunnel Configuration |
188 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Introduction to BPDU Tunnel |
|
188 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring BPDU Tunnel |
|
189 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Displaying and Debugging MSTP |
190 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
MSTP Configuration Example |
|
190 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
BPDU Tunnel Configuration Example |
192 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
14 CENTRALIZED MAC ADDRESS AUTHENTICATION CONFIGURATION |
||||||||||||
|
Introduction to Centralized MAC Address Authentication |
195 |
|
|||||||||
|
Centralized MAC Address Authentication Configuration |
196 |
|
|||||||||
|
Enabling Global/Port-based Centralized MAC Address Authentication |
196 |
||||||||||
|
Configuring an ISP Domain for MAC Address Authentication Users |
196 |
||||||||||
|
Setting Centralized MAC Address Authentication Timers 196 |
|
||||||||||
|
Displaying and Debugging Centralized MAC Address Authentication |
197 |
||||||||||
|
Centralized MAC Address Authentication Configuration Example 197 |
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
15 SSH TERMINAL SERVICES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
SSH Terminal Services |
199 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Introduction to SSH |
199 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
SSH Server Configuration |
|
201 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
SSH Client Configuration |
205 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Displaying SSH Configuration |
205 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
SSH Server Configuration Example |
206 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
SSH Client Configuration Example |
207 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
SSH Keygen Program |
209 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
SFTP Service |
210 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SFTP Overview |
210 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
SFTP Server Configuration |
|
210 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
SFTP Client Configuration |
|
211 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
SFTP Configuration Example |
|
213 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
16 IP ROUTING PROTOCOL OPERATION |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
IP Routing Protocol Overview |
|
217 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Selecting Routes Through the Routing Table |
218 |
|
|
||||||||
|
Routing Management Policy |
|
219 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Static Routes |
220 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Static Routes |
|
221 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Example: Typical Static Route Configuration |
223 |
|
|
||||||||
|
Troubleshooting Static Routes |
224 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
RIP 224 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring RIP |
225 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Traffic Sharing Across RIP Interfaces |
233 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
9
|
Displaying and Debugging RIP |
233 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Example: Typical RIP Configuration |
233 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Troubleshooting RIP |
234 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OSPF Configuration |
235 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calculating OSPF Routes |
235 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Basic Concepts Related to OSPF |
236 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring OSPF |
237 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Displaying and Debugging OSPF |
253 |
|
|
|
|
||||
254 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Example: Configuring DR Election Based on OSPF Priority |
254 |
||||||||
|
Example: Configuring OSPF Virtual Link |
256 |
|
|
||||||
|
Troubleshooting OSPF |
257 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
IP Routing Policy 258 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring an IP Routing Policy |
259 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Forwarding Layer 3 Broadcast Packets |
263 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Displaying and Debugging the Routing Policy |
264 |
|
|||||||
|
Typical IP Routing Policy Configuration Example |
264 |
|
|||||||
|
Troubleshooting Routing Protocols |
265 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Route Capacity Configuration |
265 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Limiting Route Capacity 266 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Route Capacity Configuration |
266 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Displaying and Debugging Route Capacity |
267 |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
17 NETWORK PROTOCOL OPERATION |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
IP Address Configuration |
269 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
IP Address Overview |
269 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring IP Address |
271 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Displaying and Debugging IP Address |
272 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
IP Address Configuration Example |
273 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Troubleshooting IP Address Configuration |
273 |
|
|||||||
|
ARP Configuration |
273 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring ARP |
274 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Introduction to Gratuitous ARP |
|
275 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Gratuitous ARP Packet Learning Configuration |
276 |
|
|||||||
|
Resilient ARP Configuration |
|
277 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
277 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Displaying and Debugging Resilient ARP Configuration |
278 |
||||||||
|
Resilient ARP Configuration Example |
278 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
BOOTP Client Configuration |
279 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Overview of BOOTP Client |
279 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
BOOTP Client Configuration |
280 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Debugging BOOTP Client |
280 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
DHCP Configuration |
280 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overview of DHCP 280 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Option 82 supporting |
283 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
DHCP Client Configuration |
|
285 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
DHCP Relay Configuration |
286 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Enabling DHCP |
286 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring DHCP Relay Security |
287 |
|
|
|
|||||
10 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
|
Option 82 Supporting Configuration |
288 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Prerequisites |
288 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enabling Option 82 Supporting on a DHCP Relay |
288 |
|||||||||
|
Option 82 Supporting Configuration Example |
289 |
|
||||||||
|
Introduction to DHCP Snooping |
290 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
DHCP Snooping Configuration |
291 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuration Example |
292 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Introduction to DHCP Accounting |
292 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Structure of the DHCP Accounting Packets |
|
292 |
|
|||||||
|
DHCP Accounting Fundamentals |
294 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
DHCP Accounting Configuration |
294 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Displaying and Debugging DHCP Configuration |
296 |
|
||||||||
|
DHCP Relay Configuration Example One |
297 |
|
|
|||||||
|
DHCP Relay Configuration Example Two |
298 |
|
|
|||||||
|
Troubleshooting DHCP Relay Configuration |
|
299 |
|
|||||||
|
Access Management Configuration |
299 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Access Management Overview |
299 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring Access Management |
299 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Displaying and Debugging Access Management |
301 |
|
||||||||
|
Access Management Configuration Example |
302 |
|
||||||||
|
Access Management using the Web |
302 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
UDP Helper Configuration |
303 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Overview of UDP Helper |
303 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
UDP Helper Configuration |
303 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Displaying and Debugging UDP Helper Configuration |
305 |
|||||||||
|
UDP Helper Configuration Example 305 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
IP Performance Configuration |
305 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Displaying and debugging IP Performance |
|
306 |
|
|||||||
|
Troubleshooting IP Performance |
307 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
18 MULTICAST PROTOCOL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
IP Multicast Overview |
309 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Multicast Addresses |
310 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
IP Multicast Protocols |
312 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Forwarding IP Multicast Packets |
313 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Applying Multicast |
314 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IGMP Snooping |
314 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring IGMP Snooping |
317 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Enabling IGMP Fast Leave Processing |
318 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Configuring IGMP Snooping Filter ACL |
319 |
|
|
|||||||
|
Configuring the Maximum Number of Multicast Groups on a Port 319 |
||||||||||
|
Configuring Multicast VLAN |
320 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Displaying and Debugging IGMP Snooping |
|
321 |
|
|||||||
|
Configuration Example—Enable IGMP Snooping |
322 |
|
||||||||
|
IGMP Snooping Fault Diagnosis and Troubleshooting |
322 |
|||||||||
|
Common Multicast Configuration |
323 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Enabling Multicast |
323 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring the Number Limit of Multicast Routing Entries 323 |
||||||||||
|
Multicast MAC Address Entry Configuration |
324 |
|
||||||||
11
|
Displaying Multicast MAC Address Configuration |
324 |
|
||||||||
|
Multicast Source Deny Configuration |
325 |
|
|
|||||||
|
Clearing MFC Forwarding Entries or Statistics Information 325 |
||||||||||
|
Clearing Route Entries From The Core Multicast Routing Table |
325 |
|||||||||
|
Displaying and Debugging Common Multicast Configuration |
326 |
|||||||||
|
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) |
326 |
|
|
|||||||
|
Configuring IGMP |
328 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Displaying and debugging IGMP |
|
333 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
PIM-DM Overview |
333 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring PIM-DM |
335 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Displaying and Debugging PIM-DM |
338 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
PIM-DM Configuration Example |
|
338 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
PIM-SM Overview |
339 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PIM-SM Operating Principle |
340 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Preparations before Configuring PIM-SM |
341 |
|
|
|||||||
|
Configuring PIM-SM |
341 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Displaying and Debugging PIM-SM |
346 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
PIM-SM Configuration Example |
346 |
|
|
|
||||||
349 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
19 ACL CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Brief Introduction to ACL |
351 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
ACL Supported by the Switch |
|
352 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring ACL |
352 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Defining ACL |
353 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Activating ACL |
355 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Displaying and Debugging ACL |
356 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Advanced ACL Configuration Example |
356 |
|
|
|||||||
|
Basic ACL Configuration Example |
357 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
Link ACL Configuration Example |
|
358 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
QoS Configuration |
359 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QoS Configuration |
361 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Setting Port Priority |
361 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring the Priority for Protocol Packets |
361 |
|
||||||||
|
Setting Port Mirroring |
362 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring Traffic Mirroring |
362 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Setting Traffic Limit |
364 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Setting Line Limit |
365 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Relabeling Priority Level |
365 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring Traffic Statistics |
365 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring WRED Operation |
|
366 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring Control Over Telnet |
|
366 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Displaying and Debugging QoS Configuration |
369 |
|
||||||||
|
QoS Configuration Example |
369 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Port Mirroring Configuration Example |
370 |
|
|
|||||||
|
Priority Relabeling Configuration Example |
371 |
|
|
|||||||
|
QoS Profile Configuration |
372 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring QoS Profile |
372 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuring Profile Application Mode |
373 |
|
|
|||||||
12 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
|
Applying QoS Profile to the Port 374 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
QoS Profile Configuration Example |
374 |
|
|
|||||
|
ACL Control Configuration |
376 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuring ACL for Telnet Users |
376 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Defining ACL |
376 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Importing ACL |
377 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Example |
377 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring ACL for SNMP Users |
377 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuration Example |
379 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring ACL Control over the HTTP Users |
379 |
|
||||||
|
Defining ACL |
379 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Calling ACL to Control HTTP Users |
379 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuration Example |
380 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||||||
20 CONFIGURATION FOR QOS FEATURES |
|
|
|||||||
|
RSPAN Features |
381 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Prerequisite |
382 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuration Procedures in the Source Switch |
383 |
|
||||||
|
Configuration Procedures in the Intermediate Switch |
383 |
|||||||
|
Configuration Procedures in the Source Switch |
384 |
|
||||||
|
Configuration Example |
384 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Features of Traffic Statistics |
386 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Improving the Depth First Order of ACL Matching |
386 |
|
||||||
|
Displaying Information of the display acl command |
387 |
|
||||||
|
Subdividing DSCP while Defining ACL Rules |
387 |
|
|
|||||
|
The Synchronization Feature of Queue Scheduling for Aggregation Ports 388 |
||||||||
|
Configuring Control Over Telnet |
388 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuration Preparation |
388 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Controlling Telnet using Source IP |
389 |
|
|
|||||
|
Controlling Telnet using Source IP and Destination IP |
389 |
|||||||
|
Controlling Telnet using Source MAC |
390 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuration Example |
390 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
21 802.1X CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
IEEE 802.1x Overview |
391 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
802.1x System Architecture |
391 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
802.1x Authentication Process |
392 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Implementing 802.1x on the Switch |
393 |
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring 802.1x |
393 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enabling/Disabling 802.1x |
393 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Setting the Port Access Control Mode |
394 |
|
|
|||||
|
Setting the Port Access Control Method |
394 |
|
|
|||||
|
Checking the Users that Log on the Switch using Proxy |
394 |
|||||||
|
Setting the User Number on a Port |
395 |
|
|
|||||
|
Setting the Authentication in DHCP Environment |
395 |
|||||||
|
Configuring the Authentication Method for 802.1x User 395 |
||||||||
|
802.1x PEAP Configuration |
395 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Setting the Maximum Times of Authentication Request Message |
||||||||
|
Retransmission |
|
397 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13
Configuring Timers 398 |
|
Enabling/Disabling a Quiet-Period Timer |
399 |
802.1x Client Version Checking Configuration |
399 |
Enabling the 802.1x Client Version Checking Function 399 |
|
Configuring the Maximum Number of Retires to Send Version Checking Request
Packets |
399 |
|
|
|
|
Configuring the Version Checking Timer 400 |
|
|
|||
802.1x Client Version Checking Configuration Example |
400 |
||||
Guest VLAN Configuration |
400 |
|
|
|
|
Guest VLAN Configuration |
401 |
|
|
|
|
Configure Guest VLAN in Ethernet port view 401 |
|
|
|||
Guest VLAN Configuration Example |
401 |
|
|
||
The 802.1x Trusted MAC Address Synchronization Function |
402 |
||||
802.1x Supplicant System Checking |
402 |
|
|
||
Displaying and Debugging 802.1x 403 |
|
|
|||
Auto QoS |
403 |
|
|
|
|
802.1x Configuration Example 403 |
|
|
|
||
Centralized MAC Address Authentication |
405 |
|
|
||
Centralized MAC Address Authentication Configuration |
406 |
||||
Enabling MAC Address Authentication Both Globally and On the Port 406 |
|||||
Configuring Centralized MAC Address Authentication Mode |
406 |
||||
Configuring the User Name and Password for Fixed Mode |
|
407 |
|||
Configuring Domain Name Used by the MAC Address Authentication User 407
Configuring Centralized MAC Address Authentication Timers 407 |
|
||||||
Displaying and Debugging Centralized MAC Address Authentication |
408 |
||||||
Auto VLAN |
408 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Example of Centralized MAC Address Authentication |
408 |
||||||
AAA and RADIUS Protocol Configuration |
409 |
|
|
||||
RADIUS Protocol Overview 409 |
|
|
|
|
|||
Implementing AAA/RADIUS on the Ethernet Switch |
410 |
|
|||||
Configuring AAA 410 |
|
|
|
|
|
||
Creating/Deleting an ISP Domain |
411 |
|
|
|
|||
Configuring Relevant Attributes of the ISP Domain |
411 |
|
|||||
AAA Separation |
413 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Separate AAA Schemes |
414 |
|
|
||||
Configuration Example for Separate AAA Schemes |
414 |
|
|||||
Enabling/Disabling the Messenger Alert |
415 |
|
|
||||
Configuring Self-Service Server URL |
416 |
|
|
|
|||
Dynamic VLAN Assignment |
417 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Dynamic VLAN Assignment |
417 |
|
|
||||
Configuration Example for Dynamic VLAN Assignment 417 |
|
||||||
Creating a Local User |
418 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Setting Attributes of the Local User |
419 |
|
|
|
|||
Disconnecting a User by Force |
420 |
|
|
|
|
||
Configuring the RADIUS Protocol |
420 |
|
|
|
|||
Creating/Deleting a RADIUS Scheme |
421 |
|
|
||||
Configuring RADIUS Authentication/ |
|
|
|
|
|||
Authorization Servers |
421 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring RADIUS Accounting Servers and the Related Attributes |
422 |
||||||
User Re-authentication at Reboot |
424 |
|
|
|
|
||
14 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
|
Configuring User Re-authentication at Reboot |
425 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Configuration Example for User Re-authentication at Reboot |
425 |
|
|||||||||
|
Setting the RADIUS Packet Encryption Key |
425 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Tag VLAN Assignment on Trunk/Hybrid Port Supported by 802.1x |
|
||||||||||
|
Authentication 426 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Identifier Authentication Method Attribute in RADIUS |
426 |
|
|
||||||||
|
Setting Retransmission Times of RADIUS Request Packet |
426 |
|
|
||||||||
|
Setting the Supported Type of the RADIUS Server |
426 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Setting the RADIUS Server State |
427 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Setting the Username Format Transmitted to the RADIUS Server |
427 |
|
|||||||||
|
Setting the Unit of Data Flow that Transmitted to the RADIUS Server 428 |
|
||||||||||
|
Configuring the Local RADIUS Authentication Server 428 |
|
|
|||||||||
|
Configuring Source Address for RADIUS Packets Sent by NAS |
428 |
|
|||||||||
|
Setting the Timers of the RADIUS Server |
429 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Displaying and Debugging AAA and RADIUS Protocol |
430 |
|
|
||||||||
|
AAA and RADIUS Protocol Configuration Example |
431 |
|
|
||||||||
|
Configuring the Switch 5500 |
433 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
AAA and RADIUS Protocol Fault Diagnosis and Troubleshooting |
435 |
|
|||||||||
|
Problem Diagnosis |
436 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3Com-User-Access-Level 436 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
22 FILE SYSTEM MANAGEMENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
File System Overview |
437 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Directory Operation |
438 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
File Attribute Configuration 438 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
File Attribute Configuration |
439 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
File Operation |
440 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Storage Device Operation |
440 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Setting the Prompt Mode of the File System |
441 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Configuring File Management |
441 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Displaying the Current-configuration and Saved-configuration of the Switch |
441 |
||||||||||
|
Saving the Current-configuration |
442 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Erasing Configuration Files from Flash Memory |
442 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Configuring the Name of the Configuration File used for the Next Startup. |
442 |
||||||||||
|
Configuration File Backup and Restoration |
443 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Configuration Preparation |
443 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
FTP Overview |
443 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enabling/Disabling FTP Server |
444 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuring Source IP Address for FTP Serve and Client |
444 |
|
|
||||||||
|
Configuring the FTP Server Authentication and Authorization |
445 |
|
|||||||||
|
Configuring the Running Parameters of FTP Server |
445 |
|
|
||||||||
|
Displaying and Debugging FTP Server 446 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Displaying the Source IP Address Configuration |
446 |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Introduction to FTP Client |
446 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
FTP Server Configuration Example |
448 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
TFTP Overview |
449 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Downloading Files by means of TFTP |
450 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Uploading Files by means of TFTP |
450 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
TFTP Client Configuration Example |
450 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
15
MAC Address Table Management |
451 |
|
MAC Address Table Configuration |
452 |
|
Displaying MAC Address Table |
454 |
|
MAC Address Table Management Display Example 454 |
||
MAC Address Table Management Configuration Example 455 |
||
Device Management 456 |
|
|
Device Management Configuration |
456 |
|
Device Management Configuration Example 457 |
||
System Maintenance and Debugging |
|
459 |
Setting the Daylight Saving Time |
|
459 |
459 |
|
|
Telneting with Specified Source IP Address/Source Interface IP Address 459
460 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic System Configuration |
460 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Terminating the FTP Connection of a Specified User |
461 |
|
|
|||||||
Restarting the Switch |
461 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Displaying the State and Information of the System |
461 |
|
|
|||||||
System Debugging |
462 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Testing Tools for Network Connection |
464 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
ping |
464 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tracert |
464 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Introduction to Remote-ping |
465 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Remote-ping Configuration |
|
466 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Introduction to Remote-ping Configuration |
466 |
|
|
|
||||||
Configuring Remote-ping |
466 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Configuration Example |
467 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Logging Function |
468 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Introduction to Info-center |
468 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Info-Center Configuration |
471 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Sending the Information to Loghost 474 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
Sending the Information to Control Terminal |
476 |
|
|
|||||||
Sending the Information to Telnet Terminal or Dumb Terminal |
478 |
|||||||||
Sending the Information to the Log Buffer |
480 |
|
|
|
||||||
Sending the Information to the Trap Buffer |
481 |
|
|
|
||||||
Sending the Information to SNMP Network Management |
482 |
|||||||||
Configuring Synchronous Information Output Function |
485 |
|
||||||||
Configuration Examples of Sending Log to Unix Loghost |
485 |
|||||||||
Configuration Examples for Sending Log to Linux Loghost |
486 |
|||||||||
Configuration Examples of Sending Log to Control Terminal |
488 |
|||||||||
RMON Configuration |
489 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Configuring RMON |
489 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Displaying and Debugging RMON |
491 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
RMON Configuration Example 492 |
|
|
|
|
||||||
NTP Overview 492 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
NTP Configuration |
494 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Configuring NTP Operating Mode |
494 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Displaying and Debugging NTP |
499 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Typical NTP Configuration Examples |
499 |
|
|
|
|
|||||
Configure NTP Server |
499 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
NTP peer Configuration |
|
501 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
16 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
|
Configure NTP Broadcast Mode |
502 |
|
|||
|
Configure NTP Multicast Mode |
504 |
|
|||
|
Configure Authentication-enabled NTP Server Mode |
505 |
||||
|
SSH Terminal Services |
506 |
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring SSH Server |
507 |
|
|
||
|
Setting System Protocol |
507 |
|
|
||
|
Configuring SSH Client |
510 |
|
|
||
|
SSH Configuration Example |
515 |
|
|||
|
File System Configuration |
516 |
|
|
||
|
Introduction to File System |
516 |
|
|
||
|
File System Configuration |
517 |
|
|
||
|
FTP Lighting Configuration |
518 |
|
|
||
|
Introduction to FTP |
518 |
|
|
|
|
|
FTP Lighting Procedure |
518 |
|
|
||
|
TFTP Lighting Configuration |
|
520 |
|
|
|
|
TFTP Lighting Procedure |
521 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
||||
23 PORT TRACKING CONFIGURATION |
|
|||||
|
Introduction to the Port Tracking Function 523 |
|
||||
|
Port Tracking Configuration |
523 |
|
|
||
|
Configuring the Port Tracking Function |
523 |
|
||
|
Port Tracking Configuration Example |
523 |
|
||
|
|
||||
24 DYNAMICALLY APPLY ACL BY RADIUS SERVER CONFIGURATION |
|||||
|
Introduction to Dynamically Apply ACL by RADIUS Server |
525 |
|||
|
Introduction to Dynamically Apply ACL by RADIUS Server Configurations 525 |
||||
|
Configuration Example |
526 |
|
|
|
|
Network requirements |
526 |
|
|
|
|
Network diagram |
526 |
|
|
|
|
Configuration procedure |
527 |
|
|
|
|
Configuration on the switch 529 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
25 AUTO DETECT CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|||
|
Introduction to the Auto Detect Function |
531 |
|
||
|
Configuring the auto detect function |
531 |
|
||
|
Auto Detect Configuration Example |
531 |
|
||
|
Auto Detect Implementation |
532 |
|
|
|
|
Auto Detect Implementation in Static Routing 533 |
|
|||
|
Configuring the Auto Detect Function for a Static Route |
533 |
|||
|
Configuration Example |
533 |
|
|
|
|
Auto Detect Implementation in VRRP 534 |
|
|||
|
Configuring the Auto Detect Function for VRRP 534 |
|
|||
|
Configuration Example |
534 |
|
|
|
|
Auto Detect Implementation in VLAN Interface Backup 536 |
||||
|
Configuring the Auto Detect Function for VLAN Interface Backup 536 |
||||
|
Configuration Example |
536 |
|
|
|

17
26 |
RSTP CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STP Overview 539 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Implement STP |
539 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration BPDU Forwarding Mechanism in STP |
543 |
|
||||||
|
Implement RSTP on the Switch |
543 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
RSTP Configuration |
544 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enable/Disable RSTP on a Switch |
|
547 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Enable/Disable RSTP on a Port |
547 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configure RSTP Operating Mode |
|
548 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Configure the STP-Ignore attribute of VLANs on a Switch |
548 |
|
||||||
|
Set Priority of a Specified Bridge |
|
549 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Specify the Switch as Primary or Secondary Root Bridge |
549 |
|
||||||
|
Set Forward Delay of a Specified Bridge |
550 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Set Hello Time of the Specified Bridge |
550 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Set Max Age of the Specified Bridge |
550 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Set Timeout Factor of the Bridge |
|
551 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Specifying the Maximum Transmission Rate of STP Packets on a Port |
551 |
|||||||
|
Set Specified Port to be an EdgePort |
552 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Specifying the Path Cost on a Port |
552 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Set the Priority of a Specified Port |
553 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Configure a Specified Port to be Connected to Point-to-Point Link |
553 |
|||||||
|
Set mCheck of the Specified Port |
|
554 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Configure the Switch Security Function |
554 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Display and Debug RSTP |
556 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSTP Configuration Example |
556 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
POE PROFILE CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Introduction to PoE Profile |
559 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PoE Profile Configuration |
559 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PoE Profile Configuration Tasks |
559 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
PoE Profile Configuration Example |
560 |
|
|
|
||||
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
SNMP CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
SNMP Configuration Introduction |
563 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
SNMP Versions and Supported MIB |
563 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Configure SNMP |
565 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Enabling/Disabling SNMP Agent to Send Trap 566 |
|
|
||||||
|
Setting the Destination Address of Trap |
566 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Setting Lifetime of Trap Message |
|
567 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Setting SNMP System Information |
567 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Setting the Engine ID of a Local or Remote Device |
567 |
|
|
|||||
|
Setting/Deleting an SNMP Group |
|
567 |
|
|
|
|||
|
Setting the Source Address of Trap |
568 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Adding/Deleting a User to/from an SNMP Group |
568 |
|
|
|||||
|
Creating/Updating View Information or Deleting a View |
568 |
|
||||||
|
Setting the Size of SNMP Packet Sent/Received by an Agent 568 |
|
|||||||
|
Enabling/Disabling a Port Transmitting Trap Information SNMP Agent |
569 |
|||||||
|
Disabling SNMP Agent |
569 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
|
Network Management Operation Logging Configuration |
569 |
|
|||||||
|
Displaying and Debugging SNMP |
570 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
SNMP Configuration Example |
570 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Reading Usmusr Table Configuration Example |
571 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
29 SOURCE IP ADDRESS CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Configuring Source IP Address for Service Packets 573 |
|
|
|||||||
|
Displaying the Source IP Address Configuration |
574 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
||||||||
30 PASSWORD CONTROL CONFIGURATION OPERATIONS |
|
|||||||||
|
Introduction to Password Control Configuration |
575 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Password Control Configuration |
|
576 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Prerequisites |
576 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuration Tasks |
576 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring Password Aging |
|
577 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuring the Limitation of Minimum Password Length |
578 |
|
|||||||
|
Configuring History Password Recording |
579 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring a User Login Password in Encryption Mode |
580 |
|
|||||||
|
Configuring Login Attempts Limitation and Failure Processing Mode |
580 |
||||||||
|
Configuring the Timeout Time for Users to be authenticated 581 |
|
||||||||
|
Displaying Password Control 581 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Password Control Configuration Example |
582 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 MSDP CONFIGURATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Introduction to MSDP |
585 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MSDP Working Mechanism |
587 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring MSDP Basic Functions |
590 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuration Prerequisites |
590 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring MSDP Basic Functions |
591 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring Connection Between MSDP Peers |
591 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Configuration Prerequisites |
591 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring Description Information for MSDP Peers |
592 |
|
|||||||
|
Configuring Anycast RP Application |
592 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring an MSDP Mesh Group |
592 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring MSDP Peer Connection Control |
593 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring SA Message Transmission |
593 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuration Prerequisites |
593 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuring the Transmission and Filtering of SA Request Messages |
594 |
||||||||
|
Configuring a Rule for Filtering the Multicast Sources of SA Messages |
594 |
||||||||
|
Configuring a Rule for Filtering Received and Forwarded SA Messages |
595 |
||||||||
|
Configuring SA Message Cache |
595 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Displaying and Debugging MSDP Configuration |
596 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
MSDP Configuration Example |
596 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Configuration Example of Anycast RP Application |
596 |
|
|
||||||
|
Troubleshooting MSDP Configuration |
599 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
MSDP Peer Always in the Down State |
599 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
No SA Entry in the SA Cache of the Router |
599 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
32 CLUSTERING |
|
|
|
Clustering Overview 601 |
|
|
Switch Roles 602 |
|
|
Introduction to NDP |
603 |
|
Introduction to NTDP |
603 |
|
Introduction to Cluster Roles |
604 |
|
|
Management Device Configuration |
605 |
|
|
Enabling System and Port NDP |
605 |
|
|
Configuring NDP Parameters |
|
605 |
|
Enabling System and Port NTDP |
605 |
|
|
Configuring NTDP Parameters |
|
605 |
|
Configuring Cluster Parameters |
606 |
|
|
Configuring Internal-External Interaction 607 |
||
|
NM Interface for Cluster Management Configuration 607 |
||
|
Member Device Configuration |
608 |
|
|
Enabling System and Port NDP |
608 |
|
|
Enabling System and Port NTDP |
608 |
|
|
Specifying the cluster FTP/TFTP server 608 |
||
|
Configuring Cluster Parameters |
609 |
|
|
Displaying and Maintaining Cluster Configurations 609 |
||
|
Clustering Configuration Example |
610 |
|
|
NM Interface for Cluster Management Configuration Example 612 |
||
|
|
||
33 HWTACACS CONFIGURATION |
|||
|
Configuring HWTACACS 615 |
|
|
HWTACACS configuration tasks |
615 |
Creating a HWTACAS Scheme |
616 |
Configuring HWTACACS Authentication Servers 617
Configuring HWTACACS Accounting Servers and the Related Attributes 617
|
Configuring Source Address for HWTACACS Packets Sent by NAS |
618 |
||
|
Setting a Key for Securing the Communication with TACACS Server 618 |
|||
|
Setting the Username Format Acceptable to the TACACS Server |
618 |
||
|
Setting the Unit of Data Flows Destined for the TACACS Server |
619 |
||
|
Setting Timers Regarding TACACS Server |
619 |
|
|
|
Displaying and Debugging HWTACACS Protocol 620 |
|
||
|
HWTACACS Protocol Configuration Example |
621 |
|
|
|
Configuring the FTP/Telnet User Authentication at a Remote TACACS Server 621 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
A PASSWORD RECOVERY PROCESS |
|
|
||
|
Introduction 623 |
|
|
|
|
CLI Commands Controlling Bootrom Access |
623 |
|
|
|
Bootrom Interface 624 |
|
|
|
|
Displaying all Files in Flash |
624 |
|
|
|
Skipping the Current Configuration File |
625 |
|
|
|
Bootrom Passwords 625 |
|
|
|
|
Bootrom Password Recovery |
626 |
|
|

20 CHAPTER : CONTENTS
B RADIUS SERVER AND RADIUS CLIENT SETUP
|
Setting Up A RADIUS Server |
627 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Configuring Microsoft IAS RADIUS |
627 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Configuring Funk RADIUS |
652 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Configuring FreeRADIUS |
656 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Setting Up the RADIUS Client |
658 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Windows 2000 built-in client |
658 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Windows XP built-in client |
658 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Aegis Client Installation 659 |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|||||||||
C AUTHENTICATING THE SWITCH 5500 WITH CISCO SECURE ACS |
||||||||||
|
Cisco Secure ACS (TACACS+) and the 3Com Switch 5500 |
661 |
||||||||
|
Setting Up the Cisco Secure ACS (TACACS+) server |
661 |
|
|||||||
|
Adding a 3Com Switch 5500 as a RADIUS client |
662 |
|
|||||||
|
Adding a User for Network Login |
664 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Adding a User for Switch Login |
665 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D 3COM XRN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What is XRN? |
672 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supported Switches |
672 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
XRN Terminology |
672 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Benefits of XRN |
|
673 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
XRN Features |
673 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distributed Device Management (DDM) |
673 |
|
|
||||||
|
Distributed Resilient Routing (DRR) |
673 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
Distributed Link Aggregation (DLA) |
674 |
|
|
|
|||||
|
How to Implement XRN—Overview |
|
676 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Important Considerations and Recommendations |
676 |
|
|||||||
|
Recommendations for Achieving Maximum Resilience |
677 |
||||||||
|
Unit ID Numbering Mechanism |
678 |
|
|
|
|
||||
678 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Network Example using XRN |
678 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
XRN Distributed Fabric Network |
|
678 |
|
|
|
||||
|
Recovering your XRN Network |
680 |
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Unit Failure |
|
680 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interconnect Failure |
680 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
How XRN Interacts with other 3Com Switches |
680 |
|
|||||||
|
How XRN Interacts with other Features 681 |
|
|
|
||||||
|
VLANs 681 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legacy Aggregated Links |
682 |
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
STP/RSTP |
683 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Resilient Links |
683 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How a Failure affects the Distributed Fabric |
684 |
|
|
||||||
Loss of a Switch within the XRN Distributed Fabric 684
Loss of the Fabric Interconnect 685

ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This guide provides information about configuring your network using the commands supported on the 3Com® Switch 5500 Family.
The descriptions in this guide apply to the Switch 5500-SI and Switch 5500-EI. Differences between the models are noted in the text.
Organization of the
Manual
The Switch 5500 Family Configuration Guide consists of the following chapters:
■Getting Started—Details the main features and configurations of the Switch 5500.
■Address Management—Details how to configure the switch on which the Address Manage (AM) feature is enabled.
■Port Operation—Details how to configure Ethernet port and link aggregation.
■XRN Fabric—Details how to configure an XRN fabric.
■DLDP—Drtails overview and fundamentals for Device Link Detection Protocol.
■VLAN Operation—Details how to configure VLANs.
■GVRP Configuration—Details GARP VLAN Registration Protocol configuration.
■VLAN-VPN—Details configuration information to create VLAN-VPNs.
■DHCP—Details Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
■Reliability—Details Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP).
■MSTP—Details Multiple spanning tree protocol.
■Centralized MAC address authentication—Details Centralized MAC address authentication configuration.
■SSH—Details Secure Shell authentication.
■IP Routing Protocol Operation—Details how to configure routing protocols.
■Network Protocol Operation—Details how to configure network protocols.
■Multicast Protocol—Details how to configure multicast protocols.
■ACL Configuration—Details how to configure QoS/ACL.
■QoS—Detais Quality of Service
■RSTP Configuration—Details how to configure RSTP.
■802.1x Configuration—Details how to configure 802.1x.
■File System Management—Details how to configure file system management.
■Port Tracking—Details Port Tracking Configuration.
22 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
■ACL by RADIUS—Details ACL by RADUIS Configuration.
■Auto Detect—Details Auto Detect Configuration.
■RSTP—Details Spanning Tree Protocol Configuration.
■PoE—Details PoE profile Configuration.
■SNMP—Details Simple Network Management Protocol Configuration.
■Source IP Address—Details Source IP Address Configuration for the FTP client and server .
■Password Control—Details Password Control Configuration.
■MSDP—Details MSDP Configuration.
■Clustering—Details Clustering Configuration.
■HWTACACS—Details HWTACACS Configuration.
Intended Readership The manual is intended for the following readers:
■Network administrators
■Network engineers
■Users who are familiar with the basics of networking
Conventions |
This manual uses the following conventions: |
|||
|
Table 1 |
Icons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Icon |
Notice Type |
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Information note |
Information that describes important features or instructions. |
|
|
|
Caution |
|
Information that alerts you to potential loss of data or potential |
|
|
|
|
damage to an application, system, or device. |
|
|
Warning |
|
Information that alerts you to potential personal injury. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2 |
Text conventions |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Convention |
Description |
||
|
|
|
||
|
Screen displays |
This typeface represents text as it appears on the screen. |
||
|
Keyboard key names |
If you must press two or more keys simultaneously, the key names are |
||
|
|
|
linked with a plus sign (+), for example: |
|
|
|
|
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del |
|
|
The words “enter” |
When you see the word “enter” in this guide, you must type something, |
||
|
and type” |
and then press Return or Enter. Do not press Return or Enter when an |
||
|
|
|
instruction simply says “type.” |
|
|
Fixed command |
This typeface indicates the fixed part of a command text. You must type |
||
|
text |
|
the command, or this part of the command, exactly as shown, and press |
|
|
|
|
Return or Enter when you are ready to enter the command. |
|
Example: The command display history-command must be entered exactly as shown.

|
|
Related Manuals 23 |
|
|
Table 2 Text conventions (continued) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Convention |
Description |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Variable |
This typeface indicates the variable part of a command text. You must type |
|
|
command text |
a value here, and press Return or Enter when you are ready to enter the |
|
|
|
command. |
|
|
|
Example: in the command super level, a value in the range 0 to 3 must |
|
|
|
be entered in the position indicated by level |
|
|
{ x | y | ... } |
Alternative items, one of which must be entered, are grouped in braces |
|
|
|
and separated by vertical bars. You must select and enter one of the items. |
|
|
|
Example: in the command flow-control {hardware | none | |
|
|
|
software}, the braces and the vertical bars combined indicate that you |
|
|
|
must enter one of the parameters. Enter either hardware, or none, or |
|
|
|
software. |
|
|
[ ] |
Items shown in square brackets [ ] are optional. |
|
|
|
Example 1: in the command display users [all], the square brackets |
|
|
|
indicate that the parameter all is optional. You can enter the command |
|
|
|
with or without this parameter. |
|
|
|
Example 2: in the command user-interface [type] first-number |
|
|
|
[last-number] the square brackets indicate that the parameters [type] |
|
|
|
and [last-number] are both optional. You can enter a value in place of |
|
|
|
one, both or neither of these parameters. |
|
|
|
Alternative items, one of which can optionally be entered, are grouped in |
|
|
|
square brackets and separated by vertical bars. |
|
|
|
Example 3: in the command header [shell | incoming | login] |
|
|
|
text, the square brackets indicate that the parameters shell, |
|
|
|
incoming and login are all optional. The vertical bars indicate that only |
|
|
|
one of the parameters is allowed. |
|
|
|
|
|
Related Manuals |
The 3Com Switch 5500 Family Getting Started Guide provides information about |
||
|
installation. |
|
|
The 3Com Switch 5500 Family Command Reference Guide provides all the information you need to use the configuration commands.
24 ABOUT THIS GUIDE

GETTING STARTED
1
This chapter covers the following topics:
■Product Overview
■XRN Overview
■Product Features
■Logging in to the Switch
■Command Line Interface
■User Interface Configuration
Product Overview |
The Switch 5500 Family are Layer 3 switching products supporting expandable resilient |
|
networking (XRN). The Switch 5500 can be one of two series: Switch 5500-SI or the |
|
Switch 5500-EI. The Switch 5500 family supports simple routing, basic service features, |
|
and basic XRN; the Switch 5500 family supports rather complex routing protocols, |
|
abundant service features and enhanced XRN. Besides saving user cost otherwise invested |
|
on module rack-type switches, the Switch 5500 family with XRN also offer excellent |
|
network availability, upgrade ability, performance, and power network control capacity. |
|
Table 3 lists the models in the Switch 5500 family: |
|
Table 3 Models in the Switch 5500 family |
|
Power |
Number of |
Number of 100 |
Number of 1000 |
Console |
|
|
supply unit |
service |
Mbps uplink |
|||
Model |
(PSU) |
ports |
Mbps ports |
ports |
port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500-SI |
AC-input, |
28 |
24 |
10/100 Mbps |
4 SFP |
1 |
28-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
|
|
5500-SI |
AC-input, |
52 |
48 |
10/100 Mbps |
4 SFP |
1 |
52-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
|
|
5500-EI |
AC-input, |
28 |
24 |
10/100 Mbps |
4 SFP |
1 |
28-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
|
|
5500-EI |
AC-input, |
52 |
48 |
10/100 Mbps |
4 SFP |
1 |
52-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500-EI PWR |
AC-input, |
28 |
24 |
10/100 Mbps |
4 SFP |
1 |
28-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500-EI PWR |
AC-input, |
52 |
48 |
10/100 Mbps |
4 SFP |
1 |
52-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500-EI |
AC-input, |
28 |
24 |
100 Mbps |
2 10/100/1000 |
1 |
28-Port FX |
DC-input |
|
|
|
plus2 SFP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500G-EI |
AC-input, |
24 |
— |
|
20 10/100/1000 |
1 |
24-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
Mbps plus 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10/100/1000 or SFP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500G-EI |
AC-input, |
48 |
— |
|
44 10/100/1000 |
1 |
48-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
Mbps plus 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10/100/1000 or SFP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500G-EI |
AC-input, |
24 |
— |
|
20 10/100/1000 |
1 |
PWR 24-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
|
Mbps plus 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10/100/1000 or SFP |
|

26 CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED
Table 3 Models in the Switch 5500 family (continued)
|
|
Power |
Number of |
Number of 100 |
Number of 1000 |
Console |
|
|
|
supply unit |
service |
Mbps uplink |
|||
|
Model |
(PSU) |
ports |
Mbps ports |
ports |
port |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500G-EI |
AC-input, |
48 |
— |
44 10/100/1000 |
1 |
|
|
PWR 48-Port |
DC-input |
|
|
Mbps plus 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10/100/1000 or SFP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5500G-EI |
AC-input, |
24 |
— |
20 10/100/1000 |
1 |
|
|
24-Port SFP |
DC-input |
|
|
Mbps plus 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10/100/1000 or SFP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
The Switch 5500 family supports the following services: |
|
|
|
|||
|
■ Internet broadband access |
|
|
|
|
||
|
■ MAN (metropolitan area network), enterprise/campus networking |
|
|
||||
|
■ Multicast service, multicast routing, and audio and video multicast service. |
||||||
|
|
|
|||||
XRN Overview |
With the XRN (eXpandable Resilient Networking) feature, you can connect several |
||||||
devices into a combined device and manage them as a single unit. The combined device is called the Fabric, while the member devices are units. With XRN you can:
■ Manage multiple devices in centralized manner, with low management cost.
■ Extend the number of ports and switching capacity just by adding devices. You can decide which equipment to purchase as needed, and better protect your existing investment while upgrading the network.
■ Provide backup between multiple devices to improve reliability and to eliminate single points of failure.
Major Technologies XRN includes three technologies: distributed device management (DDM), distributed link aggregation (DLA), and distributed resilient route (DRR).
■DDM: Users can treat the Fabric as a single device. They can manage the Fabric through any port or IP address connected into the Fabric, and from any unit in the fabric.
■DRR: The multiple units of a Fabric route and forward packets as a single unit, and provide uniform VLAN interfaces, routing table and L3 forwarding table, so the Fabric is regarded as a single Layer 3 switch. Failure of one of the units will not affect routing protocol and data forwarding.
■DLA: Users can aggregate multiple ports of several different units in a Fabric into a group, for centralized management within the Fabric. Trans-unit link aggregation can bring convenient aggregation setting and effectively reduce single points of failure.
The Switch 5500-SI supports basic XRN, that is DDM and DLA; the Switch 5500-EI supports enhanced XRN, including DDM, DRR, and DLA.
Typical Networking Typical XRN networking topology is as shown in Figure 1. Switches of the same type Topology (that is, units) form a Fabric. As a core switch, the Fabric can be downlinked to
workgroup switches through several aggregation links, and uplinked to the server group also through several aggregation links.
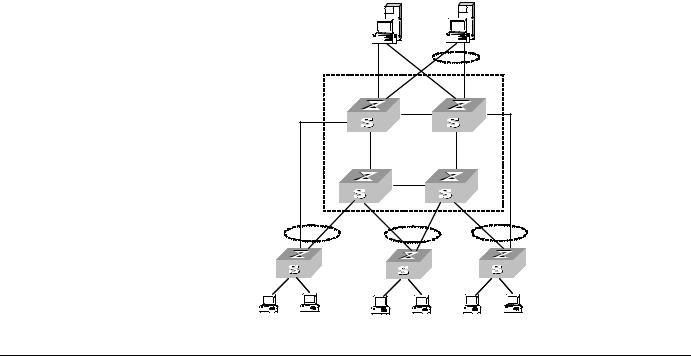
Product Features 27
Figure 1 Networking Topology with XRN
Server 
Core switches
Workgroup
switches
Desktop 
PCs
Product Features |
Table 4 describes the features: |
|
|
Table 4 Function Features |
|
|
|
|
|
Features |
Description |
|
|
|
|
Port |
802.1D Learning |
|
|
Static MAC (unicast/multicast) |
|
|
Jumbo Frame (9k) (EI models only) |
|
|
Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) |
|
VLAN |
VLAN compliant with IEEE 802.1Q Standard |
|
|
Port-based VLAN |
|
|
Protocol Based VLAN, compliant with IEEE 802.1v Standard (EI |
|
|
models only) |
|
|
Voice VLAN |
|
|
8021.Q in Q Double Tagged VLAN Support (EI models only) |
|
STP protocol |
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) / Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol |
|
|
(RSTP), compliant with IEEE 802.1D/IEEE802.1w Standard |
|
|
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP), compliant with IEEE |
|
|
802.1s Standard |
|
|
BPDU Guard |
|
|
Spanning Tree Root Guard |
|
Flow control |
IEEE 802.3 flow control (full-duplex) |
|
|
Back-pressure based flow control (half-duplex) |
|
Traffic Suppression |
Broadcast/Unicast/Multicast Suppression |

28 CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED
Table 4 Function Features (continued)
Features |
Description |
|
|
Multicast |
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Snooping |
|
Multicast VLAN Registration (MVR) |
|
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) (EI models only) |
|
Protocol-Independent Multicast-Dense Mode (PIM-DM) (EI |
|
models only) |
|
Protocol-Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) (EI |
|
models only) |
|
Mulitcast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) (EI models only) |
IP routing |
Static route |
|
RIP V1/v2 |
|
OSPF (EI models only) |
|
IP routing policy |
|
Forwarding IP layer 3 broadcast packets |
|
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Client |
|
DHCP Server (EI models only) |
|
DHCP Options 60, 82 and 184 |
|
DHCP Relay |
|
UDP Relay |
Link aggregation |
Link aggregation |
|
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP), compliant with IEEE |
|
802.3ad Standard |
Mirror |
Mirror based on the traffic classification |
|
Port-based mirror |
|
VLAN-based mirror |
|
Remote mirroring |
Security features |
Multi-level user management and password protect |
|
802.1X Network Login |
|
MAC Based Network Login |
|
Mixed 802.1X and MAC Based Network Login |
|
RADIUS and TACACS+ Authentication, Authorization and |
|
Accounting |
|
PAP, CHAP, EAP-MD5,TLS,TTLS and PEAP Authenticating |
|
Packet filtering |
Quality of Service (QoS) |
Traffic classification |
|
Bandwidth control |
|
Priority |
|
Queues of different priority on the port |
|
Queue scheduling: supports Strict Priority Queuing (SP), |
|
Weighted Round Robin (WRR), WFQ, SP+WFQ, and SP+WRR |
|
QoS profile management manner |
|
Logging in to the Switch 29 |
|
Table 4 Function Features (continued) |
||
|
|
|
Features |
Description |
|
|
|
|
Management and |
Command line interface configuration |
|
Maintenance |
Configuration through console port |
|
|
||
|
Remote configuration through Telnet or SSH |
|
|
Configuration through dialing the Modem |
|
|
SNMP v1/2c/3 |
|
|
System log |
|
|
Level alarms |
|
|
Output of debugging information |
|
|
Ping and Tracert |
|
|
Remote maintenance with Telnet, Modem and SSHv2 |
|
Loading and updates |
Loading and upgrading of software through the XModem |
|
|
protocol |
|
|
Loading and upgrading of software through File Transfer |
|
|
Protocol (FTP) , Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) and Secure File |
|
|
Transfer Protocol (SFTP) |
|
|
|
|
Logging in to the |
This section describes how to log in to the switch. |
Switch |
|
Setting up |
Perform the following procedure to set up the configuration environment through |
Configuration |
the console port. |
Environment through |
|
the Console Port |
|
1To set up the local configuration environment, connect the serial port of a PC (or a terminal) to the console port of the Switch with the console cable (see Figure 2).
Figure 2 Setting up the Local Configuration Environment through the Console Port
Console port
Console cable
2Run terminal emulator (such as Terminal on Windows 3X or the Hyper Terminal on Windows 9X) on the PC. Set the terminal communication parameters as follows:
■Baud rate = 19200
■Databit = 8
■Parity check = none
■Stopbit = 1
■Flow control = none
■Terminal type = VT100
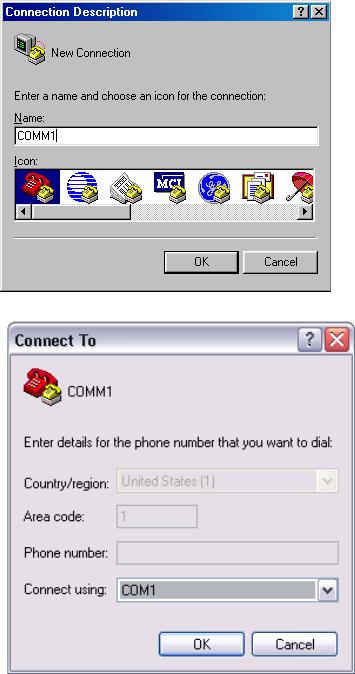
30 CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED
Figure 3 Setting up a New Connection
Figure 4 Configuring the Port for Connection
 Loading...
Loading...